Abstract
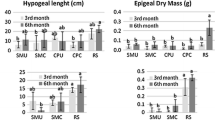
The aim of this study was to evaluate the use of mining co-products from the Irati (rhythmite and bituminous shale) and Corumbataí Formations (clayey siltstone) as sources of multi-nutrients for the cultivation of Brachiaria ruziziensis. The treatments were arranged within the double factorial scheme (7 × 2), completely randomized with 10 replications and placed into pots inside a greenhouse. Two factors were evaluated: the type of co-product and the soil class (Arenosol and Ferralsol). The mining co-products were applied in their isolated form and in composite (blended) form. At 60 and 140 days after the application of treatments, the ions available in the soil were determined. After that, four Brachiaria ruziziensis plants were cultivated per pot. After 40 days of cultivation, the aerial part of the plants was cut. Afterward, the macronutrients, as well as the production of shoot dry mass of the plants, were determined. The application of co-products, in general, increased the pH and the contents of ions available: K+ (Mehlich-1), Mg2+, Ca2+, P, SO42− and Si. As a highlight, at 140 days, rhythmite was the most efficient co-product in increasing pH, Ca2+ and Mg2+, with increases of 23%, 241% and 722% in Arenosol, respectively. Also at 140 days, bituminous shale increased the contents of SO42− by 72% and 427% in Ferralsol and Arenosol, respectively. Moreover, the accumulation of K, Ca, Mg and S, as well as the production of shoot dry mass of Brachiaria improved with the application of the co-products. In conclusion, the application of mining co-products alters the chemical attributes of both the soil and the plant, and this favors the production of shoot dry mass of Brachiaria, which demonstrates the potential to be a clean environmental solution to soil fertilization.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Addinsoft. (2016). Statistical software: version 2016 (3rd ed.). Paris: XLSTAT.
Anderson, N. P., Hart, J. M., Sullivan, D. M., Christensen, N. W., Horneck, D. A., & Pirelli, G. J. (2013). Applying lime to raise soil pH for crop production (Western Oregon) (1st ed.). Corvallis, OR: Oregon State University.
Antonijević, M. M., & Marić, M. (2008). Determination of the content of heavy metals in pyrite contaminated soil and plants. Sensors, 8, 5857–5865.
Beerling, D. J., Leake, J. R., Long, S. P., Scholes, J. D., Ton, J., & Nelson, P. N. (2018). Farming with crops and rocks to address global climate, food and soil security. Nature Plants, 4, 138–147.
Bidari, E., & Aghazadeh, V. (2018). Pyrite oxidation in the presence of calcite and dolomite: Alkaline leaching, chemical modeling and surface characterization. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 28, 1433–1443.
BRASIL. (2016). Ministério da Agricultura, Pecuária e Abastecimento. Instrução Normativa n. 5, de 10 de março de.
Broch, D. L., Pavinato, P. S., Possentti, J. C., Martin, T. N., & Del Quiqui, E. M. (2011). Produtividade da soja no cerrado influenciada pelas fontes de enxofre. Revista Ciência Agronômica, 42, 791–796.
Buol, S. W. (2009). Soils and agriculture in central-west and north Brazil. Sciencia Agricola, 66, 697–707.
Carvalho, R., Furtini, A. E. N., Santos, C. D., Fernandes, L. A., Curi, N., & Rodrigues, D. C. (2001). Interações silício-fósforo em solos cultivados com eucalipto em casa de vegetação. Pesquisa Agropecuária Brasileira, 36, 557–565.
Casagrande, J. C., Alleoni, L. R. F., Camargo, O. A., & Borges, M. (2003). Adsorção de fosfato e sulfato em solos com cargas variáveis. Revista Brasileira em Ciência do Solo, 27, 51–59.
Castilhos, R. M. V., & Meurer, E. J. (2001). Cinética de liberação de potássio em planossolo do estado do Rio Grande do Sul. Ciência Rural, 31, 979–983.
