Abstract
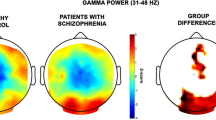
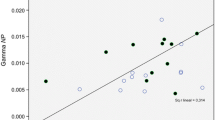
We report here studies of comparative measures of spectral density and cortical interactions in EEG rhythms in health and schizophrenia. In healthy subjects, all rhythms were symmetrical and synchronous. In “acute” schizophrenia, unlike the situation in health, there was asymmetry (predominantly right-sided) in the distribution of the spectral power of EEG rhythms. In chronic patients, asymmetry was less marked, though the power of most EEG rhythms was significantly lower than in the other two study groups. “Acute” patients showed a lack of interhemisphere interactions for all rhythms apart from the alpha rhythm, while the number of cortical interactions in chronic patients was rather lower than that in the “acute” patients, though there were significantly fewer than in healthy subjects. In addition, the gamma range showed only one interhemisphere association in the posterior areas. These neurophysiological characteristics may underlie a number of the impairments of mental activity in patients with schizophrenia. These data may also indicate that the linkage between power characteristics and synchronization of EEG rhythms is a necessary condition for normal perceptive and cognitive activity and the organization of behavior.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zh. V. Golikova and V. B. Strelets, “Development of examination stress in subjects with different levels of cortical arousal,” Zh. Vyssh. Nerv. Deyat., 53, No. 6, 697–704 (2003).
A. M. Ivanitskii, “The cerebral basis of subjective experiences: the information synthesis hypothesis,” Zh. Vyssh. Nerv. Deyat., 46, No. 2, 241–252 (1996).
V. A. Kazakova “The Monte Carlo method in quantum field theory: an experiment without amplification,” in: Experiments on Display: First Steps in Numerical Physics [in Russian], Nauka, Moscow (1989).
N. E. Sviderskaya and T. A. Korol’kova, “Spatial organization of electrical processes in the brain: questions and answers,” Zh. Vyssh. Nerv. Deyat., 47, No. 5, 792–811 (1997).
V. B. Strelets, “Inter-and intrahemisphere abnormalities in biopotentials (brain mapping) in a number of mental pathologies,” Zh. Vyssh. Nerv. Deyat., 43, No. 2, 262–270 (1993).
V. B. Strelets, R. A. Magomedov, Zh. V. Golikova, and V. Yu. Novototskii-Vlasov, “Spectral power and intracortical interactions in the beta-2 rhythm in health and schizophrenia,” Zh. Vyssh. Nerv. Deyat., 54, No. 2, 229–236 (2004).
V. B. Strelets, V. Yu. Novototskii-Vlasov, and Zh. V. Golikova, “Cortical connections in patients with schizophrenia with positive and negative symptoms,” Zh. Vyssh. Nerv. Deyat., 51, No. 4, 452–460 (2001).
G. Harman, Modern Factor Analysis [Translated from English], Statistika, Moscow (1972).
R. P. Behrendt, “Hallucinations: Synchronisation of thalamo-cortical γ oscillations underconstrained by sensory input,” Consciousness and Cognition, 12, 413–451 (2003).
M. R. Bennet, The Idea of Consciousness. Synapses and the Mind, Harwood Academic, UK (1997).
A. Burgess and L. Ali, “Functional connectivity of gamma EEG activity is modulated at low frequency during conscious recollection,” Int. J. Psychophysiol., 46, 91–100 (2002).
E. Gordon, L. Williams, A. R. Haig, J. Wright, and R. A. Meares, “Symptom profile and “ gamma” processing in schizophrenia,” Cogn. Neuropsychiatry, 6, 7–19 (2001).
J. A. Gray, “Integrating schizophrenia,” Schizo. Bull., 24, 249–266 (1998).
J. H. Gruzelier, “The factorial structure of schizotypy. I. Affinities and contrasts with syndromes of schizophrenia,” Schizo. Bull., 2, 611–620 (1996).
J. H. Gruzelier, “Theory, methods and new directions in the psychophysiology of the schizophrenic process and schizotypy,” Int. J. Psychophysiol., 48, 221–245 (2003).
W. Klimesch, M. Doppelmayr, D. Rohm, D. Pollhuber, and W. Stadler, “Simultaneous desynchronization and synchronization of different alpha responses in human electroencephalography: a neglected paradox?” Neurosci. Lett., 284, 97–100 (2000).
W. Klimesch, P. Sauseng, and C. Gerloff, “Enhancing cognitive performance with repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation at human individual alpha frequency,” Eur. J. Neurosci., 17, 1129–1133 (2003).
K. Lee, L. M. Williams, M. Breakspear, and E. Gordon, “Synchronous gamma activity: a review and contribution to an integrative neuroscience model of schizophrenia,” Brain Res. Rev., 41, 57–78 (2003).
R. R. Llinas and D. Pare, “Commentary on dreaming and wakefulness,” Neurosci., 44, 521–535 (1991).
R. R. Llinas and U. Ribary, “Coherent 40-Hz oscillation characterizes dream state in humans,” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 90, 2078–2081 (1993).
F. H. Lopes da Silva, “Neural mechanisms underlying brain waves: from neural membranes to networks,” EEG Clin. Neurophysiol., 79, 81–93 (1991).
W. Singer, “Consciousness and the binding problem,” Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci., 929, 123–146 (2001).
W. Singer and C. M. Cary, “Visual feature integration and the temporal correlations hypothesis,” Ann. Rev. Neurosci., 18, 555–586 (1995).
M. Steriade, “Synchronized activities of coupled oscillators in the cerebral cortex and thalamus at different levels of vigilance,” Cerebral Cortex, 7, 591–596 (1997).
V. B. Strelets, V. Y. Novototsky-Vlasov, and J. V. Golikova, “Cortical connectivity in high frequency beta-rhythm in schizophrenics with positive and negative symptoms,” Int. J. Psychophysiol., 44, 101–115 (2002).
G. Tononi, O. Sporns, and G. M. Edelman, “A measure for brain complexity: relating functional segregation and integration in the nervous system,” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 91, 5033–5037 (1994).
A. von Stain and J. Sarntein, “Different frequencies for different scale of cortical integration: from local gamma to long range alpha/theta synchronization,” Int. J. Psychophysiol., 38, No. 3, 301–314 (2000).
M. A. Whittington, R. D. Traub, H. G. Faulkner, I. M. Stanford, and J. G. R. Jeffreys, “Recurrent EPSPs induced by synchronised fast oscillations,” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 94, 12198–12203 (1997).
L. M. Williams, “Cognitive inhibition and schizophrenic symptom subgroups,” Schizo. Bull., 22, 139–151 (1996).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
__________
Translated from Zhurnal Vysshei Nervnoi Deyatel’nosti imeni I. P. Pavlova, Vol. 55, No. 4, pp. 496–504, July–August, 2005.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Strelets, V.B., Garakh, Z.V., Novototskii-Vlasov, V.Y. et al. Relationship between EEG power and rhythm synchronization in health and cognitive pathology. Neurosci Behav Physiol 36, 655–662 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-006-0070-4
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-006-0070-4