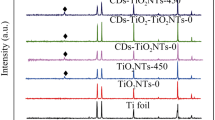
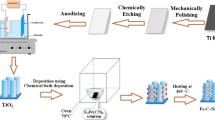
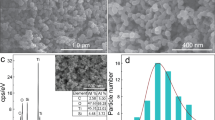
Abstract
In order to prepare highly efficient and stable photocatalytic hydrogen production catalyst, spot-coated carbon nanotube (CNT) composites were prepared by in situ growth of TiO2 on the surface of CNT by adding CNT in four butyl titanate and then sol–gel method under ultrasonic irradiation. Compared with the nanocomposites doped with dopamine, the prepared nanocomposites obviously had lower agglomerated degree and showed excellent hydrogen evolution performance. The optimal hydrogen production performance was 0.0337 mg/ml for the prepared nanocomposites, which had a stable photocatalytic efficiency.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dong F et al (2011) Enhancement of the visible light photocatalytic activity of C-doped TiO2 nanomaterials prepared by a green synthetic approach. J Phys Chem C 115(27):13285–13292
Ghicov A et al (2009) TiO2 nanotubes in dye-sensitized solar cells: critical factors for the conversion efficiency. Chemistry-an Asian J 4(4):520–525
Han ZS et al (2019) Activated TiO2 with tuned vacancy for efficient electrochemical nitrogen reduction. Appl Catal B Environ 257:117896
Huang WB et al (2015) Hybrid nanostructures of mixed-phase TiO2 for enhanced photoelectrochemical water splitting. RSC Adv 5(69):56098–56102
Hwang SH, Kim C, Jang J (2011) SnO2 nanoparticle embedded TiO2 nanofibers - highly efficient photocatalyst for the degradation of rhodamine B. Catal Commun 12(11):1037–1041
Jia JL et al (2016) Characterization and mechanism analysis of graphite/C-doped TiO2 composite for enhanced photocatalytic performance. J Ind Eng Chem 33:162–169
Kong JJ et al (2016a) Visible-light decomposition of gaseous toluene over BiFeO3-(BiNe)(2)O-3 heterojunctions with enhanced performance. Chem Eng J 302:552–559
Kong JJ et al (2016b) Multichannel charge separation promoted ZnO/P25 heterojunctions for the photocatalytic oxidation of toluene. Chin J Catal 37(6):869–877
Lee SS et al (2013) Novel-structured electrospun TiO2/CuO composite nanofibers for high efficient photocatalytic cogeneration of clean water and energy from dye wastewater. Water Res 47(12):4059–4073
Mei B et al (2015) Crystalline TiO2: a generic and effective electron-conducting protection layer for photoanodes and -cathodes. J Phys Chem C 119(27):15019–15027
Ng J et al (2010) Hybridized nanowires and cubes: a novel architecture of a heterojunctioned TiO2/SrTiO3 thin film for efficient water splitting. Adv Func Mater 20(24):4287–4294
Nie XJ et al (2021) One-step preparation of C-doped TiO2 nanotubes with enhanced photocatalytic activity by a water-assisted method. CrystEngComm 23(16):3015–3025
Nong SY et al (2018) Well-dispersed ruthenium in mesoporous crystal TiO2 as an advanced electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. J Am Chem Soc 140(17):5719–5727
Pan J et al (2011) On the true photoreactivity order of 001}, {010}, and {101 facets of anatase TiO2 crystals. Angew Chem Int Ed 50(9):2133–2137
Roy P et al (2011) TiO2 nanotubes and their application in dye-sensitized solar cells (vol 2, pg 45, 2010). Nanoscale 3(12):5180–5180
Shannon MA et al (2008) Science and technology for water purification in the coming decades. Nature 452(7185):301–310
Tang CL et al (2016) A green approach assembled multifunctional Ag/AgBr/TNF membrane for clean water production & disinfection of bacteria through utilizing visible light. Appl Catal B Environ 196:57–67
Tripathy J, Lee K, Schmuki P (2014) Tuning the selectivity of photocatalytic synthetic reactions using modified TiO2 nanotubes. Angew Chem Int Ed 53(46):12605–12608
Wang W, Tade MO, Shao ZP (2018) Nitrogen-doped simple and complex oxides for photocatalysis: a review. Prog Mater Sci 92:33–63
Wang CJ et al (2020a) Efficient Z-scheme photocatalysts of ultrathin g-C3N4-wrapped Au/TiO2-nanocrystals for enhanced visible-light-driven conversion of CO2 with H2O. Appl Catal B Environ 263:118314
Wang YX et al (2020b) Photocatalytic activity of N-TiO2/O-doped N vacancy g-C3N4 and the intermediates toxicity evaluation under tetracycline hydrochloride and Cr(VI) coexistence environment. Appl Catal B Environ 262:118308
Wu TW et al (2019) Greatly enhanced electrocatalytic N-2 reduction on TiO2 via V doping. Small Methods 3(11):1900356
Xu P et al (2010) I-2-Hydrosol-seeded growth of (I-2)(n)-C-codoped meso/nanoporous TiO2 for visible light-driven photocatalysis. J Phys Chem C 114(20):9510–9517
Zhang R et al (2009) Preparation of necklace-structured TiO2/SnO2 hybrid nanofibers and their photocatalytic activity. J Am Ceram Soc 92(10):2463–2466
Zhao J et al (2020) Fabrication and investigation on ternary heterogeneous MWCNT@TiO2-C fillers and their silicone rubber wave-absorbing composites. Compos Part A Appl Sci Manuf 129:105714
Zheng JY et al (2018) Crystalline TiO2 protective layer with graded oxygen defects for efficient and stable silicon-based photocathode. Nat Commun 9:3572
Zhou W et al (2014) Ordered mesoporous black TiO2 as highly efficient hydrogen evolution photocatalyst. J Am Chem Soc 136(26):9280–9283
Zhou W et al (2011) Well-ordered large-pore mesoporous anatase TiO2 with remarkably high thermal stability and improved crystallinity: preparation, characterization, and photocatalytic performance. Adv Func Mater 21(10):1922–1930
Funding
This study was funded by Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51773106, 51701029 and 51778088), Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (No.2020A1515011274), Guangdong Provincial Natural Science Foundation Project (No.2020A1515010437), and Natural Science Foundation of Inner Mongolia, China (No.2018MS05038).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, C., Xiang, J., Zhao, Z. et al. Improvement of hydrogen production performance by in situ doping of carbon nanotubes into TiO2 materials. J Nanopart Res 24, 61 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-021-05353-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-021-05353-8