Abstract
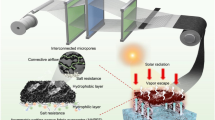
The super-hydrophobic silica nanoparticles are applied to alter the wettability of rock surface from water-wet to oil-wet. The aim of this is to reduce injection pressure so as to enhance water injection efficiency in low permeability reservoirs. Therefore, a new type of environmentally responsive nanosilica (denote as ERS) is modified with organic compound containing hydrophobic groups and “pinning” groups by covalent bond and then covered with a layer of hydrophilic organic compound by chemical adsorption to achieve excellent water dispersibility. Resultant ERS is homogeneously dispersed in water with a size of about 4–8 nm like a micro-emulsion system and can be easily injected into the macro or nano channels of ultra-low permeability reservoirs. The hydrophobic nanosilica core can be released from the aqueous delivery system owing to its strong dependence on the environmental variation from normal condition to injection wells (such as pH and salinity). Then the exposed silica nanoparticles form a thin layer on the surface of narrow pore throat, leading to the wettability from water-wet to oil-wet. More importantly, the two rock cores with different permeability were surface treated with ERS dispersion with a concentration of 2 g/L, exhibit great reduce of water injection pressure by 57.4 and 39.6%, respectively, which shows great potential for exploitation of crude oil from ultra-low permeability reservoirs during water flooding.

ᅟ










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe T, Kobayashi S, Kobayashi M (2011) Aggregation of colloidal silica particles in the presence of fulvic acid, humic acid, or alginate: effects of ionic composition. Colloid Surf A 379(1-3):21–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2010.11.052
Al-Anssari S, Barifcani A, Wang S, Maxim L, Iglauer S (2016) Wettability alteration of oil-wet carbonate by silica nanofluid. J Colloid Interface Sci 461:435–442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2015.09.051
Behzadi A, Mohammadi A (2016) Environmentally responsive surface-modified silica nanoparticles for enhanced oil recovery. J Nanopart Res 18(9):1–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-016-3580-1
Bernardos A, Aznar E, Marcos MD, Martínez-Máñez R, Sancenón F, Soto J, Barat JM, Amorós P (2009) Enzyme-responsive controlled release using mesoporous silica supports capped with lactose. Angew Chem Int Ed 48(32):5884–5887. https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.200900880
Chaudhury MK (2003) Complex fluids: spread the word about nanofluids. Nature 423(6936):131–132. https://doi.org/10.1038/423131a
Cîrcu M, Nan A, Borodi G, Liebscher J, Turcu R (2016) Refinement of magnetite nanoparticles by coating with organic stabilizers. Nanomaterials 6(12):228. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6120228
French RA, Jacobson AR, Kim B, Isley SL, Penn R, Baveye PC (2009) Influence of ionic strength, pH, and cation valence on aggregation kinetics of titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Environ Sci Technol 43(5):1354–1359. https://doi.org/10.1021/es802628n
Graf C, Gao Q, Schütz I, Noufele CN, Ruan W, Posselt U, Korotianskiy E, Nordmeyer D, Rancan F, Hadam S, Vogt A, Lademann J, Haucke V, Rühl E (2012) Surface functionalization of silica nanoparticles supports colloidal stability in physiological media and facilitates internalization in cells. Langmuir 28(20):7598–7613. https://doi.org/10.1021/la204913t
Gu CY, Di QF, Fang HP (2007) Slip velocity model of porous walls absorbed by hydrophobic nanoparticles SiO2. J Hydrodyn 19(3):365–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-6058(07)60071-7
Haugen Å, Fernø MA, Mason G, Morrow MR (2014) Capillary pressure and relative permeability estimated from a single spontaneous imbibition test. J Pet Sci Eng 115:66–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2014.02.001
Hendraningrat L, Torsæter O (2015) A stabilizer that enhances the oil recovery process using silica-based nanofluids. Transp Porous Media 108(3):679–696. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-015-0495-8
