Abstract
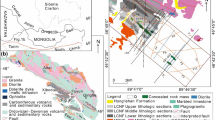
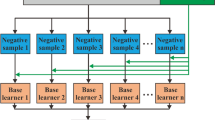
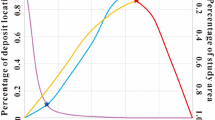
Three-dimensional (3D) mineral prospectivity mapping (MPM) uses mathematical models to integrate different types of 3D data related to mineralization to obtain mineral prospectivity information in 3D space. Existing geological data contain known deposits, non-deposits and unknown ore-bearing data, corresponding to positive samples, negative samples and unlabeled samples respectively in MPM. Different sample combination types require different mathematical models. In this paper, support vector machine class (SVMC) machine learning method is selected to compare the influence of different sample combination types on prediction results. The SVMC is a one-class SVM (OCSVM) model based on positive-only samples, the SVM is based on both positive and negative samples, and the bagging-based positive-unlabeled learning algorithm with SVM base learner (BPUL-SVM) is based on both positive and unlabeled samples. The study area is in the Sanshandao-Cangshang offshore and onshore Au district, where there are Sanshandao, Cangshang and Xinli large- and super-large-scale Au deposits. Moreover, the discovery of large-scale Sea Au deposits in the sea area indicates the great potential for mineralization in the district. According to the metallogenic geological characteristics, the Au deposits in the Sanshandao-Cangshang district are controlled by the NE-striking fault and are closely related to the Linglong intrusions and Guojialing intrusions. The ore-bearing intrusion shows low density and low-moderate magnetic susceptibility. Because the Au orebodies hosted in the Sanshandao fault and its secondary faults, the NE-striking faults are key to delineating the targets. In this paper, weights of evidence (WofE), OCSVM, SVM and BPUL-SVM are used to MPM, and the prediction-area (P-A) plot method is used to delineate the targets. According to the ROC curve, F1 score and P-A plot evaluation methods, the model performance from high to low is BPUL-SVM13, SVM12, WofE and OCSVM. The BPUL-SVM model performance with samples combination types of positive samples and unlabeled samples was optimum in SVMC prediction models. The Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) simulation and return-risk evaluation model are used to evaluate the return and risk of the targets and finally determine the I-level targets with high return and low risk. The delineated targets are mainly distributed along the F2 and F3 faults (Sanshandao-Cangshang fault). Combined with the mineralization regularity, the deep and periphery space of the known deposits are important to explore Au orebodies. The delineated targets are important to explore offshore and onshore Au orebodies in the Sanshandao-Cangshang district.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acquah, H.D.-G. (2013). Bayesian logistic regression modelling via Markov chain Monte Carlo algorithm. Journal of Social and Development Sciences, 4(4), 193–197.
Agterberg, F. P. (1992). Combining indicator patterns in weights of evidence modeling for resource evaluation. Non-renewable Resources, 1(1), 39–50.
Bergstra, J., Bardenet, R., Bengio, Y., & Kégl, B. (2011). Algorithms for hyper-parameter optimization. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2011, 2546–2554.
Boisvert, J. B., Rossi, M. E., Ehrig, K., & Deutsch, C. V. (2013). Geometallurgical modeling at olympic dam mine, South Australia. International Association for Mathematical Geosciences, 45, 901–925. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11004-013-9462-5
Bonham-Carter, G.F., Agterberg, F.P., & Wright, D.F. (1989). Weights of evidence modelling: a new approach to mapping mineral potential. In: Agterberg, F.P., Bonham-Carter, G.F.(Eds.), Statistical Applications in the Earth Sciences Geological Survey of Canada, pp. 171–183. Paper 89-9.
Buckland, M., & Gey, F. (1994). The relationship between recall and precision. Journal of the American Society for Information Science, 45(1), 12–19.
Carranza, E. J. M. (2004). Weights of evidence modeling of mineral potential: A case study using small number of prospects, Abra Philippines. Natural Resources Research, 13(3), 173–187.
