Abstract
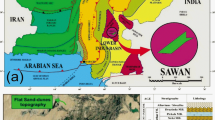
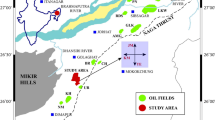
The most crucial elements in the oil and gas sector are predicting subsurface lithofacies utilizing geophysical logs for reservoir characterization and sweet spot assessment procedures. Nevertheless, accurately predicting payable lithofacies in a complex heterogeneous geological setting, such as the lower goru formation, poses considerable difficulty because conventional methods fall short in delivering highly accurate outcomes. Hence, this research proposes an advanced cost and time-saving data intelligence strategy using multiple classifiers to predict lithofacies with maximum accuracy that will aid in sweet spot evaluation in oil and gas fields globally. Geophysical log data of five wells from a mature gas field were used. The targeted reservoir formation was classified into seven facies types. We evaluated the performance of seven different models: support vector machine (SVM), K-nearest neighbors (KNN), random forest (RF), decision tree (DTr), naive Bayes (NB), adaptive boosting (AB), and ensemble (an integrated SVM, KNN, RF, and DTr classifier). RF and ensemble classifiers predicted the lithofacies with accuracies of 97.5 and 97.3%, respectively. Their efficacy in lithofacies prediction with high accuracy renders them as valuable tools in the domain of sweet spot evaluation. The proposed digital intelligence strategy could help operators identify drilling sites based on in-depth reservoir characterizations.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The authors do not have permission to share data.
References
Ahmad, N., Fink, P., Sturrock, S., Mahmood, T., & Ibrahim, M. (2004). Sequence stratigraphy as predictive tool in lower goru fairway, lower and middle Indus platform, Pakistan. PAPG, ATC, 1, 85–104.
Alalimi, A., AlRassas, A. M., Vo Thanh, H., Al-qaness, M. A., Pan, L., Ashraf, U., & Moharam, S. (2022). Developing the efficiency-modeling framework to explore the potential of CO2 storage capacity of S3 reservoir, Tahe oilfield, China. Geomechanics and Geophysics for Geo-Energy and Geo-Resources, 8(4), 1–23.
Al-Mudhafar, W. J. (2017). Integrating well log interpretations for lithofacies classification and permeability modeling through advanced machine learning algorithms. Journal of Petroleum Exploration and Production Technology, 7(4), 1023–1033.
Ali, M., Ashraf, U., Zhu, P., Ma, H., Jiang, R., Lei, G., & Anees, A. (2023a). Quantitative characterization of shallow marine sediments in tight gas fields of middle indus basin: a rational approach of multiple rock physics diagnostic models. Processes, 11(2), 323.
Ali, M., Ma, H., Pan, H., Ashraf, U., & Jiang, R. (2020). Building a rock physics model for the formation evaluation of the Lower Goru sand reservoir of the Southern Indus Basin in Pakistan. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 194, 107461.
Ali, M., Zhu, P., Jiang, R., Huolin, M., & Ashraf, U. (2024a). Improved prediction of thin reservoirs in complex structural regions using post-stack seismic waveform inversion: A case study in the Junggar Basin. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, (ja). https://doi.org/10.1139/cgj-2023-0384
Ali, M., Zhu, P., Jiang, R., Huolin, M., Ashraf, U., Zhang, H., & Hussain, W. (2024b). Data-driven lithofacies prediction in complex tight sandstone reservoirs: A supervised workflow integrating clustering and classification models. Geomechanics and Geophysics for Geo-Energy and Geo-Resources, 10(1), 1–23.
Ali, M., Zhu, P., Jiang, R., Huolin, M., Ehsan, M., Hussain, W., & Ullaah, J. (2023b). Reservoir characterization through comprehensive modeling of elastic logs prediction in heterogeneous rocks using unsupervised clustering and class-based ensemble machine learning. Applied Soft Computing, 148, 110843.
