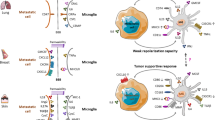
Following any type of brain injury such as lesion, stroke, and tumor/cancer invasion, microglia are rapidly activated and recruited to the site of injury. Microglia is the main immune effector cell population of the central nervous system and control immune cell recruitment. However, the molecular mechanism of brain metastasis and interaction between neuron-glia-tumor cells are poorly understood. Therefore, we established an animal model for brain metastasis using human lung cancer-derived cells (HARA-B) in nude mice. Accumulation of activated microglia was observed around tumor cells depending on the size of metastatic foci and the area of the brain. In in vitro studies, conditioned medium from primary cultured mouse microglia inhibited the proliferation of tumor cells, while tumor cell-conditioned medium inhibited the proliferation of primary cultured neurons from mouse cortex. Though the responsible factors released from microglia and tumor cells are still under investigation, these studies will contribute to the understanding of the mechanism of cell-cell interaction in the brain and the possible therapeutic target for brain metastasis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Aloisi, A. Care, G. Borsellino, P. Gallo, S. Rosa, A. Bassani, A. Cabibbo, U. Testa, G. Levi, and C. Peschle, “Production of hemolymphopoietic cytokines (IL-6, IL-8, colony-stimulating factors) by normal human astrocytes in response to IL-1 beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha,” J. Immunol., 149, 2358–2366 (1992).
F. Aloisi, F. Ria, and L. Adorini, “Regulation of T-cell responses by CNS antigen-presenting cells: different roles for microglia and astrocytes,” Immunol. Today, 21, 141–147 (2000).
J. J. Body, T. Facon, and R. E. Coleman, “A study of the biological receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaΒ ligand inhibitor, denosumab, in patients with multiple myeloma or bone metastases from breast cancer,” Clin. Cancer Res., 12, 1221–1228 (2006).
D. Davalos, J. Grutzendler, G. Yang, J. V. Kim, Y. Zuo, S. Jung, D. R. Littman, M. L. Dustin, and W. B. Gan, “ATP mediates rapid microglial response to local brain injury in vivo,” Nat. Neurosci.,8, 752–758 (2005).
I. J. Fidler, S. Yano, R. D. Zhang, et al, “The seed and soil hypothesis: vascularisation and brain metastases,” Lancet Oncol., 3, 53–57 (2002).
S. Galluzzi and P. M. Payne, “Brain metastases from primary bronchial carcinoma: a statistical study of 741 necropsies,” Biol. J. Cancer, 10, 408 (1956).
U. K. Hanisch, “Microglia as a source and target of cytokines,” Glia, 40, 140–155 (2002).
L. Hertz, D. E. McFarlin, and B. H. Waksman, “Astrocytes: auxiliary cells for immune responses in the central nervous system?” Immunol. Today, 11, 265–268 (1990).
H. Iguchi, S. Tanaka, Y. Ozawa, T. Kashiwakuma, T. Kimura, T. Hiraga, H. Ozawa, and A. Kono, “An experimental model of bone metastasis by human lung cancer cells: the role of parathyroid hormone-related protein in bone metastasis,” Cancer Res., 56, 4040–4043 (1996).
S. U. Kim and J. de Vellis, “Microglia in health and disease,” J. Neurosci. Res., 81, 302–313 (2005).
E. M. Knights, “Metastatic tumors of the brain and their relation to primary and secondary pulmonary cancer,” Cancer, 7, 259 (1954).
G. W. Kreutzberg, “Microglia: a sensor for pathological events in the CNS,” Trends. Neurosci., 19, 312–318. 1996.
D. J. Magilligan, C. Duvernoy, G. Malik, J. W. Lewis, R. Knighton, and J. I. Ausman, “Surgical approach to lung cancer with solitary cerebral metastasis: twenty-five years’ experience,” Ann. Thorac. Surg., 42, 360–364 (1986).
S. Morony, C. Capparelli, I. Sarosi, et al., “Osteoprotegerin inhibits osteolysis and decreases skeletal tumor burden in syngeneic and nude mouse models of experimental bone metastasis,” Cancer Res., 61, 4432–4436 (2001).
G. L. Nicolson, “Cancer progression and growth: relationship of paracrine and autocrine growth mechanisms to organ preference of metastasis,” Exp. Cell Res., 204, 171–180 (1993).
A. Nimmerjahn, F. Kirchhoff, and F. R. Helmchen, “Resting microglial cells are highly dynamic surveillants of brain parenchyma in vivo,” Science, 308, 1314–1318 (2005).
L. J. Schouten, J. Rutten, H. A. Huveneers, and A. Twijnstra, “Incidence of brain metastases in a cohort of patients with carcinoma of the breast, colon, kidney, and lung and melanoma,” Cancer, 94, 2698–2705 (2002).
J. J. Watters, J. M. Schartner, and B. Badie, “Microglia function in brain tumors,” J. Neurosci. Res., 81(3), 447–55 (2005).
T. Yoneda, and T. Hiraga, “Crosstalk between cancer cells and bone microenvironment in bone metastasis,” Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 328, 679–687 (2005).
M. Zhang and Y. Olsson, “Reactions of astrocytes and microglial cells around hematogenous metastases of the human brain. Expression of endothelin-like immunoreactivity in reactive astrocytes and activation of microglial cells,” J. Neurol. Sci., 134, 26–32 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Published in Rossiiskii Fiziologicheskii Zhurnal imeni I. M. Sechenova, Vol. 95, No. 12, pp. 1386–1396, December, 2009.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Noda, M., Seike, T., Fujita, K. et al. Role of Immune Cells in Brain Metastasis of Lung Cancer Cells and Neuron-Tumor Cell Interaction. Neurosci Behav Physi 41, 243–251 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-011-9406-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-011-9406-9