Abstract
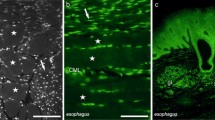
The locations and morphometric characteristics of efferent parasympathetic neurons in the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus nerve and the cruciform parasympathetic nucleus of the spinal cord, innervating the area of the ileocecal sphincter and the ascending and transverse segments of the colon, were studied. Horseradish peroxidase solution was injected beneath the serous membranes of these parts of the intestine in urethane-anesthetized cats. After 48 h, animals were subjected to transcardiac perfusion with a fixative mixture and sections of the medulla oblongata and spinal cord were prepared and processed by the Mesulam method. The results showed that all these parts of the large intestine received parasympathetic innervation from neurons in the ventrolateral part of the dorsal motor nucleus, which were uniform in terms of their morphometric characteristics. The number of neurons of this group sending axons to the ileocecal area was greater than the number of neurons innervating the ascending colon. A second group of neurons, which were smaller cells, was located in the same part of the nucleus and innervated the transverse colon. The transverse colon also received innervation from neurons in the cruciform parasympathetic nucleus of the spinal cord.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. A. Bagaev and F. N. Makarov, “The dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus nerve and its role in innervating the digestive tract,” Morfologiya, 111, No. 1, 7–14 (1997).
V. A. Bagaev, F. N. Makarov, V. L. Rybakov, et al., “Localization of neurons in the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus nerve innervating the pyloric part of the stomach,” Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR, 304, No. 4, 985–987 (1989).
V. A. Bagaev, F. N. Makarov, V. L. Rybakov, et al., “Localization of neurons innervating the superior part of the duodenum in the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus nerve,” Fiziol. Zh. SSSR, 77, No. 1, 45–52 (1991).
V. A. Bagaev, A. D. Nozdrachev, and S. S. Panteleev, The Vagovagal Reflex Arc. Elements of its Structural-Functional Organization [in Russian], St. Petersburg University Press, St. Petersburg (1997).
V. A. Bagaev, L. V. Filippova, G. N. Akoev, and F. N. Makarov, “Extraorgan sources of the parasympathetic innervation of the small intestine in the area of the ligament of Treitz,” Neirofiziologiya, 24, No. 4, 423–430 (1992).
S. M. Altschuler, J. Escardo, R. B. Lynn, and R. R. Miselis, “The central organization of the vagus nerve innervating the colon of the rat,” Gastroenterology, 104, 502–509 (1993).
S. M. Altschuler, D. A. Ferenci, R. B. Lynn, and R. R. Miselis, “Representation of the cecum in the lateral dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus nerve and commissural subnucleus of the nucleus tractus solitarii in rat,” J. Comp. Neurol., 304, No. 2, 261–274 (1991).
H.-R. Berthoud, N. R. Carlson, and T. L. Powley, “Topography of efferent vagal innervation of the rat gastrointestinal tract,” Amer. J. Physiol., 260, 200–207 (1991).
H.-R. Berthoud, A. Jedrzejewska, and T. L. Powley, “Simultaneous labeling of vagal innervation of the gut and afferent projections from the visceral forebrain with Dil injected into the dorsal vagal complex in the rat,” J. Comp. Neurol., 301, No. 1, 65–79 (1990).
N. A. Connors, J. M. Sullivan, and K. S. Kubb, “An autoradiographic study of the distribution of fibers from the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus to the digestive tube of the rat,” Acta Anat. (Basel), 115, No. 3, 266–271 (1983).
L. C. Hudson, “Horseradish peroxidase study of the location of extrinsic efferent and afferent neurons innervating the colon of dogs,” Amer. J. Vet. Res., 51, No. 11, 1875–1881 (1990).
M.-M. Mesulam, “Tetramethylbenzidine for horseradish peroxidase neurohistochemistry: a non-carcinogenic blue reaction product with superior sensitivity for visualizing neural afferents and efferents,” J. Histochem. Cytochem., 26, No. 2, 206–117 (1978).
H. Rostad, “Colonic motility in the cat. II. Extrinsic nervous control,” Acta Physiol. Scand., 89, No. 1, 91–103 (1973).
H. Satomi, T. Yamamoto, H. Ise, and H. Takatama, “Origins of the parasympathetic preganglionic fibers to the cat intestine as demonstrated by the horseradish peroxidase method,” Brain Res., 151, No. 3, 571–578 (1978).
A. Sugitani, J. Yoshida, L. M. Nyhus, and P. E. Donahue, “Viscerotopic representation of preganglionic efferent vagus nerve in the brainstem of the rat: a Fluoro-Gold study,” J. Auton. Nerv. Syst., 34, No. 2–3, 211–219 (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
__________
Translated from Morfologiya, Vol. 132, No. 6, pp. 34–38, November–December, 2007.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dorofeeva, A.A., Panteleev, S.S. & Makarov, F.N. Parasympathetic innervation of the initial segments of the large intestine in cats. Neurosci Behav Physi 38, 923–927 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-008-9073-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-008-9073-7