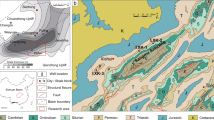
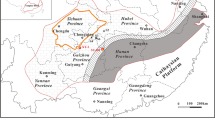
Abstract
Despite being closely relevant to resource assessment and exploitation, pore structures and methane storage behaviors of deep-marine shales remain poorly understood. In this work, systematic experimental characterization of pore structures and sorption in deep shales in the Wufeng–Longmaxi Formations was conducted. The pore structures were characterized intuitively and quantitatively by a combination of various experiments. High-pressure methane adsorption experiments were conducted at 110 °C and pressures up to 30 MPa. The governing factors of pore structures and sorption in deep shales were clarified. A novel method was proposed to quantify absolute adsorption and free gas contents at in situ deep shale conditions. In this method, absolute adsorption content is predicted by the fitted Langmuir volume and Langmuir pressure, and the free gas content is determined by the bulk gas density and the corrected void volume, taking into account the adsorbed phase volume and gas saturation. New insights on discrepancies between deep shales and shallow shales were discussed. The lower section of the Longmaxi Formation is proposed as the geological and engineering sweet spot. Compared with shallow shales, deep shales possess higher contents of micropores from organic matters and lower contents of macropores from clay minerals. Absolute adsorption does not reach the maximum at in situ deep shale conditions, and the proportion of adsorbed gas in deep shales is smaller than that in shallow shales. Total organic carbon (TOC) content is the primary controlling factor on pore structure and sorption capacity in deep shales. An increase in TOC content can lead to an increase in micropore and mesopore content and thus an increase in the absolute adsorption proportion in deep shales. The effect of clay minerals on gas sorption in deep shales is less pronounced in contrast to shallow shales. These findings facilitate the accurate reserve evaluation of deep shale gas and can guide the theoretical investigations on gas production mechanisms in deep shale gas reservoirs.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abolghasemi, E., & Andersen, P. Ø. (2022). The influence of adsorption layer thickness and pore geometry on gas production from tight compressible shales. Advances in Geo-Energy Research, 6(1), 4.
Arif, M., Mahmoud, M., Zhang, Y., & Iglauer, S. (2021). X-ray tomography imaging of shale microstructures: A review in the context of multiscale correlative imaging. International Journal of Coal Geology, 233, 103641.
Bernard, S., Horsfield, B., Schulz, H.-M., Wirth, R., Schreiber, A., & Sherwood, N. (2012). Geochemical evolution of organic–rich shales with increasing maturity: A STXM and TEM study of the Posidonia Shale (lower Toarcian, northern Germany). Marine and Petroleum Geology, 31, 70–89.
Chalmers, G. R. L., Ross, D. J. K., & Bustin, R. M. (2012). Geological controls on matrix permeability of Devonian gas Shales in the Horn river and Liard basins, northeastern British Columbia. International Journal of Coal Geology, 103, 120–131.
Chen, L., Liu, K., Jiang, S., Huang, H., Tan, J., & Zuo, L. (2021a). Effect of adsorbed phase density on the correction of methane excess adsorption to absolute adsorption in shale. Chemical Engineering Journal, 420, 127678.
Chen, S., Zhang, C., Li, X., Zhang, Y., & Wang, X. (2021b). Simulation of methane adsorption in diverse organic pores in shale reservoirs with multi-period geological evolution. International Journal of Coal Science & Technology, 8(5), 844–855.
Chen, T., Feng, X., & Pan, Z. (2015). Experimental study of swelling of organic rich shale in methane. International Journal of Coal Geology, 150, 64–73.
Etminan, S. R., Javadpour, F., Maini, B. B., & Chen, Z. (2014). Measurement of gas storage processes in shale and of the molecular diffusion coefficient in kerogen. International Journal of Coal Geology, 123, 10–19.
Gao, Z., Fan, Y., Xuan, Q., & Zheng, G. (2020). A review of shale pore structure evolution characteristics with increasing thermal maturities. Advances in Geo-Energy Research, 4(3), 247.
Gasparik, M., Ghanizadeh, A., Bertier, P., Gensterblum, Y., Bouw, S., & Krooss, B. M. (2012). High-pressure methane sorption isotherms of black shales from the Netherlands. Energy & Fuels, 26(8), 4995–5004.