Castro, G. S. A., & Crusciol, C. A. C. (2015). Effects of surface application of dolomitic limestone and calcium-magnesium silicate on soybean and maize in rotation with green manure in a tropical region. Bragantia, 74, 311–321.
Christofoletti, S. R., Moreno, M. M. T., & Batezelli, A. (2006). Análise de fácies da Formação Corumbataí (Grupo Passa Dois – Bacia do Paraná, Neopermiano), com vista ao emprego na indústria de revestimento cerâmico. Revista Brasileira Geociências, 36, 488–498.
Cordonnier, M. (2018). Brazil remains heavily dependent on imported fertilizers (1st ed.). Hinsdale, IL: Soybean & Corn Advisor Inc.
Cunha, A. M., Fontes, M. P. F., & Lani, J. L. (2019). Mineralogical and chemical attributes of soils from the Brazilian Atlantic Forest domain. Sciencia Agricola, 76, 82–92.
Dal Molin, S. J., Nascimento, C. O., Teixeira, P. C., & Benites, V. D. M. (2019). Polyhalite as a potassium and multi-nutrient source for plant nutrition. Achieves of Agronomy and Soil Sciencia, 66, 667–678.
de Souza, M. H. O. (2003). Separação do calcário e do folhelho pirobetuminoso da Formação Irati para utilização como corretivo e como aditivo na indústria cerâmica. In Smith, D. K., & Jenkins, R. (1996). The powder diffraction file: Past present and future. Journal of Research of NIST, 101, 259–220.
Deus, A. C. F., de Almeida, R. M. B., Meirelles, G. C., Soares, A. D. A. V. L., Moreira, L. L. Q., Büll, L. T., et al. (2018). The comprehensive utilization of steel slag in agricultural soils. In Y. Zhang (Ed.), Recovery and utilization of metallurgical solid waste (1st ed.). IntechOpen. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.81440.
Dominguez, M. T., Teodoro, M., Murillo, J. M., Schulin, R., & Robinson, B. (2009). Nutritional status of mediterranean trees growing in a contaminated and remediated area. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 205, 305–321.
Duarte, W. M., Mafra, Á. L., Foresti, M. M., Piccolla, C. D., & Almeida, J. A. (2013). Potencial de olivina melilitito, granito e sienito na disponibilização de potássio em solos. Revista de Ciências Agroveterinárias, 12, 68–77.
Fageria, N. K., Santos, A. B., & Moraes, M. F. (2010). Yield, potassium uptake, and use efficiency in upland rice genotypes. Communication in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 41, 2676–2684.
Ferreira, D. F. (2011). Sisvar: A computer statistical analysis system. Ciências Agrotécnicas, 35, 1039–1042.
Garcia, R. A., Crusciol, C. A. C., Calonego, J. C., & Rosolem, C. A. (2008). Potassium cycling in a corn-Brachiaria cropping system. European Journal of Agronomy, 28, 579–585.
Godoy, L. H., Sardinha, D. S., & Moreno, M. M. (2017). Redistribuição de elementos maiores e traços em argilitos intemperizados da Formação Corumbataí, Bacia Sedimentar do Paraná, São Paulo, Brasil. Brazilian Journal of Geology, 47, 615–632.
Goldberg, K., & Humayun, M. (2016). Geochemical paleoredox indicators in organic-rich shales of the Irati Formation, Permian of the Paraná Basin, southern Brazil. Brazilian Journal of Geology, 46, 377–393.
Holanda, W., dos Santos, A. C., Nogueira, C. C., Bertolino, L. C., Bergamaschi, S., Rodrigues, R., et al. (2019). Effects of igneous intrusion on the mineralogical content of Irati formation, Paraná basin, in Sapopema (PR). Brazilian Journal of Sediments (Environment), 4, 350–360.
Korndörfer, G. H. (2004). Silicon analysis: Soil, plant and fertilizer (1st ed.). Uberlândia: UFU.
