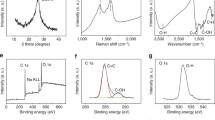
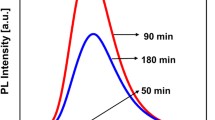
Abstract
Due to their promising numerous novel applications, such as photovoltaics, organic light-emitting diodes, fuel cells, bioimaging, biosensing, environmental monitoring, and the other interaction with biological systems, graphene quantum dots (GQDs) have steadily become a rising star as a new graphene derivatives member. In this work, we demonstrate a novel, simple, and facile technique for the synthesis of graphene quantum dots. We also investigate the optical and structural properties of the quantum dots using some characterization techniques including high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM), Fourier transform infrared (FTIR), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), UV–Vis absorption, and photoluminescence. The effect of temperature, pyrolysis time, and co-precursor concentration on quantum yield was investigated. The optimum circumstances were found to be a 5% aspartic acid concentration, a 5-min pyrolysis period, and a pyrolysis temperature of 185 °C. At the optimum conditions, the maximum quantum yield of GQDs was found to be 0.89 ± 0.02 and the spherical and crystal lattice structured GQDs were defined with a diameter of 2.05 ± 0.65 nm and the interplanar spacing in the crystalline petal of 0.189 nm. According to the results, the GQDs created are soluble and luminous in aqueous solution and have applications ranging from energy to life sciences.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bacon M, Bradley SJ, Nann T (2014) Graphene quantum dots. Part Part Syst Char 31(4):415–428
Baker SN, Baker GA (2010) Luminescent carbon nanodots: emergent nanolights. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 49(38):6726–6744
Chen RF (1967) Fluorescence quantum yields of tryptophan and tyrosine. Anal Lett 1(1):35–42
Dervishi E, Ji Z, Htoon H, Sykora M, Doorn SK (2019) Raman spectroscopy of bottom-up synthesized graphene quantum dots: size and structure dependence. Nanoscale 11(35):16571–16581
Dong YQ, Shao JW, Chen CQ, Li H, Wang RX, Chi YW, Lin XM, Chen GN (2012) Blue luminescent graphene quantum dots and graphene oxide prepared by tuning the carbonization degree of citric acid. Carbon 50(12):4738–4743
Fletcher AN (1969) Quinine sulfate as a fluorescence quantum yield standard. Photochem Photobiol 9(5):439–444
Gan Z, Xu H, Hao Y (2016) Mechanism for excitation-dependent photoluminescence from graphene quantum dots and other graphene oxide derivates: consensus, debates and challenges. Nanoscale 8(15):7794–7807
Ha HD, Jang MH, Liu F, Cho YH, Seo TS (2015) Upconversion photoluminescent metal ion sensors via two photon absorption in graphene oxide quantum dots. Carbon 81:367–375
Huang S, Wang LM, Huang CS, Hu BQ, Su W, Xiao Q (2016) Graphene quantum dot coupled with gold nanoparticle based “off-on” fluorescent probe for sensitive and selective detection of L-cysteine. Microchim Acta 183(6):1855–1864
Li LL, Wu GH, Hong T, Yin ZY, Sun D, Abdel-Halim ES, Zhu JF (2014) Graphene quantum dots as fluorescence probes for turn-off sensing of melamine in the presence of Hg2+. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6(4):2858–2864
Li K, Liu W, Ni Y, Li D, Lin D, Su Z, Wei G (2017) Technical synthesis and biomedical applications of graphene quantum dots. J Mater Chem B 5(25):4811–4826
Liu R, Wu D, Feng X, Mullen K (2011) Bottom-up fabrication of photoluminescent graphene quantum dots with uniform morphology. J Am Chem Soc 133(39):15221–15223
Liu F, Jang MH, Ha HD, Kim JH, Cho YH, Seo TS (2013) Facile synthetic method for pristine graphene quantum dots and graphene oxide quantum dots: origin of blue and green luminescence. Adv Mater 25(27):3657–3662
