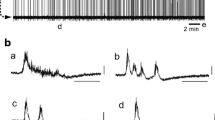
Acute experiments on rats were performed to study the effects of intraventricular microinjections of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) on the volume-time parameters of external respiration and the inspiration-inhibiting Hering–Breuer reflex. The state of this reflex before and after GABA administration was assessed in terms of the extent of changes in the duration and amplitude of inspiratory oscillations in intrathoracic pressure in response to end-expiratory occlusion of the trachea. Administration of 20 μM GABA into the lateral ventricles of the brain decreased the minute ventilation (due to reductions in the respiratory frequency and respiratory volume), weakened respiratory muscle contractions, and decreased the peak airflow rate on inspiration and expiration. The response to end-expiratory occlusion decreased significantly after administration of GABA, demonstrating the involvement of GABAergic mechanisms in mediating the inspiration-inhibiting Hering–Breuer reflex.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
I. S. Breslav and V. D. Glebovskii, The Control of Respiration [in Russian], Nauka, Leningrad (1981).
N. A. Merkulova, A. N. Inyushkin, V. I. Belyakov, R. A. Zainulin, and E. M. Inyushkina, The Respiratory Center and the Regulation of Its Activity by Suprabulbar Structures [in Russian], Samara University Press (2007).
V. A. Safonov, Humans in an Ocean of Air [in Russian], Natsional’noe Obozrenie (2006).
I. A. Tarakanov and V. A. Safonov, “Neurohumoral concept of impairments to the central regulation of respiration,” Patogenez, 1, No. 2, 11–24 (2003).
I. A. Tarakanov, L. N. Tikhomirova, and V. A. Safronov, “Dynamics of the sensitivity of the respiratory system to spike activity from mechanoreceptors in the lungs on activation of the GABAergic system,” Byull. Éksperim. Biol. Med., 128, No. 9, 274–277 (1999).
I. A. Tarakanov, L. N. Tikhomirova, and V. A. Safonov, “Significance of the GABAergic system in the mechanoreceptor regulation of respiration in rats,” in: Current Questions in the Physiology of Autonomic Functions [in Russian], Samara University Press (2001), pp. 55–68.
N. P. Aleksandrova and G. G. Isaev, “Central and peripheral components of diaphragmatic fatigue during inspiratory resistive load in cats,” Acta. Physiol. Scand., 161, 355–360 197.
A. C. Bonham, “Neurotransmitters in the CNS control of breathing,” Resp. Physiol., 101, 219–230 (1995).
P. A. Brooks, S. R. Glaum, R. J. Miller, and K. M. Spyer, “The actions of baclofen on neurons and synaptic transmission in the nucleus tractus solitarii,” J. Physiol. (London), 383, 571–585 (1992).
M. D. Burton and H. Kazemi, “Neurotransmitters in central respiratory control,” Resp. Physiol., 122, 111–121 (2000).
S. Delpierre, E. Balzamo, C. Pugnat, and Y. Jammes, “Cardiorespiratory response to bicuculline during resistive loaded breathing in anesthetized rabbits,” Neurosci. Lett., 213, No. 1, 13–16 (1996).
J. Hedner, T. Hedner, P. Wessberg, and J. Jonason, “An analysis of the mechanism by which γ-aminobutyric acid depresses ventilation in the rat,” J. Appl. Physiol., 56, 849–856 (1984).
J. R. Holtman and R. A. King, “Regulation of the respiratory motor outflow to the larynx and diaphragm by GABA receptors,” Eur. J. Pharmacol., 156, 181–187 (1988).
H. Kazemi and B. Hoop, “Glutamic acid and γ-aminobutyric acid neurotransmitters in central control of breathing,” J. Appl. Physiol., 70, 1–7 (1991).
M. P. Kneussl, P. Pappagianopoulos, B. Hoop, and H. Kazemi, “Reversible depression of ventilation and cardiovascular function by ventriculocisternal perfusion with gamma-aminobutyric acid in dogs,” Am. Rev. Respir. Dis., 133, No. 6, 1024–1028 (1986).
S. Milic-Emili, S. Mead, S. M. Tarner, and E. M. Glazer, “Improved technique for estimating pleural pressure from esophageal balloons,” J. Appl. Physiol., 19, 207–211 (1964).
J. P. Mortola and A. Noworaj, “Two-sidearm tracheal cannula for respiratory airflow measurements in small animals,” J. Appl. Physiol., 55, 250–253 (1983).
G. Paxinos and C. Watson, The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, Academic Press, London (1982).
R. S. Rao, H. E. Greenberg, A. L. Sica, and S. M. Scharf, “Gammaaminobutyric acid contributes to modulation of cardiorespiratory control after chronic ventilatory loading,” Respir. Physiol., 108, No. 1, 35–44 (1997).
E. Seifert and T. Trippenbach, “Effects of baclofen on the Hering–Breuer inspiratory-inhibitory and deflation reflexes in rats,” Am. J. Physiol., 274, 462–469 (1998).
A. M. Taveira da Silva, B. Hartley, P. Hamosh, J. A. Quest, and R. A. Gillis, “Respiratory depressant effect of GABA alpha- and beta-receptor agonists in the cat,” J. Appl. Physiol., 62, 2264–2272 (1987).
K. A. Yamada, P. Hamosh, and R. A. Gillis, “Respiratory depression produced by activation by GABA receptors in the hind-brain in the cat,” J. Appl. Physiol., 151, 1278–1286 (1981).
M. Younes, “Mechanisms of respiratory load compensation,” in: Regulation of Breathing, N.Y. Lung Biology Health Disease (1994), Vol. 79, pp. 822–867.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Rossiiskii Fiziologicheskii Zhurnal imeni I. M. Sechenova, Vol. 94, No. 12, pp. 1356–1364, December, 2008.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aleksandrova, N.P., Aleksandrov, V.G. & Ivanova, T.G. Effects of Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid on the Hering–Breuer Inspiration-Inhibiting Reflex. Neurosci Behav Physi 40, 165–171 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-009-9243-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-009-9243-2