Abstract
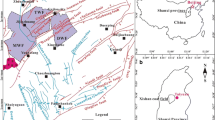
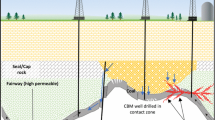
Coalbed methane (CBM) resources are abundant in eastern Yunnan and western Guizhou of China. However, despite the vast reserves, large-scale commercial development of CBM in these areas has not yet been realized. In this study, a comprehensive analysis of the productivity of CBM wells is conducted, leveraging geological and production data from a dataset comprising 19 wells. The investigation encompasses both geological and engineering perspectives, aiming to identify and assess the various factors that significantly influence CBM well productivity. The analysis of the results reveals that the well productivity is positively correlated with the proportion of Type I coal (PTIC), the ratio of critical desorption pressure to reservoir pressure (RCRP), the gas saturation (GS), the initial permeability after reservoir stimulation (IPRS) and the permeability before gas production (PBGP). The well productivity is negatively correlated with the burial depth of the coal seam floor (BDCF) and has a complex relationship with the span of the co-production coal seam. Moreover, to achieve commercial development of CBM wells, the PTIC and GS in co-production coal seam should exceed 60%, the BDCF is less than 800 m, and RCRP, IPRS and PBGP are greater than 0.6, 2.4 mD (Millidarcy. 1 mD = 0.9869233 × 10−15 m2), and 0.3 mD, respectively. The quantitative evaluation of the sensitivity of these influencing factors on CBM well productivity in eastern Yunnan and western Guizhou is accomplished using the gray relational analysis method. The study identifies GS and PBGP as the primary controlling factors impacting the productivity of CBM wells. Building upon these findings, the research presents high productive patterns for CBM wells that emphasize coordinated control of geological and engineering aspects. This research has significant implications for the exploration and development of natural gas resources, offering potential advancements in the field.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, S. D., Tang, D. Z., Tao, S., Xu, H., Li, S., Zhao, J. L., Cui, Y., & Li, Z. (2018). Characteristics of in-situ stress distribution and its significance on the coalbed methane (CBM) development in Fanzhuang-Zhengzhuang Block, Southern Qinshui Basin, China. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 161, 108–120.
Deng, J. L. (1989). Introduction to gray system theory. The Journal of Gray System, 1(1), 1–24.
Energy Institute. (2023). 72nd edition statistical review of world energy [EB/OL]. https://www.energyinst.org/statistical-review/resources-and-data-downloads.
Guo, Z. X., Zhao, J. Z., You, Z. J., Li, Y. M., Zhang, S., & Chen, Y. Y. (2021). Prediction of coalbed methane production based on deep learning. Energy, 230, 120847.
Huang, F. S., Dong, C. Y., Shang, X. S., & You, Z. J. (2021a). Effects of proppant wettability and size on transport and retention of coal fines in saturated proppant packs: Experimental and theoretical studies. Energy and Fuels, 35(15), 11976–11991.
Huang, F. S., Dong, C. Y., You, Z. J., & Shang, X. S. (2021b). Detachment of coal fines deposited in proppant packs induced by single-phase water flow: Theoretical and experimental analyses. International Journal of Coal Geology, 239, 103728.
Jiang, H. Q., Yao, J., & Jiang, R. Z. (2000). Principles and methods of reservoir engineering. China University of Petroleum Press. In Chinese.
Ju, W., Jiang, B., Miao, Q., Wang, J. L., Qu, Z. H., & Li, M. (2018a). Variation of in situ stress regime in coal reservoirs, eastern Yunnan region, South China: Implications for coalbed methane production. AAPG Bulletin, 102(11), 2283–2303.
Ju, W., Yang, Z. B., Qin, Y., Yi, T. S., & Zhang, Z. G. (2018b). Characteristics of in-situ stress state and prediction of the permeability in the Upper Permian coalbed methane reservoir, western Guizhou region, SW China. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 165, 199–211.
Li, S., Tang, D. Z., Pan, Z. J., Xu, H., & Guo, L. L. (2015). Evaluation of coalbed methane potential of different reservoirs in western Guizhou and eastern Yunnan, China. Fuel, 139, 257–267.
Liu, H. H., Sang, S. X., Wang, G. X., Li, Y. M., Li, M. X., & Liu, S. Q. (2012). Evaluation of the synergetic gas-enrichment and higher-permeability regions for coalbed methane recovery with a fuzzy model. Energy, 39, 426–439.
Ministry of Land and Resources of the Peoples Republic of China. (2010). DZ/T 0216–2010. Standards Press of China. In Chinese.
Moore, T. A. (2012). Coalbed methane: A review. International Journal of Coal Geology, 101, 36–81.
Qin, Y., & Gao, D. (2012). Prediction and evaluation of coalbed methane resource potential in Guizhou Province. China University of Mining and Technology Press. In Chinese.
Qin, Y., Luo, J., & Shen, J. (2018a). Coalbed methane resources and mining geological conditions in Yunnan Province. China University of Mining and Technology Press. In Chinese.
