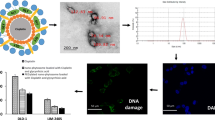
Abstract
Recently, designing a nanocarrier for carboplatin with high retention power and entrapment efficiency and its corresponding impact has sparked a heated debate. The aim of this study was to investigate the cytotoxic efficacy of the biodegradable nanocarrier loaded with carboplatin. This study focuses on (i) characterization, (ii) in vitro drug release evaluation, and (iii) cytotoxicity of liposome nanoparticles (NPs) loaded with carboplatin. The reverse-phase evaporation was used to synthesize nanoparticles and determine specifications including shape morphology, particle size, drug release rate, polydispersity index (PDI), stability, and zeta potential of prepared formulation. Furthermore, A172 and C6 glioblastoma cell lines were used to determine the efficacy of nanodrug using 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) reduction assay. NPs had an average size of 240.5 nm and zeta potential of − 25.8 mV. Drug loading and encapsulation efficiency of NPs were 2.65% and 71.45%, respectively. Moreover, entrapment efficiency and drug release rate increase in a time-dependent manner. The results reveal that the preparation method and PEGylation have a positive effect of the properties of NPs and the efficiency of encapsulation and loading rate. Results from stability study reported that using PEGylation helps to improve characteristics of NPs and results in minimal changes in their properties over the time. In addition, our data demonstrate that carboplatin cytotoxicity correlates with drug concentration which was considerably increased in NPs. PEGylated NPs have enhanced cytotoxicity against glioblastoma cell lines compared with free drug. Overall, our evaluation has shown that the PEGylated nanoliposome particles loaded with carboplatin hold high potential for nanoparticle-based therapy.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrieux K, Couvreur P (2009) Polyalkylcyanoacrylate nanoparticles for delivery of drugs across the blood–brain barrier. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol 1:463–474
Arshad A, Yang B, Bienemann AS, Barua NU, Wyatt MJ, Woolley M, Johnson DE, Edler KJ, Gill SS (2015) Convection-enhanced delivery of carboplatin PLGA nanoparticles for the treatment of glioblastoma. PLoS One 10:e0132266
Bangham AD, Horne RW (1964) Negative staining of phospholipids and their structural modification by surface-active agents as observed in the electron microscope. J Mol Biol 8:660–668
Begley DJ (2004) Delivery of therapeutic agents to the central nervous system: the problems and the possibilities. Pharmacol Ther 104:29–45
Breen W, Bancos I, Young WF, Bible KC, Laack NN, Foote RL, Hallemeier CL (2018) External beam radiation therapy for advanced/unresectable malignant paraganglioma and pheochromocytoma. Adv Radiat Oncol 3:25–29
Cooper ER (2010) Nanoparticles: a personal experience for formulating poorly water soluble drugs. J Control Release 141:300–302
Cosco D, Paolino D, Muzzalupo R, Celia C, Citraro R, Caponio D, Picci N, Fresta M (2009) Novel PEG-coated niosomes based on bola-surfactant as drug carriers for 5-fluorouracil. Biomed Microdevices 11:1115–1125
Crowley LC, Marfell BJ & Waterhouse NJ (2016) Analyzing cell death by nuclear staining with Hoechst 33342. Cold Spring Harbor Protocols, 2016, pdb.prot087205
Delaney TF, Haas RLM (2016) Innovative radiotherapy of sarcoma: proton beam radiation. Eur J Cancer 62:112–123
Dolecek TA, Propp JM, Stroup NE, Kruchko C (2012) CBTRUS statistical report: primary brain and central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2005–2009. Neuro-Oncology 14:v1–v49
Dorsey JF, Hollander AB, Alonso-Basanta M, Macyszyn L, Bohman L-E, Judy KD, Maity A, Lee JYK, Lustig RA, Phillips PC, Pruitt AA (2014) 66—Cancer of the central nervous system. In: Niederhuber JE, Armitage JO, Doroshow JH, Kastan MB, Tepper JE (eds) Abeloff’s clinical oncology (fifth edition). Content Repository Only, Philadelphia
Ebrahimifar M, Nili-Ahmadabadi A, Akbarzadeh A, Shahemabadi HE, Hasanzadegan M, Moradi-Sardareh H, Madadizadeh H, Rezaee-Diyan J (2017) Preparation, characterization and cytotoxic effects of pegylated nanoliposomal containing carboplatin on ovarian cancer cell lines. Indian J Clin Biochem 32:230–234
Ebrahimifar M, Hasanzadegan Roudsari M, Kazemi SM, Ebrahimi Shahmabadi H, Kanaani L, Alavi SA, Izadi Vasfi M Enhancing effects of curcumin on cytotoxicity of paclitaxel, methotrexate and vincristine in gastric cancer cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prevent 18:65–68
Gozde U, Ufuk G (2018) Smart drug delivery systems in cancer therapy. Curr Drug Targets 19:202–212
Hamelers IHL, Van Loenen E, Staffhorst RWHM, De Kruijff B, De Kroon AIPM (2006) Carboplatin nanocapsules: a highly cytotoxic, phospholipid-based formulation of carboplatin. Mol Cancer Ther 5:2007–2012
Honary S & Zahir F (2013) Effect of zeta potential on the properties of nano-drug delivery systems—a review (part 1) Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical 12 (2): 265–273
