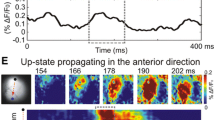
In the neonatal rat hippocampus, the first and predominant pattern of synchronized neuronal network activity is early sharp waves (eSPWs) occurring at a frequency of ~2–4 events per minute. However, how eSPWs are organized longitudinally along the septo-temporal hippocampal axis remains unknown. Using silicone probe recordings from the septal and intermediate segments of the CA1 hippocampus in neonatal rats in vivo we found that eSPWs are highly synchronized longitudinally. The amplitudes of eSPWs in the septal and intermediate segments of the hippocampus were also highly correlated. eSPWs also supported longitudinal synchronization of CA1 multiple unit activity. Spatial-temporal analysis revealed a septal-temporal gradient with more frequent initiation of eSPWs in the septal regions. The speed of eSPW longitudinal propagation attained ~ 250 mm/s. We suggest that longitudinal correlated activity supported by synchronized eSPWs emerges early during postnatal development and may participate in the formation of intrahippocampal connections in the developing hippocampus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhmetshina, D., Nasretdinov, A., Zakharov, A., et al., “The nature of the sensory input to the neonatal rat barrel cortex,” J. Neurosci., 36, 9922–9932 (2016).
Baram, T. Z. and Snead, O. C., “Bicuculline induced seizures in infant rats: ontogeny of behavioral and electrocortical phenomena,” Dev. Brain Res., 57, 291–295 (1990).
Buhl, D. L. and Buzsaki, G., “Developmental emergence of hippocampal fast-field “ripple” oscillations in the behaving rat pups,” Neuroscience, 134, 1423–1430 (2005).
Buzsaki, G., “Two-stage model of memory trace formation: a role for “noisy” brain states,” Neuroscience, 31, 551–570 (1989).
Buzsaki, G., “Hippocampal sharp wave-ripple: A cognitive biomarker for episodic memory and planning,” Hippocampus, 25, 1073–1188 (2015).
Chrobak, J. J. and Buzsaki, G., “Selective activation of deep layer (V–VI) retrohippocampal cortical neurons during hippocampal sharp waves in the behaving rat,” J. Neurosci., 14, 6160–6170 (1994).
Csicsvari, J., Hirase, H., Mamiya, A., and Buzsaki, G., “Ensemble patterns of hippocampal CA3–CA1 neurons during sharp wave-associated population events,” Neuron, 28, 585–594 (2000).
Gomez-Di Cesare, C. M., Smith, K. L., Rice, F. L., and Swann, J.,W., “Anatomical properties of fast spiking cells that initiate synchronized population discharges in immature hippocampus,” Neuroscience, 75, 83–97 (1996).
Karlsson, K. A., Mohns, E. J., di Prisco, G. V., and Blumberg, M. S., “On the co-occurrence of startles and hippocampal sharp waves in newborn rats,” Hippocampus, 16, 959–965 (2006).
Khalilov, I., Khazipov, R., Esclapez, M., and Ben-Ari, Y., “Bicuculline induces ictal seizures in the intact hippocampus recorded in vitro,” Eur. J. Pharmacol., 319, R5–R6 (1997).
Khalilov, I., Minlebaev, M., Mukhtarov, M., and Khazipov, R., “Dynamic changes from depolarizing to hyperpolarizing GABAergic actions during giant depolarizing potentials in the neonatal rat hippocampus,” J. Neurosci., 35, 12635–12642 (2015).
Khazipov, R., Zaynutdinova, D., Ogievetsky, E., et al., “Atlas of the postnatal rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates,” Front. Neuroanat., 9, 161 (2015), https://doi.org/10.3389/fnana.2015.00161.
Kirmse, K., Hubner, C. A., Isbrandt, D., et al., “GABAergic transmission during brain development: Multiple effects at multiple stages,” Neuroscientist, 24, 36–53 (2018).
Kirmse, K., Kummer, M., Kovalchuk, Y., et al., “GABA depolarizes immature neurons and inhibits network activity in the neonatal neocortex in vivo,” Nat. Commun., 6, 7750 (2015).
Lamsa, K., Palva, J. M., Ruusuvuori, E., et al., “Synaptic GABA(A) activation inhibits AMPA-kainate receptor-mediated bursting in the newborn (P0–P2) rat hippocampus,” J. Neurophysiol., 83, 359–366 (2000).
Leinekugel, X., Khalilov, I., Ben-Ari, Y., and Khazipov, R., “Giant depolarizing potentials: the septal pole of the hippocampus paces the activity of the developing intact septohippocampal complex in vitro,” J. Neurosci., 18, 6349–6357 (1998).
Leinekugel, X., Khazipov, R., Cannon, R., et al., “Correlated bursts of activity in the neonatal hippocampus in vivo,” Science, 296, 2049–2052 (2002).
Marguet, S. L., Le-Schulte, V. T., Merseburg, A., et al., “Treatment during a vulnerable developmental period rescues a genetic epilepsy,” Nat. Med., 21, 1436–1444 (2015).
Mohns, E. J. and Blumberg, M. S., “Synchronous bursts of neuronal activity in the developing hippocampus: modulation by active sleep and association with emerging gamma and theta rhythms,” J. Neurosci., 28, 10134–10144 (2008).
Mohns, E. J., Karlsson, K. A., and Blumberg, M. S., “Developmental emergence of transient and persistent hippocampal events and oscillations and their association with infant seizure susceptibility,” Eur. J. Neurosci., 26, 2719–2730 (2007).
Patel, J., Schomburg, E. W., Berenyi, A., et al., “Local generation and propagation of ripples along the septotemporal axis of the hippocampus,” J. Neurosci., 33, 17029–17041 (2013).
Suzuki, S. S. and Smith, G. K., “Spontaneous EEG spikes in the normal hippocampus. I. Behavioral correlates, laminar profiles and bilateral synchrony,” Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol., 67, 348–359 (1987).
Valeeva, G., Abdullin, A., Tyzio, R., et al., “Temporal coding at the immature depolarizing GABAergic synapse,” Front. Cell. Neurosci., 4 (2010).
Valeeva, G., Janackova, S., Nasretdinov, A., et al., “Emergence of coordinated activity in the developing entorhinal-hippocampal network,” Cereb. Cortex, 29, 906–920 (2019a).
Valeeva, G., Nasretdinov, A., Rychkova, V., and Khazipov, R., “Bilateral synchronization of hippocampal early sharp waves in neonatal rats,” Front. Cell. Neurosci., 13, 29 (2019b).
Valeeva, G., Tressard, T., Mukhtarov, M., et al., “An optogenetic approach for investigation of excitatory and inhibitory network GABA actions in mice expressing channelrhodopsin-2 in GABAergic neurons,” J. Neurosci., 36, 5961–5973 (2016).
Ylinen, A., Bragin, A., Nadasdy, Z., et al., “Sharp wave associated high-frequency oscillation (200Hz) in the intact hippocampus: network and intracellular mechanisms,” J. Neurosci., 15, 30–46 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Zhurnal Vysshei Nervnoi Deyatel’nosti imeni I. P. Pavlova, Vol. 70, No. 3, pp. 341–350, May–June, 2020.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Valeeva, G., Rychkova, V., Vinokurova, D. et al. Early Sharp Wave Synchronization along the Septo-Temporal Axis of the Neonatal Rat Hippocampus. Neurosci Behav Physi 50, 1195–1202 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-020-01021-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-020-01021-x