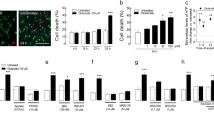
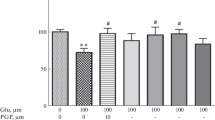
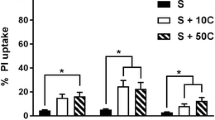
The ratio of necrosis to apoptosis and the mechanisms of apoptosis were studied during neurodegeneration induced by glutamate and selective agonists of glutamate receptors – N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) and kainate. Experiments were performed on primary cultures (seven days in vitro) of rat cerebral cortex neurons. Apoptosis and necrosis were identified using a vital fluorescence rapid test with staining with acridine orange and ethidium bromide. Immunocytochemistry in combination with confocal microscopy was used to visualize apoptotic proteins. Agonists (240 min) caused neuron death via both processes, though the proportion of necrotic cells when neurodegeneration was induced by NMDA and kainate was significantly less than when neurodegeneration was induced with glutamate. The neurotoxic effect of 3 mM glutamate was mediated via α-amino-3-(3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-yl)propionate (AMPA) and kainate receptors, as it was blocked by 6-cyano-7-nitroquinoxalin-2,3-dione (CNQX). Activation of NMDA receptors led to the development of apoptosis without involvement of caspases, due to the direct action of apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF) on neuron nuclei. Activation of AMPA-kainate receptors was accompanied by the development of apoptosis via the caspase-dependent pathway. Thus, these data identified the receptor dependence of the mechanisms of apoptosis during the neurotoxic action of glutamate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. M. Antonov, “Neurotransmitter carriers: receptor, transport, and channel functions,” Zh. Évolyuts. Biokhim. Fiziol., 37, No. 4, 248–252 (2001).
S. M. Antonov, E. V. Mironova, and A. A. Lukina, “Control of the neurotoxic action of glutamate on neurons of different ages by Mg2+ blockade of NMDA receptors,” Biol. Membrany, 23, No. 2, 129–138 (2006).
A. A. Boldyrev, “Oxidative stress and the brain,” SOZh, 4, 21–28 (2001).
E. V. Mironova and A. A. Lukina, “Dynamics of the neurodegeneration of neurons in the rat cerebral cortex evoked by toxic doses of glutamate,” Vestn. Molod. Uchen. Ros. Akad. Nauk, 2, 20–25 (2004).
E. V. Mironova, A. A. Lukina, N. B. Brovtsyna, A. I. Krivchenko, and S. M. Antonov, “Types of glutamate receptor determining the concentration dependence of glutamate neurotoxicity on rat cerebral cortex neurons,” Zh. Évolyuts. Biokhim. Fiziol., 42, No. 6, 559–566 (2006).
S. N. Skachkov, Yu. V. Kucheryavyi, S. M. Antonov, V. L. Pirson, K. J. Nicholls, A. Reichenback, and M. D. Iton, “Potassium channels with a domain consisting of two pore-forming loops and influx rectifying channels: regulation of the external K+ concentration by retinal glial cells (Müller) and cortical astrocytes,” Biol. Membrany, 23, No. 2, 85–100 (2006).
J. M. Abrams, K. White, L. I. Fessler, and H. Steller, “Programmed cell death during Drosophila embryogenesis,” Development, 117, 29–43 (1993).
S. M. Antonov, V. E. Gmiro, and J. W. Johnson, “Binding sites for permeant ions in the channel of NMDA receptors and their effects on channel block,” Nat. Neurosci., 1, No. 6, 451–461 (1998).
S. M. Antonov and J. W. Johnson, “Voltage-dependent interaction of open-channel molecules with gating of NMDA receptors in rat cortical neurons,” J. Physiol., 493, No. 2, 425–455 (1996).
S. M. Antonov and J. W. Johnson, “Permeant ion regulation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor channel block by Mg2+,” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 96, No. 25, 14571–14576 (1999).