Ge, X., Guo, T., Ma, Y., Wang, G., Li, M., Zhao, P., Yu, X., Li, S., Fan, H., & Zhao, T. (2022). Fracture development and inter-well interference for shale gas production from the Wufeng-Longmaxi formations in a gentle syncline area of Weirong shale gas field, southern Sichuan, China. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 212, 110207.
Gregg, S. J., & Sing, K. S. W. (1982). Adsorption, Surface Area and Porosity (2nd ed.). Academic Press.
He, J., Zhu, S., Shi, X., Zhao, S., Cao, L., Pan, S., Wu, F., & Wang, M. (2022). Characteristics of lithofacies in deep shale gas reservoirs in the Southeast Sichuan Basin and their influence on pore structure. Frontiers in Earth Science, 10, 857343.
He, Y., Qiao, Y., Qin, J., Tang, Y., Wang, Y., & Chai, Z. (2021). A novel method to enhance oil recovery by inter-fracture injection and production through the same multi-fractured horizontal well. Journal of Energy Resources Technology, 144(4), 043005.
Hou, L., Luo, X., Lin, S., Li, Y., Zhang, L., & Ma, W. (2022). Assessment of recoverable oil and gas resources by in-situ conversion of shale-case study of extracting the Chang 73 shale in the Ordos Basin. Petroleum Science, 19(2), 441–458.
Hu, H., Zhang, T., Wiggins-Camacho, J. D., Ellis, G. S., Lewan, M. D., & Zhang, X. (2015). Experimental investigation of changes in methane adsorption of bitumen-free Woodford Shale with thermal maturation induced by hydrous pyrolysis. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 59, 114–128.
Hu, H., Zhu, Y., Li, S., & Li, Z. (2021). Effects of green energy development on population growth and employment: Evidence from shale gas exploitation in Chongqing, China. Petroleum Science, 18(5), 1578–1588.
Huang, J., Zou, C., Li, J., Dong, D., Wang, S., Wang, S., & Cheng, K. (2012). Shale gas generation and potential of the lower Cambrian Qiongzhusi formation in the southern Sichuan Basin, China. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 39(1), 75–81.
Huang, L., Khoshnood, A., & Firoozabadi, A. (2020). Swelling of Kimmeridge kerogen by normal-alkanes, naphthenes and aromatics. Fuel, 267, 117155.
Huang, L., Ning, Z., Lin, H., Zhou, W., Wang, L., Zou, J., & Xu, H. (2021a). High–pressure sorption of methane, ethane, and their mixtures on shales from Sichuan Basin. China. Energy & Fuels, 35(5), 3989–3999.
Huang, L., Ning, Z., Wang, Q., Qi, R., Cheng, Z., Wu, X., et al. (2019a). Molecular insights into kerogen deformation induced by CO2/CH4 sorption: Effect of maturity and moisture. Energy & Fuels, 33(6), 4792–4805.
Huang, L., Ning, Z., Wang, Q., Qi, R., Cheng, Z., Wu, X., Zhang, W., & Qin, H. (2019b). Kerogen deformation upon CO2/CH4 competitive sorption: Implications for CO2 sequestration and enhanced CH4 recovery. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 183, 106460.
Huang, L., Ning, Z., Wang, Q., Qi, R., Li, J., Zeng, Y., Ye, H., & Qin, H. (2017). Thermodynamic and structural characterization of bulk organic matter in Chinese Silurian shale: Experimental and molecular modeling studies. Energy & Fuels, 31(5), 4851–4865.
Huang, L., Ning, Z., Wang, Q., Qi, R., Zeng, Y., Qin, H., Ye, H., & Zhang, W. (2018a). Molecular simulation of adsorption behaviors of methane, carbondioxide and their mixtures on kerogen: Effect of kerogen maturity and moisture content. Fuel, 211, 159–172.
Huang, L., Ning, Z., Wang, Q., Ye, H., Wang, Z., Sun, Z., & Qin, H. (2018b). Microstructure and adsorption properties of organic matter in Chinese Cambrian gas shale: Experimental characterization, molecular modeling and molecular simulation. International Journal of Coal Geology, 198, 14–28.
