Abstract
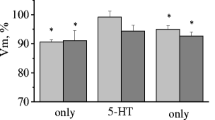
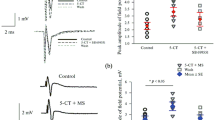
Rhythmic electrical stimulation of the snail foot leads to sensitization of the defensive reflex. This sensitization has dynamics similar to those of posttetanic potentiation of the amplitude of the acetylcholine-evoked influx current of defensive behavior command neurons in the common snail. It is likely that an increase in the cholinosensitivity of the somatic membrane of defensive behavior command neurons in the common snail may be involved in the mechanism of sensitization of the animal’s defensive response. Methiothepin, an antagonist of serotonin receptors, prevented the posttetanic potentiation of the acetylcholine-evoked influx current as well as behavioral sensitization. Serotonin, like methiothepin, also impaired posttetanic potentiation of the acetylcholine-evoked influx current. It is suggested that methiothepin-sensitive serotonin receptors are involved in the postsynaptic mechanism of behavioral sensitization.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. S. Abramova, E. I. Drozdova, V. L. Nistratova, and A. S. Pivovarov, “The relationship between posttetanic potentiation of the cholinosensitivity of neurons in the common snail and the humoral factor,” Zh. Vyssh. Nerv. Deyat., 53, No. 5, 533–536 (2003).
B. I. Kotlyar, Plasticity of the Nervous System [in Russian], Moscow State University Press, Moscow (1986).
O. A. Maksimova and P. M. Balaban, Neuronal Mechanisms of the Plasticity of Behavior [in Russian], Nauka, Moscow (1983).
A. A. Moskvitin and A. S. Pivovarov, “An apparatus for recording the defensive reactions of the terrestrial snail to tactile stimulation,” Zh. Vyssh. Nerv. Deyat., 53, No. 2, 249–252 (2003).
A. S. Pivovarov and E. I. Drozdova, “Identification of cholinoreceptors of the bodies of neurons LPa3 and RPa3 in the common snail,” Neirofiziologiya, 24, No. 1, 77–86 (1992).
A. S. Pivovarov, E. I. Drozdova, and A. A. Moskvitin, “Generalized posttetanic changes in excitatory postsynaptic and acetylcholine-evoked currents in common snail neurons,” Zh. Vyssh. Nerv. Deyat., 49, No. 6, 990–998 (1999).
A. S. Pivovarov and V. L. Nistratova, “Modulatory serotonin receptors on the bodies of command neurons in the common snail,” Byull. Éksperim. Biol. Med., 136, No. 8, 132–134 (2003).
D. Barbas, J. P. Zappulla, S. Angers, M. Bouvier, V. F. Castellucci, and L. DesGroseillers, “Functional characterization of a novel serotonin receptor (5-HTap2) expressed in the CNS of Aplysia californica,” J. Neurochem., 80, No. 2, 335–345 (2002).
H. C. Dringenberg, C. H. Vanderwolf, and P. A. Noseworthy, “Superior colliculus stimulation enhances neocortical serotonin release and electrocorticographic activation in the urethane-anesthetized rat,” Brain Res., 964, No. 1, 31–41 (2003).
J. Levenson, J. Byrne, and A. Eskin, “Levels of serotonin in the hemolymph of Aplysia are modulated by light/dark cycles and sensitization training,” J. Neurosci., 19, No. 18, 8094–8013 (1999).
G. P. Luscombe, K. F. Martin, L. J. Hutchins, J. Gosden, and D. J. Heal, “Mediation of the antidepressant-like effect of 8-OH-DPAT in mice by postsynaptic 5-HT1A receptors,” Brit. J. Pharmacol., 108, No. 3, 669–677 (1993).
A. Vehovszky, L. Hernadi, K. Elekes, and P. M. Balaban, “Serotonergic input on identified command neurons in Helix,” Acta Biol. Hung., 44, No. 1, 97–101 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
__________
Translated from Zhurnal Vysshei Nervnoi Deyatel’nosti imeni I. P. Pavlova, Vol. 55, No. 3, pp. 385–392, May–June, 2005.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abramova, M.S., Nistratova, V.L., Moskvitin, A.A. et al. Methiothepin-sensitive serotonin receptors are involved in the postsynaptic mechanism of sensitization of the defensive response in the common snail. Neurosci Behav Physiol 36, 589–596 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-006-0062-4
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-006-0062-4