Abstract
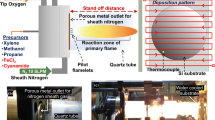
Titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles containing iron, silicon, and vanadium are synthesized using multiple diffusion flames. The growth of carbon-coated (C–TiO2), carbon-coated with iron oxide (Fe/C–TiO2), silica-coated (Si–TiO2), and vanadium-doped (V–TiO2) TiO2 nanoparticles is demonstrated using a single-step process. Hydrogen, oxygen, and argon are utilized to establish the flame, with titanium tetraisopropoxide (TTIP) as the precursor for TiO2. For the growth of Fe/C–TiO2 nanoparticles, TTIP is mixed with xylene and ferrocene. While for the growth of Si–TiO2 and V–TiO2, TTIP is mixed with hexamethyldisiloxane (HMDSO) and vanadium (V) oxytriisopropoxide, respectively. The synthesized nanoparticles are characterized using high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) with energy-filtered TEM for elemental mapping (of Si, C, O, and Ti), X-ray diffraction (XRD), Raman spectroscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), nitrogen adsorption BET surface area analysis, and thermogravimetric analysis. Anatase is the dominant phase for the C–TiO2, Fe/C–TiO2, and Si–TiO2 nanoparticles, whereas rutile is the dominant phase for the V–TiO2 nanoparticles. For C–TiO2 and Fe/C–TiO2, the nanoparticles are coated with about 3-5-nm thickness of carbon. The iron-based TiO2 nanoparticles significantly improve the catalytic oxidation of carbon, where complete oxidation of carbon occurs at a temperature of 470 °C (with iron) compared to 610 °C (without iron). Enhanced catalytic oxidation properties are also observed for model soot particles, Printex-U, when mixed with Fe/C-TiO2. With regards to Si–TiO2 nanoparticles, a uniform coating of 3 to 8 nm of silicon dioxide is observed around the TiO2 particles. This coating mainly occurs due to variance in the chemical reaction rates of the precursors. Finally, with regards to V–TiO2, vanadium is doped within the TiO2 nanoparticles as visualized by HRTEM and XPS further confirms the formation of V4+ and V5+ oxidation states.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akurati KK, Vital A, Klotz UE, Bommer B, Graule T, Winterer M (2006) Synthesis of non-aggregated titania nanoparticles in atmospheric pressure diffusion flames. Powder Technol 165:73–82
Andrews R, Jacques D, Rao AM, Derbyshire F, Qian D, Fan X, Dickey EC, Chen J (1999) Continuous production of aligned carbon nanotubes: a step closer to commercial realization. Chem Phys Lett 303:467–474
Anjum DH, Memon NK, Chung SH (2013) Investigating the growth mechanism and optical properties of carbon-coated titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Mater Lett 108:134–138
Aronniemi M, Sainio J, Lahtinen J (2005) Chemical state quantification of iron and chromium oxides using XPS: the effect of the background subtraction method. Surf Sci 578:108–123
Barreca D, Battiston GA, Berto D, Gerbasi R, Tondello E (2001) Chemical vapor deposited Fe2O3 thin films analyzed by XPS. Surf Sci Spectra 8:240–245
Belver C, Bellod R, Stewart SJ, Requejo FG, Fernández-García M (2006) Nitrogen-containing TiO2 photocatalysts: part 2. Photocatalytic behavior under sunlight excitation. Appl Catal B 65:309–314
Bhattacharyya K, Varma S, Tripathi A, Bharadwaj S, Tyagi A (2008) Effect of vanadia doping and its oxidation state on the photocatalytic activity of TiO2 for gas-phase oxidation of ethene. J Phys Chem C 112:19102–19112
Biesinger MC, Lau LW, Gerson AR, Smart RSC (2010) Resolving surface chemical states in XPS analysis of first row transition metals, oxides and hydroxides: Sc, Ti, V, Cu and Zn. Appl Surf Sci 257:887–898
Chen HX, Dobbins RA (2000) Crystallogenesis of particles formed in hydrocarbon combustion. Combust Sci Technol 159:109–128
Chen H, Nanayakkara CE, Grassian VH (2012) Titanium dioxide photocatalysis in atmospheric chemistry. Chem Rev 112:5919–5948
Choi J, Park H, Hoffmann MR (2009) Effects of single metal-ion doping on the visible-light photoreactivity of TiO2. J Phys Chem C 114:783–792
Deng L, Wang S, Liu D, Zhu B, Huang W, Wu S, Zhang S (2009) Synthesis, characterization of Fe-doped TiO2 nanotubes with high photocatalytic activity. Catal Lett 129:513–518
Egerton RF (2011) Electron energy-loss spectroscopy in the electron microscope, 3rd edn. Springer, New York
Fujii T, De Groot F, Sawatzky G, Voogt F, Hibma T, Okada K (1999) In situ XPS analysis of various iron oxide films grown by NO2-assisted molecular-beam epitaxy. Phys Rev B 59:3195