Jafari M, Soltani M, Naahidi S, Karunaratne N & Chen P (2012) Nonviral approach for targeted nucleic acid delivery, nonviral approach for targeted nucleic acid delivery, Nonviral Approach for Targeted Nucleic Acid Delivery, Current Medicinal Chemistry 19(2):197–208 https://doi.org/10.2174/092986712803414141
Kawai F (2002) Microbial degradation of polyethers. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 58:30–38
Knop K, Hoogenboom R, Fischer D, Schubert US (2010) Poly(ethylene glycol) in drug delivery: pros and cons as well as potential alternatives. Angew Chem Int Ed 49:6288–6308
Lee BK, Yun YH, Park K (2015) Smart nanoparticles for drug delivery: boundaries and opportunities. Chem Eng Sci 125:158–164
Mayer RS (2014) 55—rehabilitation of individuals with cancer. In: Niederhuber JE, Armitage JO, Doroshow JH, Kastan MB, Tepper JE (eds) Abeloff’s clinical oncology (fifth edition). Content Repository Only! Philadelphia
Moreno AC, Frank SJ, Garden AS, Rosenthal DI, Fuller CD, Gunn GB, Reddy JP, Morrison WH, Williamson TD, Holliday EB, Phan J, Blanchard P (2019) Intensity modulated proton therapy (IMPT)—the future of IMRT for head and neck cancer. Oral Oncol 88:66–74
Müller RH, Lherm C, Herbert J, Couvreur P (1990) In vitro model for the degradation of alkylcyanoacrylate nanoparticles. Biomaterials 11:590–595
Otsuka H, Nagasaki Y, Kataoka K (2012) PEGylated nanoparticles for biological and pharmaceutical applications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 64(Supplement):246–255
Persidsky Y, Ramirez SH, Haorah J, Kanmogne GD (2006) Blood–brain barrier: structural components and function under physiologic and pathologic conditions. J NeuroImmune Pharmacol 1:223–236
Ramirez SH, Haskó J, Skuba A, Fan S, Dykstra H, Mccormick R, Reichenbach N, Krizbai I, Mahadevan A, Zhang M, Tuma R, Son Y-J, Persidsky Y (2012) Activation of cannabinoid receptor 2 attenuates leukocyte–endothelial cell interactions and blood–brain barrier dysfunction under inflammatory conditions. J Neurosci 32:4004–4016
Rosenzweig KE, Dladla N, Schindelheim R, Sim SE, Braban LE, Venkatraman ES, Leibel SA (2001) Three-dimensional conformal radiation therapy (3D-CRT) for early-stage non–small-cell lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer 3:141–144
Sathyamoorthy N, Dhanaraju MD, Devendiran S & Heera B (2017) Influence of surface charge on the in vitro protein adsorption and cell cytotoxicity of paclitaxel loaded poly(Îμ-caprolactone) nanoparticles. Bulletin of Faculty of Pharmacy, Cairo University, 55, 249–258
Sefidgar M, Soltani M, Raahemifar K, Sadeghi M, Bazmara H, Bazargan M, Mousavi Naeenian M (2015) Numerical modeling of drug delivery in a dynamic solid tumor microvasculature. Microvasc Res 99:43–56
Shahzad MMK, Lopez-Berestein G, Sood AK (2009) Novel strategies for reversing platinum resistance. Drug Resist Updat 12:148–152
Soltani M, Chen P (2012) Effect of tumor shape and size on drug delivery to solid tumors. J Biol Eng 6:4
Stojanovska V, Sakkal S, Nurgali K (2015) Platinum-based chemotherapy: gastrointestinal immunomodulation and enteric nervous system toxicity. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 308:G223–G232
Stupp R, Mason WP, Van Den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJB, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn U, Curschmann J, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, Gorlia T, Allgeier A, Lacombe D, Cairncross JG, Eisenhauer E, Mirimanoff RO (2005) Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 352:987–996
Tan J, Shah S, Thomas A, Ou-Yang HD, Liu Y (2013) The influence of size, shape and vessel geometry on nanoparticle distribution. Microfluid Nanofluid 14:77–87
Veronese FM, Pasut G (2005) PEGylation, successful approach to drug delivery. Drug Discov Today 10:1451–1458
Vert M, Doi Y, Hellwich KH, Hess M, Hodge P, Kubisa P, Rinaudo M, Schué F (2012) Terminology for biorelated polymers and applications (IUPAC recommendations 2012). Pure Appl Chem 84:377–410
Wang X, Yang L, Chen Z, Shin Dong M (2008) Application of nanotechnology in cancer therapy and imaging. CA Cancer J Clin 58:97–110
Wang AZ, Langer R, Farokhzad OC (2012) Nanoparticle delivery of cancer drugs. Annu Rev Med 63:185–198
Wernyj RP, Morin PJ (2004) Molecular mechanisms of platinum resistance: still searching for the Achilles’ heel. Drug Resist Updat 7:227–232
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by Postgraduate Office, Science and Research Branch of Islamic Azad University, Tehran, Iran, and Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Waterloo, Ontario, Canada.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MH: conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, investigation, and writing original draft; MS: formal data analysis and project supervision; AA: development of methodology, providing resources, and supervision; PC: data validation and providing resources; AH: supervision and formal data analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hassanzadeganroudsari, M., Heydarinasab, A., Akbarzadeh khiyavi, A. et al. In vitro investigation of anticancer efficacy of carboplatin-loaded PEGylated nanoliposome particles on brain cancer cell lines. J Nanopart Res 21, 124 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-019-4562-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-019-4562-x