Korndörfer, G. H., Pereira, H. S., & Nolla, A. (2002). Silicatos de cálcio e magnésio na agricultura (1st ed.). Uberlândia: GPSi-ICIAG-UFU.
Leão, R. E., Giacomini, S. J., Redin, M., Souza, E. L., & Silveira, C. A. P. (2014). The addition of retorted oil shale increases carbon retention of plant residues in soil. Pesquisa Agropecuária Brasileira, 49, 818–822.
Lošák, T., Hlušek, J., Lampartová, I., Mühlbachová, G., & Čermák, P. (2017). Changes in the soil magnesium and Sulphur content after Kieserite application into Haplic Luvisol and the effect on yields of barley biomass. Acta Universitatis Agriculturae et Silviculturae Mendelianae, 65, 1225–1229.
Lucheta, A. R., & Lambais, M. R. (2012). Sulfur in agriculture. Revista Brasileira de Ciência do Solo, 36, 1369–1379.
Machado, V. J., & Souza, C. H. E. (2012). Disponibilidade de fósforo em solos com diferentes texturas após aplicação de doses crescentes de fosfato monoamônico de liberação lenta. Bioscience Journal, 28, 1–7.
Manning, D. A. C. (2010). Mineral sources of potassium for plant nutrition: A review. Agronomy for Sustainable Development, 30, 281–294.
Martins, V., Silva, D. R. G., Marchi, G., Leite, M. C. A., Martins, É. S., Gonçalves, A. S. F., et al. (2015). Effect of alternative multinutrient sources on soil chemical properties. Revista Brasileira de Ciência do Solo, 39, 194–204.
Medeiros, S. G., Dutra, R. P. S., Grilo, J. P. F., Martinelli, A. E., Paskocimas, C. A., & Macedo, D. A. (2016). Preparation of low-cost alumina-mullite composites via reactive sintering between a kaolinite clay from Paraíba and aluminum hydroxide. Cerâmica, 62, 266–271.
Medeiros, J. S., Oliveira, F. H. T., Arruda, J. A., Vieira, M. S., & Fontes, M. P. F. (2010). Efficiency of available potassium extractants in soils of Paraiba state with different degrees of pedogenetic development. Revista Brasileira de Ciência do Solo, 34, 183–194.
Mello, S. C., Tonhati, R., Neto, D. D., Darapuneni, M., & Pavuluri, K. (2018). Response of tomato to polyhalite as a multi-nutrient fertilizer in southeast Brazil. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 41, 2126–2140.
Mikkelsen, R., & Norton, R. (2013). Soil and fertilizer sulfur. Better Crops, 97, 7–9.
Moreno, M. M. T., Zanardo, A., Rocha, R. R., & Roveri, C. D. (2012). Matéria-prima da formação Corumbataí na região do pólo cerâmico de Santa Gertrudes, SP, com características naturais para fabricação de argila expandida. Cerâmica, 58, 342–348.
Nguyen, H. H., Maneepong, S., & Suraninpong, P. (2017). Effects of potassium, calcium and magnesium ratios in soil on their uptake and fruit quality of pummelo. Journal of Agricola Science, 9, 110–121.
Pereira, H. S., & Vitti, G. C. (2004). Efeito do uso do xisto em características químicas do solo e nutrição do tomateiro. Horticultura Brasileira, 22, 317–322.
Piza, P. A. T., Bertolino, L. C., Silva, A. A. S., Sampaio, J. A., & Luz, A. B. (2011). Verdete da região de Cedro do Abaeté (MG) como fonte alternativa para potássio. Geociências, 30, 345–356.
Raij, B., Andrade, J. C., Cantarella, H., & Quaggio, J. A. (2001). Chemical analysis for fertility assessment of tropical soils (1st ed.). Campinas: IAC.
Ramezanian, A., Dahlin, A., Campbell, C., Hillier, S., Mannerstedt-Fogelfors, B., & Öborn, I. (2013). Addition of a volcanic rockdust to soils has no observable effects on plant yield and nutrient status or on soil microbial activity. Plant and Soil, 367, 419–436.
