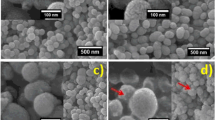
Abstract
Bismuth being a versatile material with a wide range of therapeutic, regenerative, and antimicrobial properties lacks stability which is desired for materials to interact in a desired way with the physiological environment. Hence, synthesizing such materials requires a sensible approach because, they are sensitive to the composition of constituents, processing parameters, and the environment they are synthesized. In the current work, we introduced a novel approach to entrap bismuth in the mesoporous silica network such that the stability of the nanoparticles can be increased. The stability of the nanoparticles basically depends on the functionalization, morphology, and crystallographic arrangements of elements. This stability is expected to explore its opportunities for versatile biological applications such as bone tissue engineering and therapeutic and regenerative medicine where controlled drug release is the primary requirement. In the current work, we found the synthesized Nanoparticles were found to be stable, functional, and well-suited for possible to use in biological environments. Alongside the particle size ranging from 2 to 140 nm and exhibiting mesopore structures with uniform network connectivity is of critical interest towards biological applications. However, further biological studies are needed to confirm these findings, which will be our future work, but the current work suggests that these NPs have the potential to be a valuable new tool for bone tissue engineering that is in compliance with previous literature.
Graphical Abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Black CR, Goriainov V, Gibbs D, Kanczler J, Tare RS, Oreffo RO (2015) Bone tissue engineering. Curr Mol Biol Rep 1:32–140
Amini AR, Nukavarapu Laurencin CT, SP, (2012) Bone tissue engineering: recent advances and challenges. Crit Rev™ Biomed Eng 40:5
Salgado AJ, Coutinho OP, Reis RL (2004) Bone tissue engineering: state of the art and future trends. Macromol Biosci 4:743–765
Bose S, Roy M, Bandyopadhyay A (2012) Recent advances in bone tissue engineering scaffolds. Trends Biotechnol 30:546–554
Qu H, Fu H, Han Z, Sun Y (2019) Biomaterials for bone tissue engineering scaffolds: a review. RSC Adv 9:26252
Gao J, Feng L, Chen B, Zhu FuB, M, (2022) The role of rare earth elements in bone tissue engineering scaffolds-a review. Composites Part B:109758
Lee KY, Alsberg E Mooney DJ (2001) Degradable and injectable poly (aldehyde guluronate) hydrogels for bone tissue engineering, Journal of biomedical materials research: an official journal of the society for biomaterials, the Japanese society for biomaterials, and the Australian society for biomaterials and the Korean society for biomaterials 56(2):228-233
Xue X, Hu Y, Deng Y, Su J (2021) Recent advances in design of functional biocompatible hydrogels for bone tissue engineering. Adv Funct Mater 31:2009432
Demirtaş TT, Irmak G, Gümüşderelioğlu M (2017) A bioprintable form of chitosan hydrogel for bone tissue engineering. Biofabrication 9:035003
Pazarçeviren AE, Tahmasebifar A, Tezcaner A, Keskin D, Evis Z (2018) Investigation of bismuth doped bioactive glass/graphene oxide nanocomposites for bone tissue engineering. Ceram Int 44:3791–3799
Wang L, Long NJ, Li L, Lu Y, Li M, Cao J, Zhang Y, Zhang Q, Xu S, Mao Yang Z, C, (2018) Multi-functional bismuth-doped bioactive glasses: combining bioactivity and photothermal response for bone tumor treatment and tissue repair. Light: Sci Appl 7:1
Moeini A, HassanzadehChinijani T, MalekKhachatourian A, Vinicius Lia Fook M, Baino F, Montazerian M (2023) A critical review of bioactive glasses and glass–ceramics in cancer therapy. Int J Appl Glas Sci 14(1):69–87
Targonska S, Sikora M, Marycz K, Smieszek A, Wiglusz RJ (2020) Theranostic applications of nanostructured silicate-substituted hydroxyapatite codoped with Eu3+ and Bi3+ ions—a novel strategy for bone regeneration. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 6:6148–6160
Zhou R, Liu X, Wu Y, Xiang H, Cao J, Li Y, Yin W, Zu Y, Li J, Liu R, Zhao F (2020) Suppressing the radiation-induced corrosion of bismuth nanoparticles for enhanced synergistic cancer radiophototherapy. ACS Nano 14:13016–13029
Du J, Ding H, Fu S, Li D, Yu B (2023) Bismuth-coated 80S15C bioactive glass scaffolds for photothermal antitumor therapy and bone regeneration. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 10:1098923
Ratha I, Adarsh T, Anand A, Sinha PK, Diwan P, Annapurna K, Biswas K (2018) In vitro bioactivity and antibacterial properties of bismuth oxide modified bioactive glasses. J Mater Res 33:178–190
Liu XH, Xue S, Ma JZ (2020) Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for bone tissue engineering. China Orthop Traumatol 33:784–787
Yousefiasl S, Manoochehri H, Makvandi P, Afshar S, Salahinejad E, Khosraviyan P, Saidijam M, Soleimani Asl S, Sharifi E (2023) Chitosan/alginate bionanocomposites adorned with mesoporous silica nanoparticles for bone tissue engineering. J Nanostruct Chem 13:389–403
Zhang N, Gao T, Wang Y, Wang Z, Zhang P, Liu J (2015) Environmental pH-controlled loading and release of protein on mesoporous hydroxyapatite nanoparticles for bone tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng, C 46:158–165
