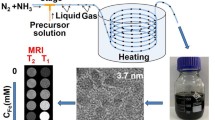
Abstract
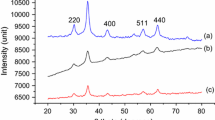
An aqueous dispersion of Fe3O4/salicylic acid magnetic nanoparticles (SaMNPs) was synthesized by a modified Massart method, characterized by Inductively Coupled Plasma–Optic Emission Spectrometry (ICP-OES), High-Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy (HRTEM) and Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) methods, and tested on the chick chorioallantoic membrane (CAM) model to evaluate biocompatibility, biodistribution, intravascular time persistence, and ability to be magnetically target driven in order to block the blood supply into a tumor xenograft. ICP-OES, DLS, and HRTEM SaMNPs sample analyses showed a 0.356 mg/mL Fe concentration, a good stability in water (average Zeta potential of 39.3 mV), a hydrodynamic diameter around 52 nm and a core diameter in the 7–15 nm range for the Fe3O4 nanoparticles. In vivo CAM assay showed that SaMNPs were biocompatible with the chick embryo, were fixed almost completely by the liver, had no embolic potential, and a threshold-dose-dependent intravascular magnetic targeting time. Study on the CAM tumor model showed that SaMNPs could be used for long-term magnetically mediated nanoblocking of the capillary networks and 70-µm smaller arterioles.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ankamwar B, Lai TC, Huang JH, Liu RS, Hsiao M, Chen CH et al (2010) Biocompatibility of Fe(3)O(4) nanoparticles evaluated by in vitro cytotoxicity assays using normal, glia and breast cancer cells. Nanotechnology 21:75102. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/21/7/075102
Barry SE (2008) Challenges in the development of magnetic particles for therapeutic applications. Int J Hyperther 24:451–466
Bartneck M, Keul HA, Zwadlo-Klarwasser G, Jr Groll (2009) Phagocytosis independent extracellular nanoparticle clearance by human immune cells. Nano Lett 10:59–63
Baxter GJ, Lawrence JR, Graham AB, Wiles D, Paterson JR (2002) Identification and determination of salicylic acid and salicyluric acid in urine of people not taking salicylate drugs. Ann Clin Biochem 39:50–55
Buteică AS, Meşină M, Mîndrilă B, Mîndrilă I (2014) In vivo models combination for B16 murine melanoma study. Rom J Funct Clin, Macro–Microsc Anat Anthropol 13:143–147
Chen D, Tang Q, Li X, Zhou X, Zang J, Xue W et al (2012) Biocompatibility of magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles and their cytotoxic effect on MCF-7 cells. Int J Nanomed 7:4973–4982. doi:10.2147/IJN.s35140
Chouly C, Pouliquen D, Lucet I, Jeune J, Jallet P (1996) Development of superparamagnetic nanoparticles for MRI: effect of particle size, charge and surface nature on biodistribution. J Microencapsul 13:245–255
Deryugina EI, Quigley JP (2008) Chick embryo chorioallantoic membrane model systems to study and visualize human tumor cell metastasis. Histochem Cell Biol 130:1119–1130
Gallo J, Long NJ, Aboagye EO (2013) Magnetic nanoparticles as contrast agents in the diagnosis and treatment of cancer. Chem Soc Rev 42:7816–7833
Gupta AK, Naregalkar RR, Vaidya VD, Gupta M (2007) Recent advances on surface engineering of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles and their biomedical applications. Nanomed (Lond) 2:23–39
Kobayashi T (2011) Cancer hyperthermia using magnetic nanoparticles. Biotechnol J 6:1342–1347. doi:10.1002/biot.201100045
Kue CS, Tan KY, Lam ML, Lee HB (2015) Chick embryo chorioallantoic membrane (CAM): an alternative predictive model in acute toxicological studies for anti-cancer drugs. Exp Anim 64:129–138. doi:10.1538/expanim.14-0059