Carranza, E. J. M., & Laborte, A. G. (2015). Data-driven predictive mapping of gold prospectivity, Baguio district, Philippines: Application of Random Forests algorithm. Ore Geology Reviews, 71, 777–787.
Carranza, E. J. M., Hale, M., & Faassen, C. (2008). Selection of coherent deposit-type locations and their application in datadriven mineral prospectivity mapping. Ore Geology Reviews, 33, 536–558.
Chen, Y. L., & Wu, W. (2017). Mapping mineral prospectivity by using one-class support vector machine to identify multivariate geological anomalies from digital geological survey data. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 64, 639–651.
Chen, Y., & Wu, W. (2019). Isolation forest as an alternative data-driven mineral prospectivity mapping method with a higher data-processing efficiency. Natural Resources Research, 28, 31–46.
Chen, G. X., Huang, N., Wu, G. P., Luo, L., Wang, D. T., & Cheng, Q. M. (2022). Mineral prospectivity mapping based on wavelet neural network and Monte Carlo simulations in the Nanling W-Sn metallogenic province. Ore Geology Reviews, 143, 104765.
Chen, T., & Guestrin, C. (2016). Xgboost: a scalable tree boosting system. In: Proc. 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 785-794. https://doi.org/10.1145/2939672.2939785
Cortes, C., & Vapnik, V. (1995). Support-vector networks. Machine Learning, 20, 273–297.
Deng, J., Liu, X. F., Wang, Q. F., & Pan, R. G. (2014). Origin of the Jiaodong-type Xinli gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, China: Constraints from fluid inclusion and C-D–O–S–Sr isotope compositions. Ore Geology Reviews, 65, 674–686.
Fawcett, T. (2006). An introduction to ROC analysis. Pattern Recognition Letters, 27, 861–874.
Gao, M., Wang, G. W., Yang, W. D., Zhang, Z. Q., Cai, D. Z., Xu, Y. C., & Yang, S. R. (2023b). Bagging-based positive-unlabeled data learning algorithm with base learners random forest and XGBoost for 3D exploration targeting in the Kalatongke District, Xinjiang China. Natural Resources Research, 32(2), 437–459.
Gao, M., Wang, G.W., Xu, Y.C., Mou, N.N., Huang, L.L., Zuo, L., & Wu, R. (2023a). 3D mineral exploration Cu-Zn targeting with multi-source geoscience datasets in the Weilasituo-bairendaba district, Inner Mongolia, China. Frontiers in Earth Science, doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2023.1102640
Ge, Y., Zhang, Z., Cheng, Q., & Wu, G. (2022). Geological mapping of basalt using stream sediment geochemical data: Case study of covered areas in Jining, Inner Mongolia China. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 232, 106888.
Getachew, N., & Meten, M. (2021). Weights of evidence modeling for landslide susceptibility mapping of Kabi-Gebro locality, Gundomeskel area. Central Ethiopia. Geoenviron Disasters, 8(1), 1–22.
Granek, J. (2016). Application of machine learning algorithms to mineral prospectivity mapping. University of British Columbia. https://doi.org/10.14288/1.0340340
Hansen, T. M., Vu, L. T., Mosegaard, K., & Cordua, K. S. (2018). Multiple point statistical simulation using uncertain (soft) conditional data. Computers & Geosciences, 114, 1–10.
Hoffman, M. D., & Gelman, A. (2014). The No-U-turn sampler: adaptively setting path lengths in hamiltonian monte carlo. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 15(1), 1593–1623.
Jia, R., Lv, Y. K., Wang, G. W., Carranza, E. J. M., Chen, Y. Q., Wei, C., & Zhang, Z. Q. (2021). A stacking methodology of machine learning for 3D geological modeling with geological-geophysical datasets, Laochang Sn camp, Gejiu (China). Computers and Geosciences, 151, 104754.
Li, Y. G., & Oldenburg, D. W. (1996). 3-D inversion of magnetic data. Geophysics, 61(2), 394–408.