Li K, Sun H, Sui H, Zhang Y, Liang H, Wu X, Zhao Q (2015) Composite mesoporous silica nanoparticle/chitosan nanofibers for bone tissue engineering. RSC Adv 5:17541–17549
Bulmahn JC, Tikhonowski G, Popov AA, Kuzmin A, Klimentov SM, Kabashin AV, Prasad PN (2020) Laser-ablative synthesis of stable aqueous solutions of elemental bismuth nanoparticles for multimodal theranostic applications. Nanomaterials 10(8):1463
Griffith DM, Li H, Werrett MV, Andrews PC, Sun H (2021) Medicinal chemistry and biomedical applications of bismuth-based compounds and nanoparticles. Chem Soc Rev 50(21):12037–12069
Yang Y, Ouyang R, Xu L, Guo N, Li W, Feng K, Ouyang L, Yang Z, Zhou S, Miao Y (2015) Bismuth complexes: synthesis and applications in biomedicine. J Coord Chem 68(3):379–397
Fernandez C, Verne E, Vogel J, Carl G (2003) Optimisation of the synthesis of glass-ceramic matrix biocomposites by the “response surface methodology.” J Eur Ceram Soc 23(7):1031–1038
Ebrahimi S, Sipaut CS (2022) Synthesis of hydroxyapatite/bioactive glass composite nanopowder using design of experiments. Nanomaterials 12(13):2264
Gurumurthy B, Pal P, Griggs JA, Janorkar AV (2020) Optimization of collagen-elastin-like polypeptide-bioactive glass scaffold composition for osteogenic differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells. Materialia 9:100572
Vazquez NI, Gonzalez Z, Ferrari B, Castro Y (2017) Synthesis of mesoporous silica nanoparticles by sol–gel as nanocontainer for future drug delivery applications. Boletín de la Sociedad Española de Cerámica y Vidrio 56:139–145
Dolai J, Mandal K, Jana NR (2021) Nanoparticle size effects in biomedical applications. ACS Appl Nano Mater 4(7):6471–6496
Yang J, Xie T, Liu C, Xu L (2018) Facile fabrication of dumbbell-like β-Bi2O3/graphene nanocomposites and their highly efficient photocatalytic activity. Materials 11(8):1359
Mehmood Y, Khan IU, Shahzad Y, Khalid SH, Asghar S, Irfan M, Asif M, Khalid I, Yousaf AM, Hussain T (2019) Facile synthesis of mesoporous silica nanoparticles using modified sol-gel method: optimization and in vitro cytotoxicity studies. Pak J Pharm Sci 32:1805–1812
Motakef-Kazemi N, Yaqoubi M (2020) Regulation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway with synthesized bismuth oxide nanoparticles from Ginger (Zingiber officinale) extract: mitigating the proliferation of colorectal cancer cells. Iran J Pharm Res 19:70
Dharmadhikari VS, Sainkar SR, Badrinarayan S, Goswami A (1982) Characterisation of thin films of bismuth oxide by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. J Electron Spectrosc Relat Phenom 25:181–189
Bertoncello R, Glisenti A, Granozzi G, Battaglin G, Caccavale F, Cattaruzza E, Mazzoldi P (1993) Chemical interactions in titanium-and tungsten-implanted fused silica. J Non-Cryst Solids 162:205–216
Khine EE, Koncz-Horvath D, Kristaly F, Ferenczi T, Karacs G, Baumli P, Kaptay G (2022) Synthesis and characterization of calcium oxide nanoparticles for CO2 capture. J Nanopart Res 24:139
Sosulnikov MI, Teterin YA (1991) X-ray photoelectron study of calcium, strontium, barium and their oxides. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR 317:418–421
Noah NM, Ndangili PM (2022) Green synthesis of nanomaterials from sustainable materials for biosensors and drug delivery. Sensors International 3:100166
Kohestani AA Pishbin F () 3D printing of bone scaffolds based on alginate/gelatin hydrogel ink containing bioactive glass 45S5 and ZIF‐8 nanoparticles with sustained drug release capability. Advanced Engineering Materials 25(1):2300563
Mao X, Chen K, Zhao Y, Xiong C, Luo J, Wang Y, Wang B, Zhang H (2023) Bioinspired surface functionalization of biodegradable mesoporous silica nanoparticles for enhanced lubrication and drug release. Friction 11(7):1194–1211
Du J, Fan L, Razal JM, Chen S, Zhang H, Yang H, Li H, Li J (2023) Strontium-doped mesoporous bioglass nanoparticles for enhanced wound healing with rapid vascularization. J Mater Chemi B 11(31):7364–7377
Liu J, Du G, Yu H, Zhang X, Chen T (2023) Synthesis of hierarchically porous bioactive glass and its mineralization activity. Molecules 28(5):2224
Al-Aghbar MA, Jainarayanan AK, Dustin ML, Roffler SR (2022) The interplay between membrane topology and mechanical forces in regulating T cell receptor activity. Commun Biol 5(1):40
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
• Conceptualization, formal analysis and investigation, and original draft preparation: Mr. Gara Dheeraj Kumar (principal author).
• Writing—review and editing, supervision: Dr. Gujjala Raghavendra
• Resources, supervision, editing and reviewing: Dr. P. Syam Prasad
• Writing—review and editing: Dr. M. S. Narayanan
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gara, D.K., Gujjala, R., P, S.P. et al. Sol–gel synthesis and characterization of silica intertwined bismuth-based bioactive glass coalescence possibility towards biological applications. J Nanopart Res 26, 85 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-024-06001-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-024-06001-7