Huang, L., Ning, Z., Wang, Q., Zhang, W., Cheng, Z., Wu, X., & Qin, H. (2018c). Effect of organic type and moisture on CO2/CH4 competitive adsorption in kerogen with implications for CO2 sequestration and enhanced CH4 recovery. Applied Energy, 210, 28–43.
Huang, L., Zhou, W., Xu, H., Wang, L., Zou, J., & Zhou, Q. (2021b). Dynamic fluid states in organic–inorganic nanocomposite: Implications for shale gas recovery and CO2 sequestration. Chemical Engineering Journal, 411, 128423.
Huang, S., Ma, X., Yang, H., Wu, J., Zhang, J., Zhao, S., Zhang, D., Ren, C., & Huang, L. (2022). Experimental characterization and molecular modeling of kerogen in Silurian deep gas shale from southern Sichuan Basin, China. Energy Reports, 8, 1497–1507.
Ji, L., Zhang, T., Milliken, K. L., Qu, J., & Zhang, X. (2012). Experimental investigation of main controls to methane adsorption in clay-rich rocks. Applied Geochemistry, 27(12), 2533–2545.
Jiang, T., Jin, Z., Liu, G., Hu, Z., Chen, X., Liu, Z., & Wang, G. (2022). Investigating the pore structure characteristics and reservoir capacities of lower Jurassic continental shale reservoirs in the northeastern Sichuan Basin, China. Frontiers in Earth Science, 10, 886907.
Jin, Z., & Firoozabadi, A. (2016). Thermodynamic modeling of phase behavior in shale media. SPE Journal, 21(1), 190–207.
Kuang, L., Hou, L., Wu, S., Cui, J., Tian, H., Zhang, L., Zhao, Z., Luo, X., & Jiang, X. (2022). Organic matter occurrence and pore-forming mechanisms in lacustrine shales in China. Petroleum Science, 19(4), 1460–1472.
Kwiecińska, B., Pusz, S., & Valentine, B. J. (2019). Application of electron microscopy TEM and SEM for analysis of coals, organic-rich shales and carbonaceous matter. International Journal of Coal Geology, 211, 103203.
Leamy, H. J. (1982). Charge collection scanning electron microscopy. Journal of Applied Physics, 53(6), 51–80.
Li, J., Li, X., Wang, X., Li, Y., Wu, K., Shi, J., Yang, L., Feng, D., Zhang, T., & Yu, P. (2016). Water distribution characteristic and effect on methane adsorption capacity in shale clay. International Journal of Coal Geology, 159, 135–154.
Li, X., Wang, Y., Lin, W., Ma, L., Liu, D., Liu, J., & Zhang, Y. (2022a). Micro-pore structure and fractal characteristics of deep shale from Wufeng Formation to Longmaxi Formation in Jingmen exploration area, Hubei Province. China. Journal of Natural Gas Geoscience, 7(3), 121–132.
Li, Y., Song, L., Tang, Y., Zuo, J., & Xue, D. (2022b). Evaluating the mechanical properties of anisotropic shale containing bedding and natural fractures with discrete element modeling. International Journal of Coal Science & Technology, 9(1), 18.
Loucks, R. G., Reed, R. M., Ruppel, S. C., & Jarvie, D. M. (2009). Morphology, genesis, and distribution of nanometer-scale pores in siliceous mudstones of the Mississippian Barnett Shale. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 79, 848–861.
Medina, F. J., Jausoro, I., Addato, M. A. F., Rodriguez, M. J., Tomassini, F. G., & Caneiro, A. (2022). On the evaluation of representative elementary area for porosity in shale rocks by field emission scanning electron microscopy. Energy, 253, 124141.
Miao, Y., Zhao, C., & Zhou, G. (2020). New rate-decline forecast approach for low-permeability gas reservoirs with hydraulic fracturing treatments. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 190, 107112.
Nie, H., Li, P., Dang, W., Ding, J., Sun, C., Liu, M., Wang, J., Du, W., Zhang, P., Li, D., & Su, H. (2022). Enrichment characteristics and exploration directions of deep shale gas of Ordovician-Silurian in the Sichuan Basin and its surrounding areas China. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 49(4), 648–659.