S. M. Antonov and L. G. Magazanik, “Intense non-quantal release of glutamate in an insect neuromuscular junction,” Neurosci. Lett., 93, 204–208 (1988).
S. Bates and K. H. Vousden, “Mechanisms of p53-mediated apoptosis,” Cell Mol. Life Sci., 55, No. 1, 28–37 (1999).
H. U. Bergmeyer and E. Bernt, “Lactate dehydrogenase UV assay with pyruvate and NADH,” in: Methods of Enzymatic Analysis [in Russian], H. U. Bergmeyer (ed.), Academic Press, New York (1974), Vol. 2, pp. 574–579.
P. Cafforio, A. Romito, M. A. Grizzuti, and F. Silvestris, “Methods for assessing programmed cell death,” Recent Prog. Med., 87, No. 7–8, 366–373 (1996).
R. Dingledine, K. Borges, D. Bowie, and S. Traymelis, “The glutamate receptor ion channels,” Pharmacol. Rev., 51, 7–61 (1999).
R. A. Gottlieb, H. A. Giesing, J. Y. Zhu, R. L. Engler, and B. M. Babior, “Cell acidification in apoptosis: granulocyte colony-stimulating factor delays programmed cell death in neutrophils by up-regulating the vacuolar H(+)-ATPase,” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 92, 5965–5968 (1995).
A. J. Gibb and D. Colquhoun, “Activation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors by L-glutamate in cells dissociated from adult rat hippocampus,” J. Physiol., 456, 143–179 (1992).
Y. Gavrieli, Y. Sherman, and S. A. Ben-Sasson, “Identification of programmed cell death in situ via specific labeling of nuclear DNA fragmentation,” J. Cell Biol., 119, 493–501 (1992).
Y. Hatanaka, K. Suzuki, and Y. Kawasaki, “A role of peroxides in Ca2+ ionophore-induced apoptosis in cultured rat cortical neurons,” Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 227, No. 2, 513–518 (1996).
S. J. Hong, T. M. Dawson, and V. L. Dawson, “Nuclear and mitochondrial conversations in cell death: PARP-1 and AIF signaling,” Trends Pharmacol. Sci., 25, No. 5, 259–264 (2004).
N. V. Jonston, “Neuronal death in development, ageing and disease,” Neurobiol. Ageing, 15, No. 2, 235–236 (1994).
B. Khodorov, “Glutamate-induced deregulation of calcium homeostasis and mitochondrial dysfunction in mammalian central neurons,” Progr. Biophys. Mol. Biol., 86, No. 2, 279–351 (2004).
N. W. Kleckner and B. S. Pallotta, “Burst kinetics of single NMDA receptor currents in cell-attached patches from rat brain cortical neurons in culture,” J. Physiol., 486, 411–426 (1995).
J. Y. Koh and D. W. Choi, “Quantitative determination of glutamate mediated cortical neuronal injury in cell culture by lactate dehydrogenase efflux assay,” J. Neurosci. Meth., 20, 83–90 (1987).
J. Li and A. Eastman, “Apoptosis in an interleukin-2-dependent cytotoxic T lymphocyte cell line is associated with intracellular acidification. Role of the Na(+)/H(+)-antiport,” J. Biol. Chem., 270, 3203–3211 (1995).
E. V. Mironova, A. A. Evstratova, and S. M. Antonov, “A fluorescence vital assay for the recognition and quantification of excitotoxic cell death by necrosis and apoptosis using the confocal microscopy on neurons in culture,” J. Neurosci. Meth., 163, 1–8 (2007).
F. D. Miller, C. D. Pozniak, and G. S. Walsh, “Neuronal life and death: an essential role for the p53 family,” Cell Death Differ., 7, No. 10, 880–888 (2000).
S. Mpoke and J. Wolfe, “Differential staining of apoptotic nuclei in living cells: application to macronuclear elimination in Tetrahymena,” J. Histochem. Cytochem., 45, 675–683 (1997).