Qin, Y., Moore, T. A., Shen, J., Yang, Z. B., Shen, Y. L., & Wang, G. (2018b). Resources and geology of coalbed methane in China: A review. International Geology Review, 60(5–6), 777–812.
Tang, D. Z., Zhao, J. L., Xu, H., Li, Z. P., Tao, S., & Li, S. (2016). Material and energy dynamic balance mechanism in middle-high rank coalbed methane (CBM) systems. Journal of China Coal Society, 41, 40–48. In Chinese with English Abstract.
Tao, S., Chen, S. D., & Pan, Z. J. (2019). Current status, challenges, and policy suggestions for coalbed methane industry development in China: A review. Energy Science and Engineering, 7(4), 1059–1074.
Tao, S., Tang, D. Z., Xu, H., Gao, L. J., & Fang, Y. (2014). Factors controlling high-yield coalbed methane vertical wells in the Fanzhuang block, Southern Qinshui basin. International Journal of Coal Geology, 134, 38–45.
Wang, Z. W., Qin, Y., Li, T., & Zhang, X. Y. (2021). A numerical investigation of gas flow behavior in two-layered coal seams considering interlayer interference and heterogeneity. International Journal of Mining Science and Technology, 31(4), 699–716.
Xu, H. J., Sang, S. X., Yi, T. S., Zhao, X., Liu, H. H., Li, L., & Zhao, Z. G. (2014). Characteristics of in-situ stress field and its tectonic origin in Western Guizhou. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 45, 1960–1966. In Chinese with English Abstract.
Yang, Z. B., Li, Y. Y., Qin, Y., Sun, H. S., Zhang, P., Zhang, Z. G., Wu, C. C., Li, C. L., & Chen, C. X. (2019). Development unit division and favorable area evaluation for joint mining coalbed methane. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 46(3), 583–593.
Yang, Z. B., Zhang, Z. G., Qin, Y., Wu, C. C., Yi, T. S., Li, Y. Y., Tang, J., & Chen, J. (2018). Optimization methods of production layer combination for coalbed methane development in multi-coal seams. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 45(2), 312–320.
Zhang, Z., Qin, Y., & Fu, X. H. (2014). The favorable developing geological conditions for CBM multi-layer drainage in southern Qinshui basin. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 43, 1019–1024.
Zhang, Z. G., Qin, Y., Wang, G., Sun, H. S., You, Z. J., Jin, J., & Yang, Z. B. (2021a). Evaluation of coal body structures and their distributions by geophysical logging methods: case study in the Laochang block, eastern Yunnan, China. Natural Resources Research, 30, 2225–2239.
Zhang, Z. G., Qin, Y., Yang, Z. B., Jin, J., & Wu, C. C. (2019a). Fluid energy characteristics and development potential of coalbed methane reservoirs with different synclines in Guizhou, China. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 71, 102981.
Zhang, Z. G., Qin, Y., Yang, Z. B., Zhao, J. L., & Yi, T. S. (2019b). Segmentation of multi-coal seam pore structure in single well profile and its sedimentary control: a case study of Well Y1 in Panguan syncline, western Guizhou, China. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 12, 1–16.
Zhang, Z. G., Qin, Y., Yi, T. S., You, Z. J., & Yang, Z. B. (2020). Pore structure characteristics of coal and their geological controlling factors in Eastern Yunnan and Western Guizhou, China. ACS Omega, 5(31), 19565–19578.
Zhang, Z. G., Qin, Y., You, Z. J., & Yang, Z. B. (2021b). Distribution characteristics of in situ stress field and vertical development unit division of CBM in Western Guizhou, China. Natural Resources Research, 30(5), 3659–3671.
Zhao, J., Tang, D., Lin, W., Qin, Y., & Xu, H. (2019). In-situ stress distribution and its influence on the coal reservoir permeability in the Hancheng area, eastern margin of the Ordos Basin, China. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 61, 119–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jngse.2018.09.002
Zhao, J. L., Tang, D. Z., Xu, H., Li, Y., Li, S., Tao, S., Lin, W. J., & Liu, Z. X. (2016). Characteristic of in situ stress and its control on the coalbed methane reservoir permeability in the eastern margin of the Ordos Basin, China. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 49, 3307–3322.
Zhao, J. L., Tang, D. Z., Xu, H., Lv, Y. M., & Tao, S. (2015). High production indexes and the key factors in coalbed methane production: A case in the Hancheng block, southeastern Ordos Basin, China. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 130, 55–67.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42130802, 42272195), the National Science and Technology Major Project of China (2016ZX05044-002), and Key Laboratory of Coalbed Methane Resources and Reservoir Formation Process of the Ministry of Education (China University of Mining and Technology) (No. 2022-001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Qin, Y., Yang, Z. et al. Primary Controlling Factors of Coalbed Methane Well Productivity and High Productive Well Patterns in Eastern Yunnan and Western Guizhou, China. Nat Resour Res 32, 2711–2726 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-023-10260-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-023-10260-x