Abstract
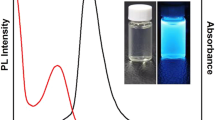
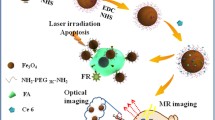
Both fluorescent and magnetic nanoprobes have great potential applications for diagnostics and therapy. In the present work, a folic acid-conjugated and silica-modified GdPO4:Tb3+ (GdPO4:Tb3+@SiO2-FA) dual nanoprobe was strategically designed and synthesized for the targeted dual-modality optical and magnetic resonance (MR) imaging via a facile aqueous method. Their structural, optical, and magnetic properties were determined using transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared (FTIR), ultraviolet-visible spectra (UV-Vis), photoluminescence (PL), and superconducting quantum interference device (SQUID). These results indicated that GdPO4:Tb3+@SiO2-FA were uniform monodisperse core-shell structured nanorods (NRs) with an average length of ~200 nm and an average width of ~25 nm. The paramagnetic property of the synthesized GdPO4:Tb3+@SiO2-FA NRs was confirmed with its linear hysteresis plot (M-H). In addition, the NRs displayed an obvious T1-weighted effect and thus it could potentially serve as a T1-positive contrast agent. The NRs emitted green lights due to the 5D4 → 7F5 transition of the Tb3+. The in vitro assays with NCI-H460 lung cancer cells and human embryonic kidney cell line 293T cells indicated that the GdPO4:Tb3+@SiO2-FA nanoprobe could specifically bind the cells bearing folate receptors (FR). The MTT assay of the NRs revealed that its cytotoxicity was very low. Further in vivo MRI experiments distinctively depict enhanced anatomical features in a xenograft tumor. These results suggest that the GdPO4:Tb3+@SiO2-FA NPs have excellent imaging and cell-targeting abilities for the folate receptor-targeted dual-modality optical and MR imaging and can be potentially used as the nanoprobe for bioimaging.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ao LJ, Wang B, Liu P, Huang L, Yue CX, Gao DY, Wu CL, Su W (2014) A folate-integrated magnetic polymer micelle for MRI and dual targeted drug delivery. Nanoscale 6:10710–10716
Bharali DJ, Lucey DW, Jayakumar H, Pudavar HE, Prasad PN (2005) Folate-receptor-mediated delivery of InP quantum dots for bioimaging using confocal and two-photon microscopy. J Am Chem Soc 127:11364–11371
Dong K, Ju EG, Liu JH, Han XL, Ren JS, Qu XG (2014) Ultrasmall biomolecule-anchored hybrid GdVO4 nanophosphors as a metabolizable multimodal bioimaging contrast agent. Nanoscale 6:12042–12049
Gao J, Gu H, Xu B (2009) Multifunctional magnetic nanoparticles: design, synthesis, and biomedical applications. Acc Chem Res 42:1097–1107
Han YH, Gai SL, Ma PA, Wang LZ, Zhang ML, Huang SH, Yang PP (2013) Highly uniform α-NaYF4:Yb/Er hollow microspheres and their application as drug carrier. Inorg Chem 52:9184–9191
Kim T, Momin E, Choi J, Yuan K, Zaidi H, Kim J, Park M, Lee N, McMahon MT, Quinones-Hinojosa A, Bulte JWM, Hyeon T, Gilad AA (2011) Mesoporous silica-coated hollow manganese oxide nanoparticles as positive T 1 contrast agents for labeling and MRI tracking of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. JACS 133:2955–2961
Laha D, Pramanik A, Chattopadhyay S, Sk D, Roy S, Pramanik P, Karmakar P (2015) Folic acid modified copper oxide nanoparticles for targeted delivery in in vitro and in vivo systems. RSC Adv 5:68169–68178
Lee H, Yu MK, Park S, Moon S, Min JJ, Jeong YY, Kang HW, Jon SY (2007) Thermally cross-linked superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis and application as a dual imaging probe for cancer in vivo. J Am Chem Soc 129:12739–12745
Li P, Song YH, Liu CG, Li XM, Zhou G, Fan YB (2014) Magnetic and fluorescent bifunctional chitosan microspheres embedding with fluorescent-labeling drug as a drug delivery system. Mater Lett 114:132–135
Lin BB, Yao XZ, Zhu YH, Shen JH, Yang XL, Jiang HL, Zhang XQ (2013) Multifunctional manganese-doped core–shell quantum dots for magnetic resonance and fluorescence imaging of cancer cells. New J Chem 37:3076–3083
Lin BB, Yao XZ, Zhu YH, Shen JH, Yang XL, Li CZ (2014) Multifunctional gadolinium-labeled silica-coated core/shell quantum dots for magnetic resonance and fluorescence imaging of cancer cells. RSC Adv 4:20641–20648
Liu J, Li ZZ, Yang XQ, Liu WS, Wang BD, Zhu YH, Mu KT, Zhu WZ (2015) A high-performance imaging probe with NIR luminescence and synergistically enhanced T1–T2 relaxivity for in vivo hepatic tumor targeting, multimodal imaging. Chem Commun 51:13369–13372
Lou L, Yu K, Zhang ZQ, Li B, Zhu JZ, Wang YT, Huang R, Zhu ZQ (2011) Functionalized magnetic-fluorescent hybrid nanoparticles for cell labelling. Nanoscal 3:2315–2323