Fujishima A (1972) Electrochemical photolysis of water at a semiconductor electrode. Nature 238:37–38
Grabowska E, Reszczyńska J, Zaleska A (2012) Mechanism of phenol photodegradation in the presence of pure and modified-TiO2: a review. Water Res 46:5453–5471
Grätzel M (1981) Artificial photosynthesis: water cleavage into hydrogen and oxygen by visible light. Acc Chem Res 14:376–384
Grätzel M (2001) Photoelectrochemical cells. Nature 414:338–344
Hung C-H, Katz JL (1992) Formation of mixed oxide powders in flames: part I. TiO2 − SiO2. J Mater Res 7:1861–1869
Inamdar SN, Haram SK (2006) Synthesis and characterization of uncapped α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles prepared by flame pyrolysis of ferrocene in ethanol. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 6:2155–2158
Ingo G, Dire S, Babonneau F (1993) XPS studies of SiO2–TiO2 powders prepared by sol–gel process. Appl Surf Sci 70:230–234
Jensen DS, Kanyal SS, Madaan N, Vail MA, Dadson AE, Engelhard MH, Linford MR (2013) Silicon (100)/SiO2 by XPS. Surf Sci Spectra 20:36–42
Kammler HK, Pratsinis SE (2003) Carbon-coated titania nanostructured particles: continuous, one-step flame-synthesis. J Mater Res 18:2670–2676
Kryukova GN, Zenkovets GA, Mestl G, Schlögl R (2003) Structural study of titanium doped vanadia and vanadium doped titania catalysts. React Kinet Catal Lett 80:161–169
Lars S, Andersson T (1990) An XPS study of dispersion and valence state of TiO2 supported vanadium oxide catalysts. Catal Lett 7:351–358
Lee MC, Choi W (2002) Solid phase photocatalytic reaction on the soot/TiO2 interface: the role of migrating OH radicals. J Phys Chem B 106:11818–11822
Legutko P, Stelmachowski P, Trębala M, Sojka Z, Kotarba A (2013) Role of electronic factor in soot oxidation process over tunnelled and layered potassium iron oxide catalysts. Top Catal 56:489–492
Li W, Ni C, Lin H, Huang C, Shah SI (2004) Size dependence of thermal stability of TiO2 nanoparticles. J Appl Phys 96:6663–6668
Lindan PJD, Harrison NM, Holender JM, Gillan MJ (1996) First-principles molecular dynamics simulation of water dissociation on TiO2 (110). Chem Phys Lett 261:246–252
Linsebigler AL, Lu G, Yates JT Jr (1995) Photocatalysis on TiO2 surfaces: principles, mechanisms, and selected results. Chem Rev 95:735–758
Matsumoto Y et al (2001) Room-temperature ferromagnetism in transparent transition metal-doped titanium dioxide. Science 291:854–856
Memon NK et al (2011) Flame synthesis of graphene films in open environments. Carbon 49:5064–5070
Memon NK, Anjum DH, Chung SH (2013) Multiple-diffusion flame synthesis of pure anatase and carbon-coated titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Combust Flame 160:1848–1856
Mendialdua J, Casanova R, Barbaux Y (1995) XPS studies of V2O5, V6O13, VO2 and V2O3. J Electron Spectrosc Relat Phenom 71:249–261
Mills A, Le Hunte S (1997) An overview of semiconductor photocatalysis. J Photochem Photobiol, A 108:1–35
Neeft J, van Pruissen OP, Makkee M, Moulijn JA (1997) Catalysts for the oxidation of soot from diesel exhaust gases II. Contact between soot and catalyst under practical conditions. Appl Catal B 12:21–31
Nie X, Zhuo S, Maeng G, Sohlberg K (2009) Doping of TiO2 polymorphs for altered optical and photocatalytic properties. Int J Photoenergy. doi:10.1155/2009/294042
Oi-Uchisawa J, Wang S, Nanba T, Ohi A, Obuchi A (2003) Improvement of Pt catalyst for soot oxidation using mixed oxide as a support. Appl Catal B 44:207–215
Pan JM, Maschhoff B, Diebold U, Madey T (1992) Interaction of water, oxygen, and hydrogen with TiO2 (110) surfaces having different defect densities. J Vac Sci Technol, A 10:2470–2476
Perez-Maqueda L, Criado J, Sanchez-Jimenez P (2006) Combined kinetic analysis of solid-state reactions: a powerful tool for the simultaneous determination of kinetic parameters and the kinetic model without previous assumptions on the reaction mechanism. J Phys Chem A 110:12456–12462
Powell QH, Fotou GP, Kodas TT, Anderson BM (1997) Synthesis of alumina-and alumina/silica-coated titania particles in an aerosol flow reactor. Chem Mater 9:685–693
Ren Y, Zhang Y, Li S, Law CK (2014) Doping mechanism of Vanadia/Titania nanoparticles in flame synthesis by a novel optical spectroscopy technique. Proc Combust Instit 35:2283–2289
Rodriguez-Torres C, Cabrera A, Errico L, Adan C, Requejo F, Weissmann M, Stewart S (2008) Local structure and magnetic behaviour of Fe-doped TiO2 anatase nanoparticles: experiments and calculations. J Phys 20:135210