Anees, A., Zhang, H., Ashraf, U., Wang, R., Thanh, H. V., Radwan, A. E., & Shi, W. (2022). Sand-ratio distribution in an unconventional tight sandstone reservoir of Hangjinqi area, Ordos Basin: Acoustic impedance inversion-based reservoir quality prediction. Frontiers in Earth Science, 10, 1018105.
Ashraf, U., Shi, W., Zhang, H., Anees, A., Jiang, R., Ali, M., & Zhang, X. (2024). Reservoir rock typing assessment in a coal-tight sand based heterogeneous geological formation through advanced AI methods. Scientific Reports, 14(1), 5659.
Ashraf, U., Zhang, H., Anees, A., Ali, M., Zhang, X., Shakeel Abbasi, S., & Nasir Mangi, H. (2020). Controls on reservoir heterogeneity of a shallow-marine reservoir in Sawan Gas Field, SE Pakistan: Implications for reservoir quality prediction using acoustic impedance inversion. Water, 12(11), 2972.
Ashraf, U., Zhang, H., Anees, A., Mangi, H. N., Ali, M., Zhang, X., & Ullah, Z. (2021). A core logging, machine learning and geostatistical modeling interactive approach for subsurface imaging of lenticular geobodies in a clastic depositional system, SE Pakistan. Natural Resources Research, 30, 2807–2830.
Ashraf, U., Zhu, P., Yasin, Q., Anees, A., Imraz, M., Mangi, H. N., & Shakeel, S. (2019). Classification of reservoir facies using well log and 3D seismic attributes for prospect evaluation and field development: A case study of Sawan gas field, Pakistan. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 175, 338–351.
Azeem, T., Chun, W. Y., Khalid, P., Ehsan, M. I., Rehman, F., & Naseem, A. A. (2018). Sweetness analysis of Lower Goru sandstone intervals of the Cretaceous age, Sawan gas field Pakistan. Episodes Journal of International Geoscience, 41(4), 235–247.
Azeem, T., Yanchun, W., Khalid, P., Xueqing, L., Yuan, F., & Lifang, C. (2016). An application of seismic attributes analysis for mapping of gas bearing sand zones in the sawan gas field, Pakistan. Acta Geodaetica et Geophysica, 51, 723–744.
Berger, A., Gier, S., & Krois, P. (2009). Porosity-preserving chlorite cements in shallow-marine volcaniclastic sandstones: Evidence from Cretaceous sandstones of the Sawan gas field Pakistan. AAPG bulletin, 93(5), 595–615.
Breiman, L. (2001). Random forests. Machine learning, 45, 5–32.
Cant, D. (1992). Subsurface facies analysis. In R. G. Walker, & N. P. James (Eds.), Facies models-response to sea level changes (pp. 27–46). Geological Association of Canada
Chen, W., Yang, L., Zha, B., Zhang, M., & Chen, Y. (2020). Deep learning reservoir porosity prediction based on multilayer long short-term memory network. Geophysics, 85(4), 213–225.
Farzi, R., & Bolandi, V. (2016). Estimation of organic facies using ensemble methods in comparison with conventional intelligent approaches: A case study of the South Pars Gas Field, Persian Gulf Iran. Modeling Earth Systems and Environment, 2, 1–13.
Friedman, J., Hastie, T., & Tibshirani, R. (2000). Additive logistic regression: A statistical view of boosting (with discussion and a rejoinder by the authors). The annals of statistics, 28(2), 337–407.
Gibbons, J. D., & Chakraborti, S. (2014). Nonparametric statistical inference: Revised and expanded. CRC Press.
Hearst, M. A., Dumais, S. T., Osuna, E., Platt, J., & Scholkopf, B. (1998). Support vector machines. IEEE Intelligent Systems and their applications, 13(4), 18–28.