Ramos, A. N., & Formoso, M. L. L. (1976). Clay mineralogy of the sedimentary rocks of the Paraná Basin, Brazil. Revista Brasileira Geociências, 6, 15–42.
Ramos, C. G., Mello, A. G., & Kautzmann, R. M. (2014). A preliminary study of acid volcanic rocks for stonemeal application. Environmental Nanotechnology, Monitoring and Management, 1, 30–35.
Ranzan, T. (2014). Nitrogen fertilization and retorted oil shale in the yield and energy production of rice biomass (1st ed.). Curitiba: UFPR.
Rezende, T. P., Pelá, A., & Pelá, G. M. (2013). Uso de pó de basalto como alternativa na adubação da cultura da alface. Revista Processo Químico, 7, 67–72.
Ribeiro, L. S., Santos, A. R., Souza, L. F. S., & Souza, J. S. (2010). Rochas silicáticas portadoras de potássio como fontes do nutriente para as plantas solo. Revista Brasileira de Ciência do Solo, 34, 891–897.
Rodrigues, M. (2017). Subprodutos da mineração de calcário da Formação Irati como fontes de cálcio, magnésio e enxofre (1st ed.). Pelotas: MACSA/UFPel.
Rodrigues, M., Nanni, M. R., Cezar, E., Santos, G. L. A. A., Reis, A. S., & Oliveira, K. M. (2020). Evaluation of the use of spectroradiometry for the determination of soil exchangeable ions after the application of mining coproducts. Applied Spectroscopy Reviews, 55, 491–508.
Santos, L. F. M., Lapaz, A. M., Tomaz, R. S., Lira, M. V. S., Moreira, A., Reis, A. R., et al. (2019). Evaluation of sulfur source and dose on the nutritional state and production of piatã forage. Semina, 40, 1237–1248.
Santos, J. V., Presbiteris, R. J. B., Santos, V. C. G., Grassi, M. T., Messerschmidt, I., Pereira, B. F., et al. (2017). Avaliação da liberação de elementos traço em solos tratados com xisto retortado. Química Nova, 40, 496–505.
Savini, I., Koala, S., & Kihara, J. (2015). Minjingu phosphate rock availability in low-pH highly weathered soil as affected by added salts. Sciencia Agricola, 72, 440–451.
SCFC-RS/SC. (2016). Liming and fertilizing manual for the states of Rio Grande do Sul and Santa Catarina (fifth ed ed.). Santa Maria: SBCS.
Seoud, A., & Megeed, A. (2012). Impact of rock materials and biofertilizations on P and K availability for maize (Zea Maize) under calcareous soil conditions. Saudi Journal of Biology Science, 19, 55–63.
Shoemaker, H. E., Mclean, E. O., & Pratt, P. F. (1961). Buffer methods for determining lime requirements of soils with appreciable amounts of extractable aluminum. Soil Science Society of America, Proceedings, 25, 274–277.
Shuman, L. M. (1994). Mineral nutrition (1st ed.). New York, NY: Marcel Dekker Inc.
Silva, F. C. (2009). Manual de análise químicas de solos, plantas e fertilizantes (2nd ed.). Brasilia: Embrapa.
Silva, D. R. G., Marchi, G., Spehar, C. R., Guilherme, L. R. G., & Faquin, V. (2013). Agronomic efficiency of potassium fertilization in lettuce fertilized with alternative nutrient sources. Revista Ciências Agronômicas, 44, 267–277.
Silva, D. R. G., Marchi, G., Spehar, C. R., Guilherme, L. R. G., Rein, T. A., Soares, D. A., et al. (2012). Characterization and nutrient release from silicate rocks and influence on chemical changes in soil. Revista Brasileira Ciência do Solo, 36, 951–962.
