Abstract
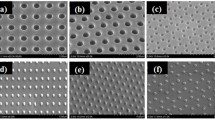
Nanoimprinting enables the implementation of nanoparticle shapes with complex 2D shapes involving different materials. In addition to these objects, this article presents 3D-shaped nanoparticles fabricated by substrate conformal imprint technique. The imprint polymer AMONIL is used either in pure form or in combination with fluorescent dyes for the preparation of particles. The substrate conformal imprint lithography process, including etching and particle release, is conducted for both materials in a similar fashion. In this work, cuboidal particles with a high aspect ratio (1:120) are compared to particles with a T-shaped cross section with respect to their abilities to enhance or reduce their stiffness. Additionally, particles with a high aspect ratio are compared to particles with a lower aspect ratio (1:20). The local stiffness is found to depend strongly on the particle thickness and the geometry of their cross section. Thicker and 3D T-shaped particles present higher local stiffness than thinner and 2D cuboidal-shaped particles. The local bending angle was determined to be 77° for 2D-shaped particles and 83° for 3D-shaped particles, of the same total height of 176 nm. Very thin particles (<50 nm) of high aspect ratio prefer to curl finally forming loops.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altavilla C, Ciliberto E (2011) Inorganic nanoparticles: synthesis, applications, and perspectives. Nanomaterials and their applications. CRC Press, Boca Raton
AMO GmbH (2015) AMONIL & AMOPRIME—low viscosity imprint resist and adhesion promoter: data sheet. http://www.amo.de/wp-content/uploads/2015/03/FactSheet_AMONIL.pdf. Accessed 12 October
Austin MD, Ge H, Wu W, Li M, Yu Z, Wasserman D, Lyon SA, Chou SY (2004) Fabrication of 5 nm linewidth and 14 nm pitch features by nanoimprint lithography. Appl Phys Lett 84(26):5299–5301. doi:10.1063/1.1766071
Banu S, Birtwell S, Galitonov G, Chen Y, Zheludev N, Morgan H (2007) Fabrication of diffraction-encoded micro-particles using nano-imprint lithography. J Micromech Microeng 17(7):S116–S121. doi:10.1088/0960-1317/17/7/S08
Buyukserin F, Aryal M, Gao J, Hu W (2009) Fabrication of polymeric nanorods using bilayer nanoimprint lithography. Small 5(14):1632–1636. doi:10.1002/smll.200801822
Champion JA, Mitragotri S (2009) Shape induced inhibition of phagocytosis of polymer particles. Pharm Res 26(1):244–249. doi:10.1007/s11095-008-9626-z
Champion JA, Katare YK, Mitragotri S (2007a) Making polymeric micro- and nanoparticles of complex shapes. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104(29):11901–11904. doi:10.1073/pnas.0705326104
Champion JA, Katare YK, Mitragotri S (2007b) Particle shape: a new design parameter for micro- and nanoscale drug delivery carriers: fourth international nanomedicine and drug delivery symposium. J Control Release 121(1–2):3–9. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2007.03.022
Choi SQ, Jang SG, Pascall AJ, Dimitriou MD, Kang T, Hawker CJ, Squires TM (2011) Synthesis of multifunctional micrometer-sized particles with magnetic, amphiphilic, and anisotropic properties. Adv Mater Weinheim 23(20):2348–2352. doi:10.1002/adma.201003604
Chou SY, Krauss PR (1997) Imprint lithography with sub-10 nm feature size and high throughput. Microelectron Eng 35(1–4):237–240. doi:10.1016/S0167-9317(96)00097-4
Chou SY, Krauss PR, Renstrom PJ (1995) Imprint of sub-25 nm vias and trenches in polymers. Appl Phys Lett 67(21):3114–3116. doi:10.1063/1.114851
Chou SY, Krauss PR, Renstrom PJ (1996) Nanoimprint lithography. J Vac Sci Technol B 14(6):4129–4133. doi:10.1116/1.588605
Chu KS, Schorzman AN, Finniss MC, Bowerman CJ, Peng L, Luft JC, Madden AJ, Wang AZ, Zamboni WC, DeSimone JM (2013) Nanoparticle drug loading as a design parameter to improve docetaxel pharmacokinetics and efficacy. Biomaterials 34(33):8424–8429. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.07.038
Colvin VL (2001) From opals to optics: colloidal photonic crystals. MRS Bull 26(08):637–641. doi:10.1557/mrs2001.159
Cui H, Feng Y, Ren W, Zeng T, Lv H, Pan Y (2009) Strategies of large scale synthesis of monodisperse nanoparticles. Recent Pat Nanotechnol 3(1):32–41. doi:10.2174/187221009787003302