Hou, M., Xiao, Y., Lei, Z., Yang, Z., Lou, Y., & Liu, Y. (2023). Machine learning algorithms for lithofacies classification of the Gulong Shale from the Songliao Basin China. Energies, 16(6), 2581.
Ippolito, M., Ferguson, J., & Jenson, F. (2021). Improving facies prediction by combining supervised and unsupervised learning methods. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 200, 108300.
Jaikla, C., Devarakota, P., Auchter, N., Sidahmed, M., & Espejo, I. (2019). FaciesNet: Machine learning applications for facies classification in well logs. In: Paper presented at the second workshop on machine learning and the physical sciences at the 33rd conference on neural information processing systems (NeurIPS).
Jiang, R., Zhao, L., Xu, A., Ashraf, U., Yin, J., Song, H., & Anees, A. (2021). Sweet spots prediction through fracture genesis using multi-scale geological and geophysical data in the karst reservoirs of Cambrian Longwangmiao Carbonate Formation, Moxi-Gaoshiti area in Sichuan Basin, South China. Journal of Petroleum Exploration and Production Technology, 12, 1–16.
Jiang, R., Ji, Z., Mo, W., Wang, S., Zhang, M., Yin, W., & Ashraf, U. (2022). A novel method of deep learning for shear velocity prediction in a tight sandstone reservoir. Energies, 15(19), 7016.
Kadri, I. B. (1995). Petroleum geology of Pakistan. Pakistan Petroleum Limited.
Khan, J., Moghal, M. A., & Jamil, M. A. (1999). Evolution of shelf margin & distribution of reservoir facies in early cretaceous of Central Indus Basin Pakistan. In: Paper presented at the annual technical conference (ATC).
Kim, J. (2022). Lithofacies classification integrating conventional approaches and machine learning technique. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 100, 104500.
Koeshidayatullah, A., Al-Azani, S., Baraboshkin, E. E., & Alfarraj, M. (2022). Faciesvit: Vision transformer for an improved core lithofacies prediction. Frontiers in Earth Science, 10, 992442.
Mandal, P. P., & Rezaee, R. (2019). Facies classification with different machine learning algorithm–An efficient artificial intelligence technique for improved classification. ASEG Extended Abstracts, 2019(1), 1–6.
Manzoor, U., Ehsan, M., Radwan, A. E., Hussain, M., Iftikhar, M. K., & Arshad, F. (2023). Seismic driven reservoir classification using advanced machine learning algorithms: A case study from the lower Ranikot/Khadro sandstone gas reservoir, Kirthar fold belt, lower Indus Basin Pakistan. Geoenergy Science and Engineering, 222, 211451.
Martin, T., Meyer, R., & Jobe, Z. (2021). Centimeter-scale lithology and facies prediction in cored wells using machine learning. Frontiers in Earth Science, 9, 659611.
McPhee, C., & Enzendorfer, C. (2004). Sand management solutions for high-rate gas wells, Sawan field, Pakistan. In: Paper presented at the SPE international conference and exhibition on formation damage control.
Merembayev, T., Kurmangaliyev, D., Bekbauov, B., & Amanbek, Y. (2021). A Comparison of machine learning algorithms in predicting lithofacies: Case studies from Norway and Kazakhstan. Energies, 14(7), 1896.
Mishra, A., Sharma, A., & Patidar, A. K. (2022). Evaluation and development of a predictive model for geophysical well log data analysis and reservoir characterization: Machine learning applications to lithology prediction. Natural Resources Research, 31(6), 3195–3222.
Misra, S., & Wu, Y. (2019). Machine learning assisted segmentation of scanning electron microscopy images of organic-rich shales with feature extraction and feature ranking. Machine learning for subsurface characterization, 289(3), 4.
Mohamed, I. M., Mohamed, S., Mazher, I., & Chester, P. (2019). Formation lithology classification: Insights into machine learning methods. In: Paper presented at the SPE annual technical conference and exhibition.