Pan, L., Xiao, X., Tian, H., Zhou, Q., & Cheng, P. (2016). Geological models of gas in place of the Longmaxi shale in Southeast Chongqing, South China. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 73, 433–444.
Pang, H., Xiong, L., Wei, L., Shi, H., Dong, X., Zhang, T., & Cai, Z. (2019). Analysis on geological factors of enrichment and high yield of deep shale gas in southern Sichuan: A case in Weirong shale gas field. Natural Gas Industry, 39(S1), 78–84.
Rexer, T. F. T., Mathia, E. J., Aplin, A. C., & Thomas, K. M. (2014). High-pressure methane adsorption and characterization of pores in Posidonia shales and isolated kerogens. Energy & Fuels, 28, 2886–2901.
Ruska, E. (1987). The development of the electron microscope and of electron microscopy (Nobel Lecture). Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English, 26(7), 595–605.
Sang, G., Liu, S., Zhang, R., Elsworth, D., & He, L. (2018). Nanopore characterization of mine roof shales by SANS, nitrogen adsorption, and mercury intrusion: Impact on water adsorption/retention behavior. International Journal of Coal Geology, 200, 173–185.
Slatt, R. M., & O’Brien, N. R. (2011). Pore types in the Barnett and Woodford gas shales: Contribution to understanding gas storage and migration pathways in fine-grained rocks. AAPG bulletin, 95(12), 2017–2030.
Song, W., Yao, J., Zhang, K., Yang, Y., & Sun, H. (2022). Understanding gas transport mechanisms in shale gas reservoir: Pore network modelling approach. Advances in Geo-Energy Research, 6(4), 359.
Su, Y., Sun, Q., Wang, W., Guo, X., Xu, J., Li, G., et al. (2022). Spontaneous imbibition characteristics of shale oil reservoir under the influence of osmosis. International Journal of Coal Science & Technology, 9(1), 69.
Sun, Y., Ju, Y., Zhou, W., Qiao, P., Tao, L., & Xiao, L. (2022). Nanoscale pore and crack evolution in shear thin layers of shales and the shale gas reservoir effect. Advances in Geo-Energy Research, 6(3), 221.
Wang, F., Guan, J., Feng, W., & Bao, L. (2013). Evolution of overmature marine shale porosity and implication to the free gas volume. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 40, 819–824.
Wang, Y., Dong, D., Cheng, X., Huang, J., Wang, S., & Wang, S. (2014). Electricproperty evidences of the carbonification of organic matters in marine shales and its geologic significance. Natural Gas Industry, 34, 1–7.
Wang, Y., Zhu, Y., Zhang, R., Anovitz, L. M., Bleuel, M., Liu, S., & Chen, S. (2020). SANS coupled with fluid invasion approaches for characterization of overall nanopore structure and mesopore connectivity of organic-rich marine shales in China. International Journal of Coal Geology, 217, 103343.
Warwick, T., Franck, K., Kortright, J. B., Meigs, G., Moronne, M., Myneni, S., Rotenberg, E., & SealSteele, S. F. (1998). A scanning transmission x-ray microscope for materials science spectromicroscopy at the advanced light source. Review of Scientific Instruments, 69(8), 2964–2973.
Wei, L., Wang, Y., Zhang, T., & Zhou, H. (2019). Construction of geological model of deep shale reservoir in southern Sichuan Basin. Natural Gas Industry, 39(S1), 66–70.
Wei, L., Wang, Y., Zhang, T., Zhou, H., Wen, Z., & Dong, A. (2020). Main control factors of enrichment and high production of shale gas: A case study of Wufeng–Longmaxi Formation in Southern Sichuan. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 27(6), 700–704.
Wood, D. A. (2022). Predicting brittleness indices of prospective shale formations from sparse well-log suites assisted by derivative and volatility attributes. Advances in Geo-Energy Research, 6(4), 334.
Wu, T., Zhao, H., Tesson, S., & Firoozabadi, A. (2019). Absolute adsorption of light hydrocarbons and carbon dioxide in shale rock and isolated kerogen. Fuel, 235, 855–867.