Dumond JJ, Low HY (2008) Residual layer self-removal in imprint lithography. Adv Mater Weinheim 20(7):1291–1297. doi:10.1002/adma.200701659
Euliss LE, DuPont JA, Gratton SEA, DeSimone JM (2006) Imparting size, shape, and composition control of materials for nanomedicine. Chem Soc Rev 35(11):1095–1104. doi:10.1039/B600913C
Fader R, Rommel M, Bauer A, Rumler M, Frey L, Antonius Verschuuren M, van den Laar R, Ji R, Schömbs U (2013) Accuracy of wafer level alignment with substrate conformal imprint lithography. J Vac Sci Technol B 31(6):–6. doi:10.1116/1.4824696
Freeling JP, Koehn J, Shu C, Sun J, Ho RJY (2015) Anti-HIV drug-combination nanoparticles enhance plasma drug exposure duration as well as triple-drug combination levels in cells within lymph nodes and blood in primates. AIDS Res Hum Retrovir 31(1):107–114. doi:10.1089/aid.2014.0210
Gharpure KM, Chu KS, Bowerman CJ, Miyake T, Pradeep S, Mangala SL, Han H-D, Rupaimoole R, Armaiz-Pena GN, Rahhal TB, Wu SY, Luft JC, Napier ME, Lopez-Berestein G, De Simone JM, Sood AK (2014) Metronomic docetaxel in PRINT nanoparticles and EZH2 silencing have synergistic antitumor effect in ovarian cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 13(7):1750–1757. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-13-0930
Glangchain LCS, Caldorera-Moore M, Shi L, Roy K (2008) Nanoimprint lithography based fabrication of shape-specific, enzymatically-triggered smart nanoparticles. J Control Release 125(3):263–272. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2007.10.021
Gratton SEA, Pohlhaus PD, Lee J, Guo J, Cho MJ, DeSimone JM (2007) Nanofabricated particles for engineered drug therapies: a preliminary biodistribution study of PRINT™ nanoparticles. J Control Release 121(1–2):10–18. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2007.05.027
Gratton SEA, Ropp PA, Pohlhaus PD, Luft JC, Madden VJ, Napier ME, DeSimone JM (2008a) The effect of particle design on cellular internalization pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105(33):11613–11618. doi:10.1073/pnas.0801763105
Gratton SEA, Williams SS, Napier ME, Pohlhaus PD, Zhou Z, Wiles KB, Maynor BW, Shen C, Olafsen T, Samulski ET, DeSimone JM (2008b) The pursuit of a scalable nanofabrication platform for use in material and life science applications. Acc Chem Res 41(12):1685–1695. doi:10.1021/ar8000348
Groneberg DA, Giersig M, Welte T, Pison U (2006) Nanoparticle-based diagnosis and therapy. Curr Drug Targets 7(6):643–648. doi:10.2174/138945006777435245
Hamouda F, Barbillon G, Held S, Agnus G, Gogol P, Maroutian T, Scheuring S, Bartenlian B (2009) Nanoholes by soft UV nanoimprint lithography applied to study of membrane proteins. Microelectron Eng 86(4–6):583–585. doi:10.1016/j.mee.2008.11.086
Han K-S, Hong S-H, Lee H (2007) Fabrication of complex nanoscale structures on various substrates. Appl Phys Lett 91(12):123118. doi:10.1063/1.2789735
Hernandez CJ, Mason T (2007) Colloidal alphabet soup: monodisperse dispersions of shape-designed LithoParticles. J Phys Chem C 111(12):4477–4480. doi:10.1021/jp0672095
Hornung M, Ji R, Verschuuren MA, van den Laar R (2010) 6 inch full field wafer size nanoimprint lithography for photonic crystals patterning. In: IEEE (ed) Nanotechnology IEEE-Nano 2010, pp 339–342
Hua F, Sun Y, Gaur A, Meitl MA, Bilhaut L, Rotkina L, Wang J, Geil P, Shim M, Rogers JA (2004) Polymer imprint lithography with molecular-scale resolution. Nano Lett 4(12):2467–2471. doi:10.1021/nl048355u
Iskandar F (2009) Nanoparticle processing for optical applications—a review. Adv Powder Technol 20(4):283–292. doi:10.1016/j.apt.2009.07.001
Jang J-H, Ullal CK, Kooi SE, Koh C, Thomas EL (2007) Shape control of multivalent 3D colloidal particles via interference lithography. Nano Lett 7(3):647–651. doi:10.1021/nl0626277
Ji R, Hornung M, Verschuuren MA, van den Laar R, van Eekelen J, Plachetka U, Moeller M, Moormann C (2010) UV enhanced substrate conformal imprint lithography (UV-SCIL) technique for photonic crystals patterning in LED manufacturing. Microelectron Eng 87(5–8):963–967. doi:10.1016/j.mee.2009.11.134