Li, Y. G., & Oldenburg, D. W. (1998). 3-D inversion of gravity data. Geophysics, 63(1), 109–119.
Li, W., Teng, J. J., & Wang, Z. J. (2007). Features of ore-control structure of Cangshang gold ore deposit and practice of searching for gold ore in lower plate. Mining Engineering, 5(3), 19–20. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Li, R. X., Wang, G. W., & Carranza, E. J. M. (2016). GeoCube: A 3D mineral resources quantitative prediction and assessment system. Computers & Geosciences, 89, 161–173.
Li, S., Chen, J. P., Liu, C., & Wang, Y. (2021). Mineral prospectivity prediction via convolutional neural networks based on geological big data. Journal of Earth Science, 32(2), 327–347.
Lisitsin, V. A., Porwal, A., & McCuaig, T. C. (2014). Probabilistic fuzzy logic modelimodels using monte carlo simulations. International Association for Mathematical Geosciences, 46, 747–769.
Liu, D. H., Lv, G. X., Zhang, P. J., Ding, Z. J., Zhang, J. J., Lin, D. W., Ma, B., Lv, C. X., & Wang, Z. Y. (2015). A study of 3D ore-controlling of the tectonic altered rocks of the Sanshandao fault in Jiaodong Peninsular and the discovery of an offshore super-large gold deposit in China. Earth Science Frontiers, 22(4), 162–172. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu, X. P., Feng, T., Deng, Q. H., Lei, Y. X., & Wang, X. (2017). Geological characteristics and prospecting indicators of Zhengyangshan molybdenum deposit in Sunwu County Heilongjiang Province. Gold, 38(2), 15–23. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu, R. F., Zhou, X., Lv, Y. L., & Xu, Y. B. (2019a). Ore-Controlling regularity and prospecting practice in the Sanshandao-Cangshang fault zone Jiaodong Area. Geology and exploration, 55(2), 528–541. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu, S. P., Wang, S. Y., Feng, X. X., & Yin, C. Y. (2019b). Integrated Geophysical constraint to the NW-trending fault zone in the Xiling Gold Deposit, Sanshandao Shandong Province. Gold Science and Technology, 27(1), 25–32. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Mao, X. C., Ren, J., Liu, Z. K., Chen, J., Tang, L., Deng, H., Bayless, R. C., Yang, M., Wang, M. J., & Liu, C. M. (2019). Three-dimensional prospectivity modeling of the Jiaojia-type gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, Eastern China: A case study of the Dayingezhuang deposit. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 203, 27–44.
Markowitz, H. (1952). Portfolio selection*. The Journal of Finance, 7(1), 77–91.
Mordelet, F., & Vert, J. P. (2014). A bagging SVM to learn from positive and unlabeled examples. Pattern Recognition Letters, 37, 201–209.
Neal, R. (1993). Probabilistic inference using Markov chain Monte Carlo methods. Technical Report CRG-TR-93-1, Department of Computer Science, University of Toronto.
Neal, R. (2011). Handbook of Markov Chain Monte Carlo, chapter 5: MCMC Using Hamiltonian Dynamics. CRC Press.
Nykänen, V., Lahti, I., Niiranen, T., & Korhonen, K. (2015). Receiver operating characteristics (ROC) as validation tool for prospectivity models—A magmatic Ni–Cu case study from the Central Lapland Greenstone Belt, northern Finland. Ore Geology Reviews, 71, 853–860.
Porwal, A., Carranza, E. J. M., & Hale, M. (2003). Artificial neural networks for mineral potential mapping: A case study from Aravalli Province, Western India. Natural Resources Research, 12, 156–171.
Porwal, A., Carranza, E. J. M., & Hale, M. (2006). A hybrid fuzzy weights-of-evidence model for mineral potential mapping. Natural Resources Research, 15, 1–14.
