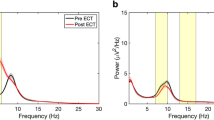
Objective. To perform a comparative analysis of changes in the functional status of the brain by quantitative electroencephalography (EEG) during combined antidepressant treatment (venlafaxine and Cerebrolysin) and monotherapy (venlafaxine) of elderly patients with depression. Materials and methods. A total of 40 patients aged 60–79 (mean 67.1 ± 5.7) years took part in the study and were randomized to two groups. Patients of group 1 received venlafaxine at a dose of 75–150 mg/day for four weeks. Patients of group 2 received venlafaxine for four weeks along with Cerebrolysin (20 i.v. drip infusions of 20.0 ml in 100 ml of isotonic NaCl solution). Results and discussion. Both groups of patients noted signifi cant improvements in status by the end of treatment courses in terms of clinical assessment and the HAMD-17, CGI-S, CGI-I, and MMSE scales. Quantitative EEG studies showed that combined therapy with venlafaxine and Cerebrolysin in patients of group 2 led to more marked improvements in the functional state of the brain (increases in spectral power and normalization of the frequency of the parietal-occipital α rhythm) than seen in patients of group 1, who received monotherapy with venlafaxine.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. A. Churkin, Epidemiology of Mental Disorders, T. B. Dmitrieva et al. (eds.), GEOTAR-Media, Moscow (2009).
A. F. Iznak, “Neuronal plasticity as one aspect of the pathogenesis and treatment of affective disorders,” Pskhiatr. Psikhofarmakoter., 7, No. 1, 24–27 (2005).
A. N. Bogdan, P. V. Morozov, and Yu. V. Seiku, “Nootropic agents in the complex pathogenetically based therapy of depression (literature review),” Psikhich. Rasstr. Obshch. Med., No. 3–4, 68–73 (2011).
B. L. Jacobs, H. van Praag, and F. H. Gage, “Depression and the birth and death of brain cells,” Am Sci., 88, 340–345 (2000), doi: 10.1511/2000.4.340.
H. K. Manji and R. S. Duman, “Impairments of neuroplasticity and cellular resilience in severe mood disorder: implications for the development of novel therapeutics,” Psychopharmacol Bull., 35, 5–49 (2001).
Y. Tatebayashi, “The dentate gyrus neurogenesis: a common therapeutic target for Alzheimer disease and senile depression?” Seishin Shinkeigaku Zasshi, 105, 398–404 (2003).
Y. Noda, N. Nakamura, T. Saeki, et al., “Potentiation of quantitative electroencephalograms following prefrontal repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in patients with major depression,” Neurosci. Res., 77, No. 1–2, 70–77 (2013); 10.1016/j.neures.2013.06.002.
A. F. Iznak, “Neuroprotectors in the prophylaxis of depressive disorders,” Sibir. Vestn. Psikhiatr. Narkol., Supplement, 103–105 (2006).
M. Windisch, A. Gschanes, and B. Hutter-Paier, “Neurotrophic activities and therapeutic experience with a brain derived peptide preparation,” JNeuralTransm., 53,289–298(1998), doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-6467-9_25.
S. I. Gavrilov, “Potential for preclinical diagnosis and preventive therapeutic interventions in Alzheimer’s disease,” Psikhiatriya, No. 1, 18–29 (2009).
A. F. Iznak, E. V. Iznak, N. N. Zavadenko, and L. S. Guzilova, “Dynamics of measures of the P300 component in adolescents during the treatment of the asthenic sequelae of craniocerebral trauma,” Psikhiatriya, No. 4, 25–31 (2009).
E. V. Iznak, A. F. Iznak, E. A. Pankratova, et al., “Electrophysiological correlates of the efficacy of the nootropic sequelae of craniocerebral trauma in adolescents,” Zh. Nevrol. Psikhiat., 110, No. 5, 27–32 (2010).
M. Funke, J. Fiehler, I. Mewes, et al., “Dose-dependent effects of Cerebrolysin on EEG and short term memory of healthy volunteers during control and hyperventilation induced cerebral ischemia,” J. Neural Transm., 53, 385–398 (1998), doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-6467-9_34.
X. A. Alvarez, V. R. Lombardi, L. Corzo, et al., “Oral Cerebrolysin enhances brain alpha activity and improves cognitive performance in elderly control subjects,” J Neural Transm., 59, 315–328 (2000).
G. P. Panteleeva, V. V. Artyukh, W. S. Krylova, et al., “Cerebrolysin as a substance optimizing the psychopharmacotherapy of endogenous depression,” Psikhiatriya, No. 4–6, 70–84 (2008).
A. Ciobanu, C. Petcu, and A. Surdu, “Cerebrolysin augmentation in treatment-resistant depression at elderly,” in: Proc. 10th World Congr. of Biological Psychiatry (2011).
A. F. Iznak, E. V. Iznak, V. V. Kornilov, and V. A. Kontsevoi, “Dynamics of neurophysiological measures on the treatment of protracted psychogenically provoked depression,” Psikhiatriya, No. 1, 32–37 (2011).
A. F. Iznak, E. V. Iznak, O. B. Yakovleva, et al., “Neurophysiological measures of the efficacy of the treatment of depression in the elderly,” Zh. Nevrol. Psikhiat., 112, No. 6, 49–54 (2012).
A. A. Mitrofanov, A Computer System for the Analysis and Topographic Mapping of Brain Electrical Activity with a Neurometric EEG Database (description and application), Moscow (2005).
N. Gorbachevskaya, V. Bashina, V. Gratchev, and A. Iznak, “Cerebrolysin therapy in Rett syndrome: clinical and EEG mapping study,” Brain Dev., 23, Suppl. 1, 90–93 (2001), doi: 10.1016/s0387-7604(01)00349-7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Zhurnal Nevrologii i Psikhiatrii imeni S. S. Korsakova, Vol. 116, No. 1, Iss. 1, pp. 47–50, January, 2016.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iznak, A.F., Iznak, E.V., Kalyn, Y.B. et al. Comparative Dynamics of EEG Parameters in Elderly Patients with Depression during Monotherapy and Combined Treatment. Neurosci Behav Physi 47, 382–385 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-017-0410-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-017-0410-6