Abstract
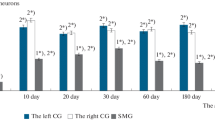
The neurotransmitter composition of neurons in the stellate ganglion of rats of different ages (neonatal, 10, 20, 30, and 60 days) was studied by an immunocytochemical method using double labeling. Most neurons in rat pups of all age groups contained tyrosine hydroxylase. Most choline acetyltransferase-positive neurocytes in neonatal and 10-day-old rat pups were also tyrosine hydroxylase-positive. Only occasional cells in 30-and 60-day rat pups contained both of these enzymes. There were increases in the proportions of cells containing tyrosine hydroxylase and neuropeptide Y from birth to all time points of the study. In addition, there was a decrease in the proportion of somatostatin-positive neurons. The proportions of VIP-positive cells and choline acetyltransferase-containing neurons increased to age 10 days and then decreased. Somatostatin-positive neurons in all rat pups were small cells, while those containing choline acetyltransferase were large. Maturation of the neurotransmitter set in the rat stellate ganglion was complete by the end of the second month of life.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. D. Nozdrachev, “The chemical structure of a peripheral autonomic (visceral) reflex,” Usp. Fiziol. Nauk., 27, No. 2, 28–60 (1996).
A. D. Nozdrachev and A. V. Yantsev, Autonomic Transmission [in Russian], St. Petersburg (1995).
A. D. Nozdrachev and M. M. Fateev, The Stellate Ganglion. Structure and Function [in Russian], St. Petersburg (2002).
V. S. Sheveleva, Evolution of the Functions of the Sympathetic Ganglia in Ontogenesis [in Russian], Leningrad (1977).
A. G. M. Bullock, “Somatostatin enhances neurite outgrowth and electrical coupling of regenerating neurons in Helisoma,” Brain Res., 412, 6–17 (1987).
P. Cochard, M. Goldstein, and I. B. Black, “Initial development of the noradrenergic phenotype in autonomic neuroblasts of the rat embryo in vivo,” Dev. Biol., 71, 109–114 (1979).
H. H. Dale and W. Feldberg, “The chemical transmission of secretory impulses to the sweat glands of the cat,” J. Physiol., 82, 121–128 (1934).
U. Ernsberger, “The development of postganglionic sympathetic neurons: coordinating neuronal differentiation and diversification,” Auton. Neurosci. Basic Clin., 94, 1–13 (2001).
U. Ernsberger and H. Rohrer, “Development of the cholinergic neurotransmitter phenotype in postganglionic sympathetic neurons,” Cell Tiss. Res., 297, 339–361 (1999).
U. S. von Euler, “A specific sympathomimetic ergone in sympathetic nerve fibers (sympathin) and its relation to adrenaline and noradrenaline,” Acta Physiol. Scand., 12, 73–97 (1946).
J. B. Furness, J. L. Morris, I. L. Gibbins, and M. Costa, “Chemical coding of neurons and plurichemical transmission,” Ann. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol., 29, 289–306 (1989).
I. L. Gibbins, “Vasocomotor, pilomotor and secretomotor neurons distinguished by size and neuropeptide content in superior cervical ganglia of mice,” J. Auton. Nerve Syst., 34, 171–183 (1991).
L. Klimaschewski, W. Kummer, and C. Heym, “Localization, regulation and function of neurotransmitters and neuromodulators in cervical sympathetic ganglia,” Microsc. Res. Tech., 35, 44–68 (1996).
P. M. Masliukov, V. A. Pankov, A. A. Strelkov, E. A. Masliukova, V. V. Shilkin, and A. D. Nozdrachev, “Morphological features of neurons innervating different viscera in the cat stellate ganglion in postnatal ontogenesis,” Aut. Neurosci. Basic Clin., 84, 169–175 (2000).
P. M. Masliukov, V. V. Shilkin, A. D. Nozdrachev, and J.-P. Timmermans, “Histochemical features of neurons in the cat stellate ganglion during postnatal ontogenesis,” Aut. Neurosci. Basic Clin., 106, 84–90 (2003).
M. A. Morales, K. Holmberg, Z. Q. Xu, C. Cozzari, B. K. Hartman, P. Emson, M. Goldstein, L. G. Elfvin, and T. Hokfelt, “Localization of choline acetyltransferase in rat peripheral sympathetic neurons and its coexistence with nitric oxide synthase and neuropeptides,” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 92, 11819–11823 (1995).
D. W. Pincus, E. M. DiCicco-Bloom, and I. B. Black, “Vasoactive intestinal peptide regulates mitosis, differentiation and survival of cultured sympathetic neuroblasts,” Nature, 343, 564–567 (1990).
V. Roudenok, “Changes in the expression of neuropeptide Y (NPY) during maturation of human sympathetic ganglionic neurons: correlations with tyrosine hydroxylase immunoreactivity,” Ann. Anat., 182, 515–519 (2000).
H. M. Young, R. B. Anderson, and C. R. Anderson, “Guidance cues involved in the development of the peripheral autonomic nervous system,” Aut. Neurosci. Basic Clin., 112, 1–14 (2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
__________
Translated from Rossiiskii Fiziologicheskii Zhurnal imeni I. M. Sechenova, Vol. 92, No. 2, pp. 214–220, February, 2006.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maslyukov, P.M., Nozdrachev, A.D. & Timmermans, JP. Age-related characteristics of the neurotransmitter composition of neurons in the stellate ganglion. Neurosci Behav Physiol 37, 349–353 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-007-0020-9
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-007-0020-9