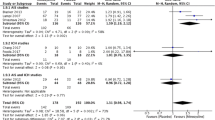
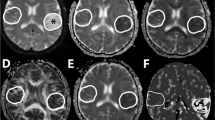
The dynamics of neurological symptoms were assessed using the Scandinavia Stroke Scale and functional disease outcomes with the Barthel index and modified Rankin scale in 89 patients during the acute period of ischemic stroke of moderate severity, whose treatment included citicoline (Ceraxon) i.v. and p.o. The results were compared with those from a reference group (52 patients) selected in terms of clinical and demographic parameters, who received similar treatment without citicoline. By discharge from hospital (days 21–24 of illness), there was significantly (p < 0.05) greater recovery in the study group. The efficacy of citicoline was significantly (p < 0.05) greater in patients aged less than 70 years and when citicoline was given in the first hours of illness.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. I. Gusev, V. I. Skvortsova, and L. V. Stakhovskaya, “The problem of stroke in the Russian Federation: a time for positive actions,” Zh. Nevrol. Psikhiat., 107, No. 6, 4–10 (2007).
P. A. Lapchak, “Emerging therapies: pleiotropic multi-target drugs to treat stroke victims,” Transl. Stroke Res., 2, 129–135 (2011).
M. D. Ginsberg, “Adventures in the pathophysiology of brain ischemia: penumbra, gene expression, neuroprotection: The 2002 Thomas Willis Lecture,” Stroke, 34, 214–223 (2003).
E. I. Gusev, A. N. Boiko, V. L. Baratashvili, et al., “Results obtained using citicoline (Ceraxon) in patients with acute cerebral stroke,” Med. Krit. Sostoyanii, 2, 42–47 (2010).
A. Rogalewski, A. Schneider, B. E. Ringelstein, and W. R. Schabitz, “Toward a multimodal neuroprotective treatment of stroke,” Stroke, 37, 1129–1136 (2006).
A. A. Mangoni and S. H. Jackson, “Age-related changes in pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics: basic principles and practical applications,” Brit. J. Clin. Pharmacol., 57, No. 1, 6–14 (2004).
G. Trifiró and E. Spina, “Age-related changes in pharmacodynamics: focus on drugs acting on central nervous and cardiovascular systems,” Curr. Drug. Metab., 12, No. 4, 542–549 (2011).
X. Bao, P. J. Mills, B. K. Rana, et al., “Interactive effects of common β2-adrenoceptor haplotypes and age on susceptibility to hypertension and receptor function,” Hypertension, 46, 301–307 (2005).
M. Meller, S. Jakobsen, and A. Gjedde, “Parametric and regional maps of free serotonin 5-HT1A receptor sites in human brain as function of age in healthy humans,” Neuropsychopharmacology, 32, 1707–1714 (2007).
R. M. Adibhatla, J. F. Hatcher, E. C. Larsen, et al., “CDP-choline significantly restores phosphatidylcholine levels by differentially affecting phospholipase A2 and CTP:phosphocholine cytidyltransferase after stroke,” J. Biol. Chem., 281, No. 10, 6718–6725 (2005).
A. Farooqui, L. Horrocks, and T. Farooqui, “Glycerophospholipids in brain: their metabolism, incorporation to membranes, functions, and involvement in neurological disorders,” Chem. Phys. Lipids, 106, 1–29 (2000).
Z. Li and D. E. Vance, “Phosphatidylcholine and choline homeostasis,” J. Lipid Res., 49, 1187–1194 (2008).
O. Hurtado, M. A. Moro, A. Cárdenas, et al., “Neuroprotection afforded by prior citicoline administration in experimental brain ischemia: effects on glutamate transport,” Neurobiol. Dis., 18, 336–345 (2005).
M. Martinet, P. Fonlupt, and H. Pacheco, “Effects of cytidine 5'-diphosphocholine on norepinephrine, dopamine and serotonin synthesis in various regions of the rat brain,” Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn. Ther., 239, 52–61 (1979).
M. Alonso de Laciñana, M. Gutiérrez, J. M. Rada, et al., “Effect of combined therapy with thrombolysis and citicoline in a rat model of embolic stroke,” J. Neurol. Sci., 247, 121–129 (2006).