Mubarak, Y., & Koeshidayatullah, A. (2023). Hierarchical automated machine learning (AutoML) for advanced unconventional reservoir characterization. Scientific Reports, 13(1), 13812.
Munir, K., Iqbal, M. A., Farid, A., & Shabih, S. M. (2011). Mapping the productive sands of Lower Goru Formation by using seismic stratigraphy and rock physical studies in Sawan area, southern Pakistan: A case study. Journal of Petroleum Exploration and Production Technology, 1, 33–42.
Qi, L., & Carr, T. R. (2006). Neural network prediction of carbonate lithofacies from well logs, Big Bow and Sand Arroyo Creek fields Southwest Kansas. Computers & Geosciences, 32(7), 947–964.
Quadri, V.-N., & Shuaib, S. M. (1987). Geology and hydrocarbon prospects of Pakistan’s offshore Indus basin. Oil and Gas J., 85(35), 65–67.
Raeesi, M., Moradzadeh, A., Ardejani, F. D., & Rahimi, M. (2012). Classification and identification of hydrocarbon reservoir lithofacies and their heterogeneity using seismic attributes, logs data and artificial neural networks. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 82, 151–165.
Radwan, A. E. (2021). Modeling the depositional environment of the sandstone reservoir in the Middle Miocene Sidri Member, Badri Field, Gulf of Suez Basin, Egypt: Integration of gamma-ray log patterns and petrographic characteristics of lithology. Natural Resources Research, 30(1), 431–449.
Radwan, A. E., Nabawy, B. S., Kassem, A. A., & Hussein, W. S. (2021). Implementation of rock typing on waterflooding process during secondary recovery in oil reservoirs: A case study, El Morgan Oil Field, Gulf of Suez Egypt. Natural Resources Research, 30(2), 1667–1696.
Rashid, M., Luo, M., Ashraf, U., Hussain, W., Ali, N., Rahman, N., & Anees, A. (2022). Reservoir quality prediction of gas-bearing carbonate sediments in the Qadirpur field: Insights from advanced machine learning approaches of SOM and cluster analysis. Minerals, 13(1), 29.
Ren, X., Hou, J., Song, S., Liu, Y., Chen, D., Wang, X., & Dou, L. (2019). Lithology identification using well logs: A method by integrating artificial neural networks and sedimentary patterns. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 182, 106336.
Rizwan, M., Akhter, G., Mustafa, A., Bin Nisar, U., & Ashfaq, K. (2018). Amplitude versus offset (AVO) modelling and analysis for quantitative interpretation of porosity and saturation: A case study for Sawan gas field, middle Indus basin Pakistan. Geofísica internacional, 57(2), 151–160.
Robison, C. R., Smith, M. A., & Royle, R. A. (1999). Organic facies in Cretaceous and Jurassic hydrocarbon source rocks, Southern Indus basin Pakistan. International journal of coal geology, 39(1–3), 205–225.
Rogers, S. J., Fang, J., Karr, C., & Stanley, D. (1992). Determination of lithology from well logs using a neural network. AAPG Bulletin, 76(5), 731–739.
Schapire, R. E. (1999). A brief introduction to boosting. In: Paper presented at the Ijcai.
Shahid, M., Rahman, S. U., Syed, S. S., Haq, M. Z. U., & Palekar, A. (2008). Identification of low resistivity hydrocarbon bearing reservoirs in lower & middle indus basin using available wireline logs. In: Paper presented at the Annual Technical Conference, Islamabad, Pakistan.
Shen, C., Asante-Okyere, S., Yevenyo Ziggah, Y., Wang, L., & Zhu, X. (2019). Group method of data handling (GMDH) lithology identification based on wavelet analysis and dimensionality reduction as well log data pre-processing techniques. Energies, 12(8), 1509.
Soucy, P., & Mineau, G. W. (2001). A simple KNN algorithm for text categorization. In: Paper presented at the Proceedings 2001 IEEE international conference on data mining.