Jia C-J, Schüth F (2011) Colloidal metal nanoparticles as a component of designed catalyst. Phys Chem Chem Phys 13(7):2457. doi:10.1039/c0cp02680h
Kelly JY, DeSimone JM (2008) Shape-specific, monodisperse nano-molding of protein particles. J Am Chem Soc 130(16):5438–5439. doi:10.1021/ja8014428
Kersey FR, Merkel TJ, Perry JL, Napier ME, DeSimone JM (2012) Effect of aspect ratio and deformability on nanoparticle extravasation through nanopores. Langmuir 28(23):8773–8781. doi:10.1021/la301279v
Khlebtsov NG, Dykman LA (2010) Optical properties and biomedical applications of plasmonic nanoparticles. J Quant Spectrosc Radiat Transf 111(1):1–35. doi:10.1016/j.jqsrt.2009.07.012
Landis S (2011) Nano-lithography. ISTE. Wiley, London
Low HY, Zhao W, Dumond JJ (2006) Combinatorial-mold imprint lithography: a versatile technique for fabrication of three-dimensional polymer structures. Appl Phys Lett 89(2):23109. doi:10.1063/1.2219148
Matsukawa D, Okamura H, Shirai M (2011) Reworkable dimethacrylates with low shrinkage and their application to UV nanoimprint lithography. J Mater Chem 21(28):10407. doi:10.1039/C0JM04386A
Mendes MJ, Hernández E, López E, García-Linares P, Ramiro I, Artacho I, Antolín E, Tobías I, Martí A, Luque A (2013) Self-organized colloidal quantum dots and metal nanoparticles for plasmon-enhanced intermediate-band solar cells. Nanotechnology 24(34):345402. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/24/34/345402
Menz W, Mohr J, Paul O (2001) Microsystem technology. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim
Merkel TJ, Herlihy KP, Nunes JK, Orgel RM, Rolland JP, DeSimone JM (2010) Scalable, shape-specific, top-down fabrication methods for the synthesis of engineered colloidal particles. Langmuir 26(16):13086–13096. doi:10.1021/la903890h
Merkel TJ, Jones SW, Herlihy KP, Kersey FR, Shields AR, Napier M, Luft JC, Wu H, Zamboni WC, Wang AZ, Bear JE, DeSimone JM (2011) Using mechanobiological mimicry of red blood cells to extend circulation times of hydrogel microparticles. Proc Natl Acad Sci 108(2):586–591. doi:10.1073/pnas.1010013108
Messow FJ, Welch C, Eifert A, Ang WC, Hoe NS, Kusserow T, Hillmer H (2014) Deep single step vertical ICP–RIE etching of ion beam sputter deposited SiO2/Si multilayer stacks. Microelectron Eng 113:70–73. doi:10.1016/j.mee.2013.07.018
Morton SW, Herlihy KP, Shopsowitz KE, Deng ZJ, Chu KS, Bowerman CJ, DeSimone JM, Hammond PT (2013) Scalable manufacture of built-to-order nanomedicine: spray-assisted layer-by-layer functionalization of PRINT nanoparticles. Adv Mater Weinheim 25(34):4707–4713. doi:10.1002/adma.201302025
Mueller SN, Tian S, DeSimone JM (2015) Rapid and persistent delivery of antigen by lymph node targeting PRINT nanoparticle vaccine carrier to promote humoral immunity. Mol Pharm 12(5):1356–1365. doi:10.1021/mp500589c
Park S-H, Yang D-Y, Lee K-S (2009) Two-photon stereolithography for realizing ultraprecise three-dimensional nano/microdevices. Laser Photonics Rev 3(1–2):1–11. doi:10.1002/lpor.200810027
Perry JL, Herlihy KP, Napier ME, DeSimone JM (2011) PRINT: a novel platform toward shape and size specific nanoparticle theranostics. Acc Chem Res 44(10):990–998. doi:10.1021/ar2000315
Petros RA, DeSimone JM (2010) Strategies in the design of nanoparticles for therapeutic applications. Nat Rev Drug Discov 9(8):615–627. doi:10.1038/nrd2591
Rolland JP, Maynor BW, Euliss LE, Exner AE, Denison GM, DeSimone JM (2005) Direct fabrication and harvesting of monodisperse, shape-specific nanobiomaterials. J Am Chem Soc 127(28):10096–10100. doi:10.1021/ja051977c
Rudzinski A, Barth U, Kahl M, Huhn B-A, Kopetz S, Rabe E, Neyer A (2007) Fabrication of 3-D PDMS nano-template for UV nano-imprint lithography and micro contact printing by means of grey scale electron beam lithography. In: Fourteenth international workshop on the physics of semiconductor devices. Wiley-Interscience; IEEE, [Piscataway, N.J.], pp 840–842
Schift H (2015) Nanoimprint lithography: 2D or not 2D? A review. Appl. Phys. A. doi: 10.1007/s00339-015-9106-3
Schleunitz A, Guzenko VA, Schander A, Vogler M, Schift H (2011) Selective profile transformation of electron-beam exposed multilevel resist structures based on a molecular weight dependent thermal reflow. J Vac Sci Technol B 29(6):6. doi:10.1116/1.3634013