Lu SZ, Zhang JH, Zhang JS, Zhao HF, Luo YS, Ren XG (2010) Remarkably enhanced photoluminescence of hexagonal GdPO4.nH2O: Eu with decreasing size. Nanotechnology 21:2431–2443
Ma JB, Huang P, He M, Pan LY, Zhou ZJ, Feng LL, Gao G, Cu DX (2012) Folic acid-conjugated LaF3:Yb,Tm@SiO2 nanoprobes for targeting dual-modality imaging of upconversion luminescence and X-ray computed tomography. J Phys Chem B 116:14062–14070
Ma ZY, Liu YP, Bai LY, An J, Zhang L, Xuan Y, Zhang XS, Zhao YD (2015) Folic acid-targeted magnetic Tb-doped CeF3 fluorescent nanoparticle as bimodal probe for cellular fluorescence and magnetic resonance imaging. Dalton Trans 44:16304–16312
Majeed S, Shivashankar SA (2014) Rapid, microwave-assisted synthesis of Gd2O3 and Eu:Gd2O3 nanocrystals: characterization, magnetic, optical and biological studies. J Mater Chem B 2:5585–5593
Ren WL, Tian G, Zhou LJ, Yin WY, Yan L, Jin S, Zu Y, Li SJ, Gu ZJ, Zhao YL (2012) Lanthanide ion-doped GdPO4 nanorods with dual-modal bio-optical and magnetic resonance imaging properties. Nanoscale 4:3754–3760
Rodriguez-Liviano S, Becerro AI, Alcantara D, Grazu V, Fuente JMDL, Ocana M (2013) Synthesis and properties of multifunctional tetragonal Eu:GdPO4, nanocubes for optical and magnetic resonance imaging applications. ChemInform 44:647–654
Singh HP, Mitra S, Sharma RK (2014) Surface modified silica nanoparticles for synchronous magnetic resonance imaging and drug delivery applications. RSC Adv 105:61028–61035
Xia A, Chen M, Gao Y, Wu DM, Feng W, Li FY (2012) Gd3+ complex-modified NaLuF4-based upconversion nanophosphors for trimodality imaging of NIR-to-NIR upconversion luminescence, X-ray computed tomography and magnetic resonance. Biomaterials 33:5394–5405
Xu H, Cheng L, Wang C, Ma X, Li Y, Liu Z (2011b) Polymer encapsulated upconversion nanoparticle/iron oxide nanocomposites for multimodal imaging and magnetic targeted drug delivery. Biomaterials 32:9364–9373
Xu ZH, Yu C, Li CX, Ma XF, Huang SS, Kang XJ, Shang MM, Yang DM, Dai YL, Lin J (2011a) Urchin-like GdPO4 and GdPO4:Eu3+ hollow spheres—hydrothermal synthesis, luminescence and drug-delivery properties. J Mater Chem 21:3686–3694
Yang YG (2013) Synthesis and luminescent properties of LaPO4:Eu3+ microspheres. Mater Sci Eng B 178:807–810
Yin F, Zhang BT, Zeng SW, Lin GM, Tian JL, Yang CB, Wang K, Xu GX, Yong KT (2015) Folic acid-conjugated organically modified silica nanoparticles for enhanced targeted delivery in cancer cells and tumor in vivo. J Mater Chem B 3:6081–6093
Yu J, Hao R, Sheng FG, Xu LL, Li GJ, Hou YL (2012) Hollow manganese phosphate nanoparticles as smart multifunctional probes for cancer cell targeted magnetic resonance imaging and drug delivery. Nano Res 5:679–694
Zhang L, Qiao SZ, Jin YG, Chen ZG, Gu HC, Lu GQ (2008) Magnetic hollow spheres of periodic mesoporous organosilica and Fe3O4 nanocrystals: fabrication and structure control. Adv Mater 20:805–810
Zhang LH, Yin ML, You HP, Yang M, Song YH, Huang YJ (2011) Mutifuntional GdPO4:Eu3+ hollow spheres: synthesis and magnetic and luminescent properties. Inorg Chem 50:10608–10613
Zhou CH, Wu H, Huang CS, Wang ML, Jia NQ (2014) Facile synthesis of single-phase mesoporous Gd2O3:Eu nanorods and their application for drug delivery and multimodal imaging. Part Part Syst Charact 31:675–684
Zhou J, Sun Y, Du XX, Xiong LQ, Hu H, Li FY (2010) Dual-modality in vivo, imaging using rare-earth nanocrystals with near-infrared to near-infrared (NIR-to-NIR) upconversion luminescence and magnetic resonance properties. Biomaterials 31:3287–3295
Zhu HE, Tao J, Wang WH, Zhou YJ, Li PH, Li Z, Yan K, Wu SL, Yeung KWK, Xu ZS (2012) Magnetic, fluorescent, and thermo-responsive Fe3O4/rare earth incorporated poly(St-NIPAM) core–shell colloidal nanoparticles in multimodal optical/magnetic resonance imaging probes. Biomaterials 34:2296–2306
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Science and Technology Education Department of Jiangxi Province (Grant No. KJLD13018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All the animal treatments were conducted in conformity with institutional guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals in Jiangxi Normal University.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, X., Zhang, X. & Wu, Y. Folic acid-conjugated GdPO4:Tb3+@SiO2 Nanoprobe for folate receptor-targeted optical and magnetic resonance bi-modal imaging. J Nanopart Res 18, 334 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-016-3649-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-016-3649-x