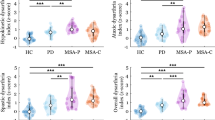
Objective. To study the clinical and neurophysiological features of speech impairments in Parkinson’s disease (PD), multiple system atrophy (MSA), and progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP). Materials and methods. A total of 31 patients with PD and 14 patients with MSA and PSP were studied. Studies were carried out using the Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale of the International Movement Disorder Society (MDS-UPDRS) and a neurophysiological method of analysis of speech disorders using acoustic spectral voice and speech analysis by the Rusz et al. method. Results and conclusions. Disease progression in patients with PD was associated with parallel increases in the severity of axial motor disorders (hypomimia, gait impairment, postural disorders) and speech disorders. Patients with multiple system neurodegeneration such as MSA and PSP differed not only from those with PD but also from each other in terms of clinical manifestations (motor, autonomic, cognitive) and the features of speech dysfunction. The clinical-neurophysiological features of speech disorders identified in patients with different variants of parkinsonism may be of value in the differential diagnosis of these diseases and the development of approaches to rehabilitating patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. H. Fernandez, A. G. Machado, and M. Pandya, A Practical Approach to Movement Disorders, Demos Medical Publishing, New York (2015), 2nd ed.
M. Hunter Manasco, Introduction to Neurogenic Communication Disorders, Jones & Bartlett Learning, Burlington (2017) 2nd ed.
K. Dashtipour, A. Tafreshi, J. Lee, and B. Crawley, “Speech disorders in Parkinson’s disease: pathophysiology, medical management and surgical approaches,” Neurodegener. Dis. Manag., 8, No. 5, 337–348 (2018), https://doi.org/10.2217/nmt-2018-0021.
J. Johnson, “Speech, voice and communication,” Int. Rev. Neurobiol., 134, 1189–1205 (2017), https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.irn.2017.04.014.
N. V. Fedorova, F. K. Tekaeva, and O. S. Orlova, “Speech and voice disorders and their influence on quality of life in patients with Parkinson’s disease,” Otorinolaringologiya, 4, 41, 152–155 (2009).
S. A. Parashos, R. L. Wichmann, and T. Melby, Navigating Life with Parkinson’s Disease, Oxford University Press, New York (2013).
J. Hlavnicka, R. Cmejla, T. Tykalova, et al., “Automated analysis of connected speech reveals early biomarkers of Parkinson’s disease in patients with rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder,” Sci. Rep., 7, No. 1 (2017), https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-00047-5.
J. Rusz, C. Bonnet, J. Klempır, et al., “Speech disorders reflect differing pathophysiology in Parkinson’s disease, progressive supranuclear palsy and multiple system atrophy,” J. Neurol., 262, No. 4, 992–1001 (2015), https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-015-7671-1.
C. Goetz, B. Tilley, S. Shaftman, et al., “Movement Disorder Societysponsored revision of the Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (MDS-UPDRS, Scale presentation and clinimetric testing results,” Mov. Disord., 23, No. 15, 2129–2170 (2008), https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.22340.
C. A. Payan, F. Viallet, B. G. Landwehrmeyer, et al., “Disease severity and progression in progressive supranuclear palsy and multiple system atrophy: validation of the NNIPPS-PARKINSON PLUS SCALE,” PLoS One, 6, No. 8, e 22293 (2011), https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0022293.
J. Hlavnicka, R. Cmejla, J. Klempır, et al., “Acoustic tracking of pitch, modal, and subharmonic vibrations of vocal folds in Parkinsonism,” IEEE Access, 7, 150339–150354 (2019), https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2019.2945874.
M. Novotny, J. Rusz, R. Cmejla, and E. Ruzicka, “Automatic evaluation of articulatory disorders in Parkinson’s disease,” IEEE/ACME Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Proceedings, 22, No. 9, 1366–1378 (2014), https://doi.org/10.1109/taslp.2014.2329734.
M. Novotny, J. Rusz, R. Cmejla, et al., “Hypernasality associated with basal ganglia dysfunction: Evidence from Parkinson’s disease and Huntington’s disease,” Peer J., 4, e2530 (2016), https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.2530.
J. Rusz, R. Cmejla, H. Ruzickova, and E. Ruzicka, “Quantitative acoustic measurements for characterization of speech and voice disorders in early untreated Parkinson’s disease,” J. Acoust. Soc. Am., 129, No. 1, 350–367 (2011), https://doi.org/10.1121/1.3514381.
J. Rusz, J. Hlavndicka, R. Cmejla, and E. Ruzicka, “Automatic evaluation of speech rhythm instability and acceleration in dysarthrias associated with basal ganglia dysfunction,” Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol., 3, 104 (2015), https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2015.00104.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Translated from Zhurnal Nevrologii i Psikhiatrii imeni S. S. Korsakova, Vol. 120, No. 10, Iss. 2, Neurology and Psychiatry in the Elderly, pp. 61–66, October, 2020.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Skripkina, N.A., Arefyeva, A.P. Speech Disorders in Parkinsonism. Neurosci Behav Physi 51, 850–855 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-021-01143-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-021-01143-w