Schmid G (2004) Nanoparticles: from theory to application. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim
Schmid G, Vogel V (2009) Nanomedicine. Nanotechnology, / G. Schmid … (ed.); Vol. 5. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim
Schmitt H, Duempelmann P, Fader R, Rommel M, Bauer AJ, Frey L, Brehm M, Kraft A (2012) Life time evaluation of PDMS stamps for UV-enhanced substrate conformal imprint lithography. Microelectron Eng 98:275–278. doi:10.1016/j.mee.2012.04.032
Schudy S, Smolarczyk MA, Hillmer H, Worapattrakul N, Pilger F (2011) Nano-Formgebungsstruktur (DE 102011054789 A1, WO 2013/060618 A1, EP 2771161)
Shields CW IV, Zhu S, Yang Y, Bharti B, Liu J, Yellen BB, Velev OD, López GP (2013) Field-directed assembly of patchy anisotropic microparticles with defined shape. Soft Matter 9(38):9219. doi:10.1039/C3SM51119G
Smolarczyk MA, Reuter S, Jablonka L, Hillmer H (2014) Implementation of a novel Self-Aligned NanoShaping (SANS) technology to fabricate 3D nanoparticles: presentation. In: 13th international conference on nanoimprint and nanoprint technology (NNT2014), p 24
Taniguchi J, Unno N (2010) Three dimensional nanoimprint lithography using inorganic electron beam resist. In: Wang M (ed) Lithography. InTech, pp 557–571
Thanh NTK, Green LAW (2010) Functionalisation of nanoparticles for biomedical applications. NanoToday 5(3):213–230. doi:10.1016/j.nantod.2010.05.003
Tsuda A, Gehr P (2015) Nanoparticles in the lung: environmental exposure and drug delivery. CRC Press; Taylor & Francis Group, Boca Raton
Verschuuren MA (2010) Substrate conformal imprint lithography for nanophotonics. Dissertation, Utrecht University
Wang X, Albrecht A, Mai HH, Woidt C, Meinl T, Hornung M, Bartels M, Hillmer H (2013) High resolution 3D NanoImprint technology: template fabrication, application in Fabry–Pérot-filter-array-based optical nanospectrometers. Microelectron Eng 110:44–51. doi:10.1016/j.mee.2013.04.038
Wei S, Wang Q, Zhu J, Sun L, Lin H, Guo Z (2011) Multifunctional composite core-shell nanoparticles. Nano 3(11):4474–4502. doi:10.1039/c1nr11000d
Wu W, Hu M, Ou FS, Li Z, Williams RS (2010) Cones fabricated by 3D nanoimprint lithography for highly sensitive surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Nanotechnology 21(25):255502. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/21/25/255502
Xu J, Wong DHC, Byrne JD, Chen K, Bowerman C, DeSimone JM (2013) Future of the particle replication in nonwetting templates (PRINT) technology. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 52(26):6580–6589. doi:10.1002/anie.201209145
Yang W, Peters JI, Williams RO (2008) Inhaled nanoparticles—a current review. Int J Pharm 356(1–2):239–247. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2008.02.011
Zhang H, Nunes JK, Gratton SEA, Herlihy KP, Pohlhaus PD, DeSimone JM (2009) Fabrication of multiphasic and regio-specifically functionalized PRINT® particles of controlled size and shape. New J Phys 11(7):75018. doi:10.1088/1367-2630/11/7/075018
Zhou W, Wang ZL (2011) Three-dimensional nanoarchitectures: designing next-generation devices. Springer, New York
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the technical assistance by Kerstin Fuchs, Florian Schnabel, Jens Krumpholz, Dietmar Gutermuth and Anita Dück. We also want to thank Moriz Beck-Broichsitter, Thomas Schmehl and Thomas Kissel of the University of Marburg for their inspiring discussions and material support in the case of fluorescent dyes and nanoimprint material. This work was supported by the “Zentrale Forschungsförderung” of the University of Kassel.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was funded by the “Zentrale Forschungsförderung” of the University of Kassel.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reuter, S., Smolarczyk, M.A., Istock, A. et al. Bending properties of two- and three-dimensional-shaped nanoparticles fabricated via substrate conformal imprint lithography. J Nanopart Res 19, 184 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-017-3886-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-017-3886-7