Schölkopf, B., Platt, J. C., Shawe-Taylor, J., Smola, A. J., & Williamson, R. C. (2001). Estimating the support of a high-dimensional distribution. Neural computation, 13(7), 1443–1471.
SDGSI (Shandong institute of geological survey). (2020). Verification of gravity and magnetic anomalies in the west of Sanshandao district, Shandong Province, China. 1-65 (in Chinese).
Singer, D. A., & Kouda, R. (1999). Examining risk in mineral exploration. Natural Resources Research, 8(2), 111–122.
Song, M. C., Cui, S. X., & Jiang, H. L. (2011). Metallogenic structural system for Jiaojia gold field and Jiaoxibei gold deposits concentrated areas in Shandong Province China. Geological Bulletin of China, 30(4), 573–578. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Song, X. L., Li, J. J., Li, X. Z., Dang, Z. C., Zhao, Z. L., & Yu, C. K. (2014). The research progress of ore-forming fluids, stable isotope and mineralizing age in Jiaodong peninsular of eastern China. Contributions to Geology and Mineral Resources Research, 29(1), 13–19. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Song, M. C., Zhang, J. J., Zhang, P. J., Yang, L. Q., Liu, D. H., Ding, Z. J., & Song, Y. X. (2015a). Discovery and tectonic-magmatic background of superlarge gold deposit in offshore of Northern Sanshandao, Shandong Peninsula China. Acta Geologica Sinica, 89(2), 365–383. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Song, M. C., Li, S. Z., Santosh, M., Zhao, S. J., Yu, S., Yi, P. H., Cui, S. X., Lv, G. X., Xu, J. X., Song, Y. X., & Zhou, M. L. (2015b). Types, characteristics and metallogenesis of gold deposits in the Jiaodong Peninsula, Eastern North China Craton. Ore Geology Reviews, 65, 612–625.
Song, Y. X., Song, M. C., Ding, Z. J., Wei, X. F., Xu, S. H., Li, J., Tan, X. F., Li, S. Y., Zhang, Z. L., Jiao, X. M., Hu, H., & Cao, J. (2017). Major advances on deep prospecting in jiaodong gold ore cluster and its metallogenic characteristics. Gold Science and Technology, 25(3), 4–18. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Song, Y. X., Li, S. R., Shen, J. F., Zhang, L., Li, W. T., & Zeng, Y. J. (2021). Characteristics and prospecting significance of thermoluminescence patterns and cell parameters of quartz from the undersea gold deposit off northern Sanshandao Jiaodong Peninsula. Earth Science Frontiers, 28(2), 305–319. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang, J. H., & Tian, J. X. (2017). The determination of position of the northern extension of sanshandao fault toward waters and metallogenic prediction. Acta Geologica Sinica, 91(12), 2771–2780. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang, G. W., Li, R. X., Carranza, E. J. M., Zhang, S. T., Yan, C. H., Zhu, Y. Y., Qu, J. N., Hong, D. M., Song, Y. W., Han, J. W., Ma, Z. B., Zhang, H., & Yang, F. (2015). 3D geological modeling for prediction of subsurface Mo targets in the Luanchuan district, China. Ore Geology Reviews, 71, 592–610.
Wang, J., Zuo, R. G., & Xiong, Y. H. (2020a). Mapping mineral prospectivity via semi-supervised random forest. Natural Resources Research, 29, 189–202.
Wang, Z. Y., Yin, Z., Caers, J., & Zuo, R. G. (2020b). A Monte Carlo-based framework for risk-return analysis in mineral prospectivity mapping. Geoscience Frontiers, 11, 2297–2308.
Wang, G. W., Zhang, Z. Q., Li, R. X., Li, J. J., Sha, D. M., Zeng, Q. D., Pang, Z. S., Li, D. P., & Huang, L. L. (2021a). Resource prediction and assessment based on 3D/4D big data modeling and deep integration in key ore districts of North China. Science China Earth Sciences, 64(9), 1590–1606.