Sun, Z., Jiang, B., Li, X., Li, J., & Xiao, K. (2020). A data-driven approach for lithology identification based on parameter-optimized ensemble learning. Energies, 13(15), 3903.
Tahmasebi, P., Javadpour, F., & Sahimi, M. (2017). Data mining and machine learning for identifying sweet spots in shale reservoirs. Expert Systems with Applications, 88, 435–447.
Tewari, S., & Dwivedi, U. D. (2020). A comparative study of heterogeneous ensemble methods for the identification of geological lithofacies. Journal of Petroleum Exploration and Production Technology, 10(5), 1849–1868.
Thanh, H. V., Zamanyad, A., Safaei-Farouji, M., Ashraf, U., & Hemeng, Z. (2022). Application of hybrid artificial intelligent models to predict deliverability of underground natural gas storage sites. Renewable Energy, 200, 169–184.
Thode, H. C. (2002). Statistics: textbooks and monographs. Testing for normality. (Vol. 164). New York: Marcel Dekker.
Ullah, J., Li, H., Ashraf, U., Ehsan, M., & Asad, M. (2023a). A multidisciplinary approach to facies evaluation at regional level using well log analysis, machine learning, and statistical methods. Geomechanics and Geophysics for Geo-Energy and Geo-Resources, 9(1), 1–24.
Ullah, S., Hanif, M., Radwan, A. E., Luo, C., Rehman, N. U., Ahmad, S., & Ashraf, U. (2023b). Depositional and diagenetic modeling of the Margala Hill Limestone, Hazara area (Pakistan): Implications for reservoir characterization using outcrop analogues. Geoenergy Science and Engineering, 224, 211584.
Vapnik, V. (1999). The nature of statistical learning theory. Springer.
Wandrey, C. J., Law, B. E., & Shah, H. A. (2004). Patala-Nammal composite total petroleum system, Kohat-Potwar geologic province, Pakistan (pp. 1-18). Reston: US Department of the Interior, US Geological Survey.
Wood, D. A. (2021). Enhancing lithofacies machine learning predictions with gamma-ray attributes for boreholes with limited diversity of recorded well logs. Artificial Intelligence in Geosciences, 2, 148–164.
Wong, P. M., Gedeon, T. D., & Taggart, I. J. (1995). An improved technique in porosity prediction: A neural network approach. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 33(4), 971–980.
Xing, Y., Lv, C., & Cao, D. (2020). Advanced driver intention inference. Elsevier.
Xu, C., Fu, L., Lin, T., Li, W., & Ma, S. (2022). Machine learning in petrophysics: Advantages and limitations. Artificial Intelligence in Geosciences, 3, 157–161.
Yasin, Q., Sohail, G. M., Ding, Y., Ismail, A., & Du, Q. (2020). Estimation of petrophysical parameters from seismic inversion by combining particle swarm optimization and multilayer linear calculator. Natural Resources Research, 29, 1–27.
Zheng, D., Hou, M., Chen, A., Zhong, H., Qi, Z., Ren, Q., & Ma, C. (2022). Application of machine learning in the identification of fluvial-lacustrine lithofacies from well logs: A case study from Sichuan Basin, China. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 215, 110610.
Zhou, Y., Zhou, N., Gong, L., & Jiang, M. (2020). Prediction of photovoltaic power output based on similar day analysis, genetic algorithm and extreme learning machine. Energy, 204, 117894.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Directorate General of Petroleum Concessions (DGPC), Ministry of Petroleum, Pakistan, for the release of well data.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. U2202207), and the Special Project for Social Development of Yunnan Province (Grant No. 202103AC100001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ashraf, U., Zhang, H., Thanh, H.V. et al. A Robust Strategy of Geophysical Logging for Predicting Payable Lithofacies to Forecast Sweet Spots Using Digital Intelligence Paradigms in a Heterogeneous Gas Field. Nat Resour Res (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-024-10350-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-024-10350-4