Smith, D. K., & Jenkins, R. (1996). The powder diffraction file: Past, present, and future. Journal of Research of the National Institute of Standards and Technology, 101(3), 259.
Souza, M. C. A., Deliberali, D., Jucksch, I., Brown, G., Mendonça, E., & Cardoso, I. (2013). Vermicomposting with rock powder increases plant growth. Applied Soil Ecololgy, 69, 56–60.
Tavakkoli, E., Lyons, G., English, P., & Guppy, C. N. (2011). Silicon nutrition of rice is affected by soil pH, weathering and silicon fertilisation. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 174, 437–446.
Tavares, F. L., Carvalho, A. M. X., Camargo, L. G. B., de Fátima Pereira, S. G., & Cardoso, I. M. (2018). Nutrients release from powder phonolite mediated by bioweathering actions. International Journal of Recycling of Organic Waste in Agriculture, 7, 89–98.
Teixeira, P. C., Donagema, G. K., Fontana, A., & Teixeira, W. G. (2017). Soil analysis methods manual (third ed ed.). Brasília: Embrapa.
Theodoro, S. C. H., Leonardos, O. H., & de Almeida, E. (2010). Mecanismos para disponibilização de nutrientes minerais a partir de processos biológicos. In: Congresso Brasileiro de Rochagem, 1, 2010, Brasília. Anais. Brasília: Embrapa, 2010. pp. 173–181.
Toscani, R. G. S., & Campos, J. E. G. (2017). Uso de pó de basalto e rocha fosfatada como fertilizante natural em solos lixiviados. Geociências, 36, 259–274.
Usher, C. R., Cleveland, C. A., Strongin, D. R., & Schoonen, M. A. (2004). Origin of oxygen in sulfate during pyrite oxidation with water and dissolved oxygen: An in situ horizontal attenuated total reflectance infrared spectroscopy isotope study. Environmental Science and Technology, 38, 5604–5606.
van Straaten, P. (2006). Farming with rocks and minerals: challenges and opportunities. Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciências, 78, 731–747.
van Straaten, P. (2007). Agrogeology: the use of rocks for crops (first ed ed.). Ontario: Cambridge.
Vetterlein, D., Kühn, T., Kaiser, K., & Jahn, R. (2013). Illite transformation and potassium release upon changes in composition of the rhizophere soil solution. Plant and Soil, 371, 267–279.
Vinci, G., Cozzolino, V., Mazzei, P., Monda, H., Spaccini, R., & Piccolo, A. (2018). An alternative to mineral phosphorus fertilizers: The combined effects of Trichoderma harzianum and compost on Zea mays, as revealed by 1H NMR and GC–MS metabolomics. PLoS One. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0209664.
WRB—IUSS Working Group. (2015). World reference base for soil resource (sixth ed ed.). Munchen: WRB. https://doi.org/10.1108/09504121011021959.
Yang, Z., Haneklaus, S., Singh, B. R., & Schnug, E. (2008). Effect of repeated applications of elemental sulfur on microbial population, sulfate concentration, and pH in soils. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 39, 124–140.
Yermiyahu, U., Ziporia, I., Faingolda, I., Yusopova, L., Fausta, N., & Bar-Talb, A. (2017). Polyhalite as a multinutrient fertilizer—potassium, magnesium, calcium and sulfate. Israel Journal Plant Science, 64, 145–157.
Zanardo, A., Montibeller, C. C., Navarro, G. R. B., Moreno, M. M. T., da Rocha, R. R., Del Roveri, C., et al. (2016). Formação Corumbataí na região de Rio Claro/SP: petrografia e implicações genéticas. Geociências, 35, 322–345.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES) (Grant Number 88882.344504/2019-01) for the financial support and the State University of Maringá for the use of their infrastructure and logistics.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodrigues, M., Nanni, M., Posser Silveira, C. et al. Mining Co-products as Sources of Multi-nutrients for Cultivation of Brachiaria ruziziensis. Nat Resour Res 30, 849–865 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-020-09745-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-020-09745-w