Wang, J. H., Zhang, G. L., Tao, Y. B., Wang, Y. P., & Zhu, P. G. (2021b). Discovery of structural belt in Western Sanshan island and its geological significance. Shandong Land and Resources, 37(5), 1–8. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang, J. H., Zhang, J. J., Li, X. Z., Ding, Z. J., & Mao, M. Q. (2022a). Gold exploration method and prospecting practice in Jiaodong Sea area (pp. 1–210). Geology Press.
Wang, Z. Y., Zuo, R. G., & Yang, F. F. (2022b). Geological mapping using direct sampling and a convolutional neural network based on geochemical survey data. Mathematical Geosciences, 55, 1035–1058.
Wu, B., Qiu, W., Jia, J., & Liu, N. (2020). Landslide susceptibility modeling using bagging-based positive-unlabeled learning. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 18(5), 766–770.
Xia, Y. F., Liu, C. Z., Li, Y. Y., & Liu, N. N. (2017). A boosted decision tree approach using Bayesian hyper-parameter optimization for credit scoring. Expert Systems With Applications, 78, 225–241.
Xiong, Y., & Zuo, R. (2016). Recognition of geochemical anomalies using a deep autoencoder network. Computers and Geosciences, 86, 75–82.
Xiong, Y., & Zuo, R. (2018). GIS-based rare events logistic regression for mineral prospectivity mapping. Computers and Geosciences, 111, 18–25.
Xiong, Y., & Zuo, R. (2020). Recognizing multivariate geochemical anomalies for mineral exploration by combining deep learning and one-class support vector machine. Computers & Geosciences, 140, 104484.
Xiong, Y. H., & Zuo, R. G. (2021). A positive and unlabeled learning algorithm for mineral prospectivity mapping. Computers and Geosciences, 147, 104667.
Yang, Z. Y., Yu, X. W., Zhang, W., Wang, L. G., Wang, Q. W., & Guo, R. P. (2020). Ar-Ar age and its significance of sericite in pyrite sericite in Sanshandao gold deposit in Northwest of Shandong Province. Shandong Land and Resources, 36(7), 1–8. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang, F. F., Wang, Z. Y., Zuo, R. G., Sun, S. Q., & Zhou, B. (2023). Quantification of uncertainty associated with evidence layers in mineral prospectivity mapping using direct sampling and convolutional neural network. Natural Resources Research, 32(1), 79–98.
Yousefi, M., & Carranza, E. J. M. (2015a). Fuzzification of continuous-value spatial evidence for mineral prospectivity mapping. Computers & Geosciences, 74, 97–109.
Yousefi, M., & Carranza, E. J. M. (2015b). Prediction-area (P-A) plot and C-A fractal analysis to classify and evaluate evidential maps for mineral prospectivity modeling. Computers & Geosciences, 79, 69–81.
Yuan, F., Zhang, M. M., Li, X. H., Ge, C., Lu, S. M., Li, J. S., Zhou, Y. Z., & Lan, X. Y. (2019). Prospectivity modelling: From two-dimension to three-dimension. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 35(12), 3863–3874. https://doi.org/10.18654/1000-0569/2019.12.18. Chinese with English abstract.
Zhai, Y. S. (1999). On the metallogenic system. Earth Science Frontiers, 6(1), 13–27.
Zhang, X. O., Cawood, P. A., Wilde, S. A., Liu, R. Q., Song, H. L., Li, W., & Snee, L. W. (2003). Geology and timing of mineralization at the Cangshang gold deposit, north-western Jiaodong Peninsula, China. Mineralium Deposita, 38, 141–153.
Zhang, J. J., Ding, Z. J., Liu, D. H., Zhang, P. J., Zou, J., Ma, B., & Luan, G. D. (2016). Exploration practice and prospecting results of super -large gold mine of Sanshandao Northern Sea Area in Laizhou City Shandong Province. Gold Science and Technology, 24(1), 1–10. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang, W. G., Wu, C. Z., Zhong, H. Y., Li, Y. Q., & Wang, L. (2020). Prediction of undrained shear strength using extreme gradient boosting and random forest based on Bayesian optimization. Geoscience Frontiers, 12(1), 469–477.