Liu JF, Qin LX, Kang SZ, Li GD, Li XQ (2017) Gold nanoparticles/glycine derivatives/graphene quantum dots composite with tunable fluorescence and surface enhanced Raman scattering signals for cellular imaging. Mater Des 123:32–38
More MP, Lohar PH, Patil AG, Patil PO, Deshmukh PK (2018) Controlled synthesis of blue luminescent graphene quantum dots from carbonized citric acid: assessment of methodology, stability, and fluorescence in an aqueous environment. Mater Chem Phys 220:11–22
Peng J, Gao W, Gupta BK, Liu Z, Romero-Aburto R, Ge L, Song L, Alemany LB, Zhan X, Gao G, Vithayathil SA, Kaipparettu BA, Marti AA, Hayashi T, Zhu JJ, Ajayan PM (2012) Graphene quantum dots derived from carbon fibers. Nano Lett 12(2):844–849
Qi B-P, Zhang X, Shang B-B, Xiang D, Zhang S (2018) Solvothermal tuning of photoluminescent graphene quantum dots: from preparation to photoluminescence mechanism. J Nanopart Res 20(2):1–9
Qu D, Zheng M, Du P, Zhou Y, Zhang L, Li D, Tan H, Zhao Z, Xie Z, Sun Z (2013) Highly luminescent S, N co-doped graphene quantum dots with broad visible absorption bands for visible light photocatalysts. Nanoscale 5(24):12272–12277
Qu D, Zheng M, Zhang L, Zhao H, Xie Z, Jing X, Haddad RE, Fan H, Sun Z (2014) Formation mechanism and optimization of highly luminescent N-doped graphene quantum dots. Sci Rep 4:5294
Rashid SA, Zobir SAM, Krishnan S, Hassan MM, Lim HN (2015) One-pot synthesis of graphene oxide sheets and graphene oxide quantum dots from graphite nanofibers. J Nanopart Res 17(5):1–11
Ryu J, Lee E, Lee K, Jang J (2015) A graphene quantum dots based fluorescent sensor for anthrax biomarker detection and its size dependence. J Mater Chem B 3(24):4865–4870
Sari E, Üzek R, Merkoçi A (2019) Paper based photoluminescent sensing platform with recognition sites for tributyltin. ACS Sensors 4(3):645–653
Shen J, Zhu Y, Yang X, Li C (2012) Graphene quantum dots: emergent nanolights for bioimaging, sensors, catalysis and photovoltaic devices. Chem Commun 48(31):3686–3699
Sk MA, Ananthanarayanan A, Huang L, Lim KH, Chen P (2014) Revealing the tunable photoluminescence properties of graphene quantum dots. J Mater Chem C 2(34):6954–6960
Sun HJ, Wu L, Wei WL, Qu XG (2013) Recent advances in graphene quantum dots for sensing. Mater Today 16(11):433–442
Üzek R, Sari E, Şenel S, Denizli A, Merkoçi A (2019) A nitrocellulose paper strip for fluorometric determination of bisphenol A using molecularly imprinted nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 186(4):1–10
Wang YF, Hu AG (2014) Carbon quantum dots: synthesis, properties and applications. J Mater Chem C 2(34):6921–6939
Wang SJ, Chen ZG, Cole I, Li Q (2015) Structural evolution of graphene quantum dots during thermal decomposition of citric acid and the corresponding photoluminescence. Carbon 82:304–313
Wu X, Tian F, Wang WX, Chen J, Wu M, Zhao JX (2013) Fabrication of highly fluorescent graphene quantum dots using L-glutamic acid for in vitro/in vivo imaging and sensing. J Mater Chem C 1(31):4676–4684
Zhang Y, Gao H, Niu JJ, Liu BT (2014) Facile synthesis and photoluminescence of graphene oxide quantum dots and their reduction products. New J Chem 38(10):4970–4974
Zhang Y, Wang Y, Feng X, Zhang F, Yang Y, Liu X (2016) Effect of reaction temperature on structure and fluorescence properties of nitrogen-doped carbon dots. Appl Surf Sci 387:1236–1246
Zhu SJ, Song YB, Zhao XH, Shao JR, Zhang JH, Yang B (2015) The photoluminescence mechanism in carbon dots (graphene quantum dots, carbon nanodots, and polymer dots): current state and future perspective. Nano Res 8(2):355–381
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sari, E. Synthesis and characterization of high quantum yield graphene quantum dots via pyrolysis of glutamic acid and aspartic acid. J Nanopart Res 24, 37 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-022-05428-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-022-05428-0