Schnitzler MC, Oliveira MM, Ugarte D, Zarbin AJ (2003) One-step route to iron oxide-filled carbon nanotubes and bucky-onions based on the pyrolysis of organometallic precursors. Chem Phys Lett 381:541–548
Shangguan W, Teraoka Y, Kagawa S (1997) Kinetics of Soot–O2, Soot–NO and Soot–O2–NO reactions over spinel-type CuFe2O4 catalyst. Appl Catal B 12:237–247
Song J, Wang J, Boehman AL (2006) The role of fuel-borne catalyst in diesel particulate oxidation behavior. Combust Flame 146:73–84
Stark WJ, Wegner K, Pratsinis SE, Baiker A (2001) Flame aerosol synthesis of vanadia-titania Nanoparticles: structural and catalytic properties in the selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3. J Catal 197:182–191
Strobel R, Baiker A, Pratsinis SE (2006) Aerosol flame synthesis of catalysts. Adv Powder Technol 17:457–480
Teleki A, Pratsinis S, Wegner K, Jossen R, Krumeich F (2005) Flame-coating of titania particles with silica. J Mater Res 20:1336–1347
Teleki A, Suter M, Kidambi PR, Ergeneman O, Krumeich F, Nelson BJ, Pratsinis SE (2009) Hermetically coated superparamagnetic Fe2O3 particles with SiO2 nanofilms. Chem Mater 21:2094–2100
Teoh WY, Amal R, Mädler L (2010) Flame spray pyrolysis: an enabling technology for nanoparticles design and fabrication. Nanoscale 2:1324–1347
Teraoka Y, Nakano K, Shangguan W, Kagawa S (1996) Simultaneous catalytic removal of nitrogen oxides and diesel soot particulate over perovskite-related oxides. Catal Today 27:107–113
Thompson TL, Yates JT (2006) Surface science studies of the photoactivation of TiO2 new photochemical processes. Chem Rev 106:4428–4453
Tian B, Li C, Gu F, Jiang H, Hu Y, Zhang J (2009) Flame sprayed V-doped TiO2 nanoparticles with enhanced photocatalytic activity under visible light irradiation. Chem Eng J 151:220–227
Tiefenthaler K, Lukosz W (1989) Sensitivity of grating couplers as integrated-optical chemical sensors. JOSA B 6:209–220
Tryba B, Toyoda M, Morawski A, Inagaki M (2005) Modification of carbon-coated TiO2 by iron to increase adsorptivity and photoactivity for phenol. Chemosphere 60:477–484
Tryba B, Morawski AW, Inagaki M, Toyoda M (2006) The kinetics of phenol decomposition under UV irradiation with and without H2O2 on TiO2, Fe-TiO2 and Fe–C–TiO2 photocatalysts. Appl Catal B 63:215–221
Vyazovkin S (2000) Kinetic concepts of thermally stimulated reactions in solids: a view from a historical perspective. Int Rev Phys Chem 19:45–60
Wang H, Liu J, Zhao Z, Wei Y, Xu C (2012) Comparative study of nanometric Co–Mn- and Fe-based perovskite-type complex oxide catalysts for the simultaneous elimination of soot and NOx from diesel engine exhaust. Catal Today 184:288–300
Williams A, McCormick RL, Hayes RR, Ireland J, Fang HL (2006) Effect of biodiesel blends on diesel particulate filter performance, SAE technical paper
Xiong Y, Pratsinis SE (1993) Formation of agglomerate particles by coagulation and sintering—Part I. A two-dimensional solution of the population balance equation. J Aerosol Sci 24:283–300
Xu J, Liu J, Zhao Z, Zheng J, Zhang G, Duan A, Jiang G (2010) Three-dimensionally ordered macroporous LaCoxFe1-xO3 perovskite-type complex oxide catalysts for diesel soot combustion. Catal Today 153:136–142
Xu P, Zeng GM, Huang DL, Feng CL, Hu S, Zhao MH, Lai C, Wei Z, Huang C, Xie GX (2012) Use of iron oxide nanomaterials in wastewater treatment: a review. Sci Total Environ 424:1–10
Yoshida M, Prasad PN (1996) Sol-gel-processed SiO2/TiO2/poly (vinylpyrrolidone) composite materials for optical waveguides. Chem Mater 8:235–241
Zhang Y-H, Chan CK, Porter JF, Guo W (1998) Micro-Raman spectroscopic characterization of nanosized TiO2 powders prepared by vapor hydrolysis. J Mater Res 13:2602–2609
Zhang Z, Wei B, Ajayan P (2001) Self-assembled patterns of iron oxide nanoparticles by hydrothermal chemical-vapor deposition. App Phys Lett 79:4207–4209
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Competitive Research Funding from King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST). We are grateful to Drs. Hua Tan and Omar El Tall at the Analytical Core Lab at KAUST for their help in performing the BET nitrogen adsorption experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ismail, M.A., Memon, N.K., Hedhili, M.N. et al. Synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles containing Fe, Si, and V using multiple diffusion flames and catalytic oxidation capability of carbon-coated nanoparticles. J Nanopart Res 18, 22 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-016-3332-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-016-3332-2