O. Hurtado, A. Cardenas, J. M. Pradillo, et al., “A chronic treatment with CDP-choline improves functional recovery and increases neuronal plasticity after experimental stroke,” Neurobiol. Dis., 26, 105–111 (2007).
J. Alvarez-Sabín and G. C. Román, “Citicoline in vascular cognitive impairment and vascular dementia after stroke,” Stroke, 42, Suppl., 40–43 (2011).
R. A. Cohen, J. N. Browndyke, D. J. Moser, et al., “Long-term citicoline (cytidine diphosphate choline) use in patients with vascular dementia: neuroimaging and neuropsychological outcomes,” Cerebrovasc. Dis., 16, 199–204 (2003).
M. M. Odinak and I. A. Voznyuk, “The role of exogenous choline in protection and recovery of brain matter in stroke. Quality of life,” Meditsina, 21, No. 4, 1–7 (2007).
W. M. Clark, S. J. Warach, L. C. Pettigrew, et al., “A randomized dose–response trial of citicoline in acute ischemic stroke patients. Citicoline Stroke Study Group,” Neurology, 49, 671–678 (1997).
A. Davalos, J. Castillo, J. Alvarez-Sabin, et al., “Oral citicoline in acute ischemic stroke: An individual patient data pooling analysis of clinical trials,” Stroke, 33, No. 12, 2850–2857 (2002).
S. Warach, L. C. Pettigrew, J. F. Dashe, et al., “Effect of citicoline on ischemic lesions as measured by diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging,” Citicoline 010 investigators,” Ann. Neurol., 48, No. 5, 713–722 (2000).
M. F. Kuo, J. Grosch, E. Fregni, et al., “Focusing effect of acetylcholine on neuroplasticity in the human motor cortex,” J. Neurosci., 27, No. 52, 14442–14447 (2007).
F. Meintzschel and U. Ziemann, “Modification of practice-dependent plasticity in human motor cortex by neuromodulators,” Cerebral Cortex, 16, 1106–1115 (2006).
M. M. Silveri, J. Dikan, A. J. Ross, et al., “Citicoline enhances frontal lobe bioenergetics as measured by phosphorus magnetic resonance spectroscopy,” NMR Biomed., 21, 1066–1075 (2008).
V. Rema, K. K. Bali, R. Ramachandra, et al., “Cytidine-5-diphosphocholine supplement early in life induces stable increase in dendritic complexity of neurons in the somatosensory cortex of adult rats,” Neurosci., 155, No. 2, 556–564 (2008).
V. Bramanti, D. Bronzi, D. Tomassoni, et al., “Effect of choline-containing phospholipids on transglutaminase activity in primary astroglial cell cultures,” Clin. Exp. Hypertens., 30, No. 8, 798–807 (2008).
I. D. Grachev and A. V. Apkarian, “Aging alters regional multichemical profile of the human brain: an in vivo 1H-MRS study of young versus middle-aged subjects,” J. Neurochem., 76, 582–593 (2001).
K. Haga, Y. Khor, A. Farrall, and J. M. Wardlaw, “A systematic review of brain metabolite changes, measured with 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy, in healthy aging,” Neurobiol. Aging, 30, 353–363 (2009).
M. Castellanos, T. Sobrino, and J. Castillo, “Evolving paradigms for neuroprotection: molecular identification of ischemic penumbra,” Cerebrovasc. Dis., 21, No. 2, 71–79 (2006).
T. J. Quinn, P. Langhorne, and D. J. Stott, “Barthel index for stroke trials: development, properties, and application,” Stroke, 42, 1146–1151 (2011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Zhurnal Nevrologii i Psikhiatrii imeni S. S. Korsakova, Vol. 112, No. 3, Iss. II, Stroke, pp. 21–26, February, 2012.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martynov, M.Y., Boiko, A.N., Kamchatnov, P.R. et al. Neuroprotective Therapy with Citicoline (Ceraxon) in Patients with Ischemic Stroke. Neurosci Behav Physi 43, 706–711 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-013-9797-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-013-9797-x