J. Noraberg, B. W. Kristensen, and J. Zimmer, “Markers for neuronal degeneration in organotypic slice cultures,” Brain Res. Protoc., 3, 278–290 (1999).
J. W. Oiney, “Excitatory transmitter neurotoxicity,” Aging, 15, No. 2, 259–260 (1994).
M. K. Patterson, Jr., “Measurement of growth and viability of cells in culture,” Meth. Enzymol., 58, 141–152 (1979).
K. L. Philpott, M. J. McCarthy, D. Backer, C. Gatchalian, and L. L. Rubin, “Morphological and biochemical changes in neurons: apoptosis versus mitosis,” Eur. J. Neurosci., 8, No. 9, 1906–1915 (1996).
L. Pulliam, M. Stubblebine, and W. Hyun, “Quantification of neurotoxicity and identification of cellular subsets in a three-dimensional brain model,” Cytometry, 32, No. 1, 66–69 (1998).
S. Rabizadeh, J. Oh, L. T. Zhong, J. Yang, C. M. Bitler, L. L. Butcher, and D. E. Bredesen, “Induction of apoptosis by the low-affinity NGF receptor,” Science, 261, 345–348 (1993).
D. D. Schoepp and A. I. Sacaan, “Metabotropic glutamate receptors and neuronal degenerative disorders,” Neurobiol. Aging, 15, No. 2, 261–263 (1994).
A. Tapia, “NMDA-receptor activation stimulates phospholipase A2 and somatostatin release from rat cortical neurons in primary cultures,” Eur. J. Pharmacol., 225, No. 2, 253–262 (1992).
T. F. Uliasz and S. J. Hewett, “A microtiter trypan blue absorbance assay for the quantitative determination of excitotoxic neuronal injury in cell culture,” J. Neurosci. Meth., 100, No. 1–2, 157–163 (2000).
H. Wang, S. W. Yu, D. W. Koh, J. Lew, C. Coombs, W. Bowers, H. J. Federoff, G. G. Poirier, T. M. Dawson, and V. L. Dawson, “Apoptosis-inducing factor substitutes for caspase executioners in NMDA-triggered excitotoxic neuronal death,” J. Neurosci., 24, No. 48, 10963–10973 (2004).
C. M. Waters, “Mechanisms of neuronal cell death. An overview,” Mol. Chem. Neuropathol., 28, No. 1–3, 145–151 (1995).
K. White, M. E. Grether, J. M. Abrams, L. Young, K. Farrell, and H. Steller, “Genetic control of programmed cell death in Drosophila,” Science, 264, 677–678 (1994).
L. Wise-Faberowski, R. D. Pearlstein, and D. S. Warner, “NMDA-induced apoptosis in mixed neuronal/glial cortical cell cultures: the effects of isoflurane and dizocilpine,” J. Neurosurg. Anesthesiol., 18, No. 4, 240–246 (2006).
A. Y. Xiao, M. Homma, X. Q. Wang, X. Wang, and S. P. Yu, “Role of K(+) efflux in apoptosis induced by AMPA and kainate in mouse cortical neurons,” Neurosci., 108, No. 1, 61–67 (2001).
S. W. Yu, H. Wang, M. F. Poitras, C. Coombs,W. J. Bowers, H. J. Federoff, G. G. Poirier, T. M. Dawson, and V. L. Dawson, “Mediation of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1-dependent cell death by apoptosis-inducing factor,” Science, 297, No. 5579, 259–263 (2002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Rossiiskii Fiziologicheskii Zhurnal imeni I. M. Sechenova, Vol. 94, No. 4, pp. 380–393, April, 2008.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Evstratova, A.A., Mironova, E.V., Dvoretskova, E.A. et al. Apoptosis and the Receptor Specificity of Its Mechanisms During the Neurotoxic Action of Glutamate. Neurosci Behav Physi 39, 353–362 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-009-9141-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-009-9141-7