Wu, Y., Cheng, L., Killough, J., Huang, S., Fang, S., Jia, P., Cao, R., & Xue, Y. (2021). Integrated characterization of the fracture network in fractured shale gas reservoirs-stochastic fracture modeling, simulation and assisted history matching. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 205, 108886.
Xie, W., Wang, M., Chen, S., Vandeginste, V., Yu, Z., & Wang, H. (2022). Effects of gas components, reservoir property and pore structure of shale gas reservoir on the competitive adsorption behavior of CO2 and CH4. Energy, 254, 124242.
Xiong, L., Pang, H., Zhao, Y., Wei, L., Zhou, H., & Cao, Q. (2021). Micro pore structure characterization and classification evaluation of reservoirs in Weirong deep shale gas field. Petroleum Reservoir Evaluation and Development, 11(2), 20–29.
Xu, J., Wu, K., Li, R., Li, Z., Li, J., Xu, Q., Li, L., & Chen, Z. (2019). Nanoscale pore size distribution effects on gas production from fractal shale rocks. Fractals, 27(8), 1950142.
Xue, L., Gu, S., Jiang, X., Liu, Y., & Yang, C. (2021). Ensemble-based optimization of hydraulically fractured horizontal well placement in shale gas reservoir through Hough transform parameterization. Petroleum Science, 18(3), 839–851.
Yang, F., Ning, Z., Wang, Q., Zhang, R., & Krooss, B. M. (2016). Pore structure characteristics of lower Silurian shales in the southern Sichuan Basin, China: Insights to pore development and gas storage mechanism. International Journal of Coal Geology, 156, 12–24.
Yang, F., Ning, Z., Zhang, R., Zhao, H., & Krooss, B. M. (2015). Investigations on the methane sorption capacity of marine shales from Sichuan Basin, China. International Journal of Coal Geology, 146, 104–117.
Yang, Y., Zhang, J., Xu, L., Li, P., Liu, Y., & Dang, W. (2022). Pore structure and fractal characteristics of deep shale: A case study from Permian Shanxi Formation Shale, from the Ordos Basin. ACS Omega, 7(11), 9229–9243.
Yasin, Q., Sohail, G., Liu, K., Du, Q., & Boateng, C. D. (2021). Study on brittleness templates for shale gas reservoirs-a case study of Longmaxi shale in Sichuan Basin, southern China. Petroleum Science, 18(5), 1370–1389.
Yuan, Y., Rezaee, R., Verrall, M., Hu, S., Zou, J., & Testmanti, M. (2018). Pore characterization and clay bound water assessment in shale with a combination of NMR and low-pressure nitrogen gas adsorption. International Journal of Coal Geology, 194, 11–21.
Zhang, T., Ellis, G. S., Ruppel, S. C., Milliken, K., & Yang, R. (2012). Effect of organic-matter type and thermal maturity on methane adsorption in shale-gas systems. Organic Geochemistry, 47, 120–131.
Zhou, H., Wei, L., Wang, T., Wang, Y., Pang, H., & Zhang, T. (2021). Evaluation method of Weirong deep shale gas reservoir and its application. Petroleum Reservoir Evaluation and Development, 11(2), 42–49.
Zhu, H., Ju, Y., Qi, Y., Huang, C., & Zhang, L. (2018). Impact of tectonism on pore type and pore structure evolution in organic-rich shale: Implications for gas storage and migration pathways in naturally deformed rocks. Fuel, 228, 272–289.
Zou, J., Rezaee, R., Xie, Q., You, L., Liu, K., & Saeedi, A. (2018). Investigation of moisture effect on methane adsorption capacity of shale samples. Fuel, 232, 323–332.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 52204031, 41972137, and 42002157), the Natural Science Foundation of Sichuan Province (Grant No. 2023NSFSC0947), and the Open Fund (Grant No. PLC20210303) of State Key Laboratory of Oil and Gas Reservoir Geology and Exploitation (Chengdu University of Technology).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, T., Meng, X., Lei, W. et al. Characteristics and Governing Factors of Pore Structure and Methane Sorption in Deep-Marine Shales: A Case Study of the Wufeng–Longmaxi Formations, Weirong Shale Gas Field, Sichuan Basin. Nat Resour Res 32, 1733–1759 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-023-10215-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-023-10215-2