Abstract
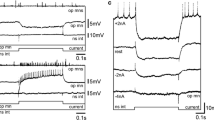
A new method of making preparations was used to analyse the neuroeffector connections of the paired giant neurons of the African snail Achatina fulica. These neurons were found to induce postsynaptic potentials in the muscles of the mantle, heart, the wall of the pulmonary cavity, and the muscular elements of the renal complex, the pericardium, the sexual apparatus, the walls of the cerebral arteries, the filaments of the columellar muscles, the wall of the abdomen, and the tentacle retractor muscles. Rhythmic neuron activity led to the development of marked facilitation and long-term potentiation of synaptic potentials. The possible significance of the multiple neuroeffector connections of giant neurons is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
V. P. Babmindra, V. L. Zhuravlev, I. N. Pavlenko, T. A. Safonova, and V. A. Mestnikov, “Identification of neurons in the common snail by a peroxidase method,” Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR, 245, No.3, 743–745 (1979).
V. L. Zhuravlev, M. Yu. Inyushin, and T. A. Safonova, “Studies of postsynaptic potentials in the myocardium of snails of the genus Helix,” Zh. Evolyuts. Biokhim. Fiziol., 25, No.5, 589–597 (1989).
V. N. Ierusalimskii, I. S. Zakharov, T. A. Palikhova, and P. M. Balaban, “The nervous system and mapping of neurons in the pulmonate mollusk Helix lucorum,” Zh. Vyssh. Nerv. Deyat., 42, No.6, 1075–1089 (1992).
M. Yu. Inyushin, V. L. Zhuravlev, and T. A. Safonova, “Command neurons of the pneumostoma initiate synaptic potentials in the heart and lung of the snail,” Zh. Vyssh. Nerv. Deyat., 37, No.3, 581–583 (1987).
P. D. Lisachev and V. P. Tret’yakov, “Distribution of process of neurons LPa3 and RPa3 in the nerves of the pedal ganglia of the common snail,” Zh. Vyssh. Nerv. Deyat., 38, No.6, 1132–1137 (1988).
O. A. Maksimova and P. M. Balaban, Neural Mechanisms of Behavioral Plasticity [in Russian], Nauka, Moscow (1993).
A. A. Mokrushin and M. O. Samoilov, “Peptide-dependent mechanisms of long-term post-tetanic potentiation, ” Usp. Fiziol. Nauk., 30, No.1, 3–28 (1999).
T. A. Safonova, V. A. Mestnikov, and V. L. Zhuravlev, “Characteristics of neurons associated with pneumostoma movements in the snail Helix pomatiaa,” Zh. Evolyuts. Biokhim. Fiziol., 20, No.5, 488–495 (1984).
A. Alevizos, C. H. Bailey, M. Chen, and J. Koester, “Innervation of vascular and cardiac muscle of Aplysia by multimodal motoneuron L7,” J. Neurophysiol., 61, No.5, 1053–1063 (1989).
K. J. Buckett, M. Peters, G. J. Dockray, J. Van Minnen, and P. R. Benjamin, “Regulation of heartbeat in Lymnaea by motoneurons containing FMRFamide-like peptides,” J. Neurophysiol., 63, No.6, 1426–1435 (1990).
R. Bychkov, V. Zhuravlev, S. Kadirov, and T. Safonova, “Cardiac inhibitory neurons in the snail Achatina fulicaa,” J. Brain Res., 38, No.3, 263–278 (1997).
K. Elekes and D. R. Nassel, “Distribution of FMRFamide-like immunoreactive neurons in the central nervous system of the snail Helix pomatia,” Cell Tiss. Res., 262, 177–190 (1990).
M. Fujiwara-Sakata and M. Kobayashi, “Localization of FMRFa-mide and ACEP-1-like immunoreactivities in the nervous system and heart of a pulmonate mollusc, Achatina fulica,” Cell Tiss. Res., 278, 451–460 (1994).
T. Goto, B. S. Ku, and H. Takeuchi, “Axonal pathways of giant neurons identified in the right parietal and visceral ganglia in the suboesophageal ganglia of an African giant snail (Achatina fulica Ferussac),” Comp. Biochem. Physiol., 83A, 93–104 (1986).
R. M. Kerkhoven, M. D. Ramkema, J. Van Minnen, R. P. Croll, T. Pin, and H. H. Boer, “Neurons in a variety of molluscs react to antibodies raised against the VD1/RPD2 alpha-neuropeptide of the pond snail Lymnaea stagnalis,” Cell Tiss. Res., 23, No.2, 371–379 (1993).
K. L. Magleby, “The effect of tetanic and post-tetanic potentiation on facilitation of transmitter release at the frog neuromuscular junction,” J. Physiol. (London), 234, No.2, 353–373 (1973).
D. P. Munoz, P. A. Pawson, and R. Chase, Symmetrical giant neurones in asymmetrical ganglia: implications for evolution of the nervous system in pulmonate molluscs,” J. Exptl. Biol., 107, 147–161 (1983).
J. Ripplinger, “Contribution a l’etude de la physiologie de coeur et son innervation extrinsique chez l’escargot (Helix pomatia),” Zool. Physiol., 8, 3–179 (1957).
H. Van Wilgenburg and J. V. Milligan, “Neurons in the suboesophageal ganglion of the snail, Helix pomatia, having functional relations to cardiorespiratory activity,” in: Neurobiology of Invertebrates. Gastropoda Brain, Akademiai Kiado, Budapest (1976), pp. 615–627.
V. L. Zhuravlev, V. V. Bugaj, T. A. Safonova, and S. A. Kodirov, “New cardioinhibitory neurons and new type of inhibitory postsynaptic potentials in the heart of giant African snail, Achatina fulica,” in: Abstracts of XXXIII International Congress of Physiological Sciences, St. Petersburg (1997), N P072.11.
V. Zhuravlev, V. Bugaj, T. Safonova, O. Senkov, and S. Kodirov, “The chronoinotropic effects of new regulatory input to the heart of land pulmonates,” Acta Biological Hungarica, 50, No.1–3, 309–318 (1999).
V. Zhuravlev, V. Bugaj, S. Kodirov, T. Safonova, and A. Staruschenko, “Giant multimodal heart motoneurons of Achatina fulica: a new cardioregulatory input in pulmonates,” Comp. Biochem. Physiol., 130A, 183–196 (2001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated from Rossiiskii Fiziologicheskii Zhurnal imeni I. M. Sechenova, Vol. 90, No. 2, pp. 169–180, February, 2004.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bugai, V.V., Zhuravlev, V.L. & Safonova, T.A. Neuroeffector Connections of Giant Multimodal Neurons in the African Snail Achatina Fulica . Neurosci Behav Physiol 35, 605–613 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-005-0100-7
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-005-0100-7