Zhang, Z. Q., Wang, G. W., Liu, C., Cheng, L. Z., & Sha, D. M. (2021). Bagging-based positive-unlabeled learning algorithm with Bayesian hyperparameter optimization for three-dimensional mineral potential mapping. Computers and Geosciences, 154, 104817.
Zhang, Z. Q., Wang, G. W., Carranza, E. J. M., Fan, J. J., Liu, X. X., Zhang, X., Dong, Y. L., Chang, X. P., & Sha, D. M. (2022). An integrated framework for data-driven mineral prospectivity mapping using bagging-based positiveunlabeled learning and bayesian cost-sensitive logistic regression. Natural Resources Research, 31(6), 3041–3060.
Zhao, D. D., Jin, G., Li, H. S., & Huang, J. Y. (2013). Geological characteristics of Sanshandao island gold deposit in Laizhou, Shandong Province and the genetic discussion. Contributions to Geology and Mineral Resources Research, 28(4), 546–551. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zheng, Y., Deng, H., Wu, J. J., Wang, R. S., Liu, Z. K., Wu, L. X., Mao, X. C., & Chen, J. (2023a). Space-associated domain adaptation for three-dimensional mineral prospectivity modeling. International Journal of Digital Earth, 16(1), 2885–2911.
Zhu, R. X., Zhang, H. F., Zhu, G., Meng, Q. R., Fan, H. R., Yang, J. H., Wu, F. Y., Zhang, Z. Y., & Zheng, T. Y. (2017). Craton destruction and related resources. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 106, 2233–2257. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-016-1441-x
Zuo, R. G., & Carranza, E. J. M. (2011). Support vector machine: A tool for mapping mineral prospectivity. Computers & Geosciences, 37, 1967–1975.
Zuo, R., & Wang, Z. (2020). Effects of random negative training samples on mineral prospectivity mapping. Natural Resources Research, 29(6), 3443–3455.
Zuo, R. G., Zhang, Z. J., Zhang, D. J., Carranza, E. J. M., & Wang, H. C. (2015). Evaluation of uncertainty in mineral prospectivity mapping due to missing evidence: a case study with skarn-type Fe deposits in Southwestern Fujian Province, China. Ore Geology Reviews, 71, 502–515.
Zuo, R. G., Xiong, Y., Wang, J., & Carranza, E. J. M. (2019). Deep learning and its application in geochemical mapping. Earth-Science Reviews, 129, 1–14.
Zuo, R. G., Kreuzer, O. P., Wang, J., Xiong, Y. H., Zhang, Z. J., & Wang, Z. Y. (2021). Uncertainties in GIS-based mineral prospectivity mapping: key types, potential impacts and possible solutions. Natural Resources Research, 30(5), 3059–3079.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge two anonymous reviewers for their useful comments to improve this paper. Funding support for research was provided by the “Deep-time Digital Earth” Science and Technology Leading Talents Team Funds for the Central Universities for the Frontiers Science Center for Deep-time Digital Earth, China University of Geosciences (Beijing) (Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities; grant number: 2652023001), the National Key Research and Development Programs of China (Grant No. 2022YFC2903604) and 2021 Graduate Innovation Fund Project of China University of Geosciences, Beijing (Grant No. ZD2021YC008). The authors thank Ruixi Li, Jing Li, Nini Mou, Shuren Yang, Xiaoning Liu, Leilei Huang and other group members for their help in this study. The authors thank all those who provide help to this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing any financial interest, non-financial interest or personal relationships that could influence the work reported in this paper.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, M., Wang, G., Carranza, E.J.M. et al. 3D Au Targeting using Machine Learning with Different Sample Combination and Return-Risk Analysis in the Sanshandao-Cangshang District, Shandong Province, China. Nat Resour Res 33, 51–74 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-023-10279-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-023-10279-0