Huber F, Enzmann F, Wenka A, Bouby M, Dentz M, Schäfer T (2012) Natural micro-scale heterogeneity induced solute and nanoparticle retardation in fractured crystalline rock. J Contam Hydrol 133:13340–13352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconhyd.2012.03.004
Jin L, Wojtanowicz AK (2014) Progression of injectivity damage with oily waste water in linear flow. Pet Sci 11(4):550–562. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12182-013-0371-0
Karimi A, Fakhroueian Z, Bahramian A, Pour KN, Darabad JB, Azin R, Arya S (2012) Wettability alteration in carbonates using zirconium oxide nanofluids: EOR implications. Energy Fuel 26(2):1028–1036. https://doi.org/10.1021/ef201475u
Li XH, Cao Z, Zhang ZJ, Dang HX (2006) Surface-modification in situ of nano-SiO2 and its structure and tribological properties. Appl Surf Sci 252(22):7856–7861. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2005.09.068
Li XH, Liu PS, Zhang ZJ, Rong MM, Li N (2015) A small-diameter nano-silica emulsion and its preparation method. Invention patent of China CN201510215770.2
Lin D, Story SD, Walker SL, Huang Q, Liang W, Cai P (2017) Role of pH and ionic strength in the aggregation of TiO 2 nanoparticles in the presence of extracellular polymeric substances from Bacillus subtilis. Environ Pollut 228:35–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.05.025
Liu PS, Guo S, Lian MM, Li XH, Zhang ZJ (2015) Improving water-injection performance of quartz sand proppant by surface modification with surface-modified nanosilica. Colloid Surf A 470:114–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2015.01.073
Liu J, Janjua ZA, Roe M, Xu F, Turnbull B, Choi KS, Hou X (2016) Super-hydrophobic/icephobic coatings based on silica nanoparticles modified by self-assembled monolayers. Nanomaterials 6(12):232. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6120232
Parvazdavani M, Masihi M, Ghazanfari MH (2012) Monitoring the influence of dispersed nano-particles on oil–water relative permeability hysteresis. J Pet Sci Eng 124:222–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2014.10.005
Rancan F, Gao Q, Graf C, Troppens S, Hadam S, Hackbarth S, Kembuan C, Blume-Peytavi U, Rühl E, Lademann J, Vogt A (2012) Skin penetration and cellular uptake of amorphous silica nanoparticles with variable size, surface functionalization, and colloidal stability. ACS Nano 6(8):6829–6842. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn301622h
Sepehrinia K, Mohammadi A (2016) Wettability alteration properties of fluorinated silica nanoparticles in liquid-loaded pores: an atomistic simulation. Appl Surf Sci 371:349–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.02.218
Yan YL, Cui MY, Jiang WD, He AL, Liang C (2017) Drag reduction in reservoir rock surface: hydrophobic modification by SiO2 nanofluids. Appl Surf Sci 396:1556–1561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.11.209
Zakaria AS, Nasr-El-Din HA (2015) A novel polymer-assisted emulsified-acid system improves the efficiency of carbonate matrix acidizing. SPE J 2(03):1061–1074. https://doi.org/10.2118/173711-PA
Zhang JQ, Zhang GC, Ge JJ, Feng AZ, Jiang P, Zhang YG, Fu X (2012) Laboratory studies of depressurization with a high concentration of surfactant in low-permeability reservoirs. J Dispers Sci Technol 33(11):1589–1595. https://doi.org/10.1080/01932691.2011.620533
Zheng N, Liu K, Li XH, Zhang ZJ (2012) Preparation of super-hydrophobic nano-silica aqueous dispersion and study of its application for water resistance reduction at low-permeability reservoir. Micro Nano Lett 7(6):526–528. https://doi.org/10.1049/mnl.2012.0192
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support of this research by the National Natural Science Foundational of China (grant No. 21371047), Plan for Scientific Innovation Talent of Henan Province (164200510005), and The Program for Innovative Research Team from the University of Henan Province (17IRTSTHN004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, P., Niu, L., Li, X. et al. Environmental response nanosilica for reducing the pressure of water injection in ultra-low permeability reservoirs. J Nanopart Res 19, 390 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-017-4086-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-017-4086-1