Lee EA, Yim H, Heo J, Kim H, Jung G, Hwang NS (2014) Application of magnetic nanoparticle for controlled tissue assembly and tissue engineering. Arch Pharm Res 37:120–128
Liu J, Flores GA, Sheng R (2001) In-vitro investigation of blood embolization in cancer treatment using magnetorheological fluids. J Magn Magn Mater 225:209–217
Mihaiescu DE, Buteică AS, Neamţu J, Istrati D, Mîndrilă I (2013) Fe3O4/salicylic acid nanoparticles behavior on chick CAM vasculature. J Nanopart Res 15:1–10. doi:10.1007/s11051-031-1857-1
Pathi S, Jutooru I, Chadalapaka G, Nair V, Lee SO, Safe S (2012) Aspirin inhibits colon cancer cell and tumor growth and downregulates specificity protein (Sp) transcription factors. PLoS ONE. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0048208
Peng XH, Qian X, Mao H, Wang AY (2008) Targeted magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for tumor imaging and therapy. Int J Nanomed 3:311–321
Pisanic TR II, Blackwell JD, Shubayev VI, Fiñones RR, Jin S (2007) Nanotoxicity of iron oxide nanoparticle internalization in growing neurons. Biomaterials 28:2572–2581
Ribatti D (2014) The chick embryo chorioallantoic membrane as a model for tumor biology. Exp Cell Res 328:314–324
Satchell SC, Braet F (2009) Glomerular endothelial cell fenestrations: an integral component of the glomerular filtration barrier. Am J Physiol Ren Psysiol 296:947–956
Schlachter EK, Widmer HR, Bregy A, Lönnfors-Weitzel T, Vajtai I, Corazza N et al (2011) Metabolic pathway and distribution of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: in vivo study. Int J Nanomed 6:1793–1800. doi:10.2147/IJN.S23638
Shubayev VI, Pisanic TR II, Jin S (2009) Magnetic nanoparticles for theragnostics. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 61:467–477
Singh SP, Rahman M, Murty U, Mahboob M, Grover P (2013) Comparative study of genotoxicity and tissue distribution of nano and micron sized iron oxide in rats after acute oral treatment. Toxicol Appl Pharm 266:56–66
Smolkova IS, Kazantseva NE, Makoveckaya KN, Smolka P, Saha P, Granov AM (2015) Maghemite based silicone composite for arterial embolization hyperthermia. Mater Sci Eng, C 48:632–641. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2014.12.046
Vargas A, Zeisser-Labouèbe M, Lange N, Gurny R, Delie F (2007) The chick embryo and its chorioallantoic membrane (CAM) for the in vivo evaluation of drug delivery systems. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 59:1162–1176
Varna M, Ratajczak P, Ferreira I, Leboeuf C, Bousquet G, Janin A (2012) In vivo distribution of inorganic nanoparticles in preclinical models. J Biomater Nanobiotechnol 3:269–279. doi:10.4236/jbnb.2012.322033
Villanueva A, Canete M, Roca AG, Calero M, Veintemillas-Verdaguer S, Serna CJ et al (2009) The influence of surface functionalization on the enhanced internalization of magnetic nanoparticles in cancer cells. Nanotechnology 20:115103
Xie J, Lee S, Chen X (2010) Nanoparticle-based theranostic agents. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 62:1064–1079
Ying E, Hwang HM (2010) In vitro evaluation of the cytotoxicity of iron oxide nanoparticles with different coatings and different sizes in A3 human T lymphocytes. Sci Total Environ 408:4475–4481
Acknowledgments
The participation of Buteică Sandra Alice was supported by the Project “Excellence program for multidisciplinary doctoral and postdoctoral research in chronic diseases,” Grant No. POSDRU/159/1.5/S/133377, partially supported by the Sectoral Operational Programme Human Resources Development 2007–2013, financed from the European Social Fund. The participation of Mihaiescu DE on this work was supported by the Sectoral Operational Programme Human Resources Development 2007-2013 of the Ministry of European Founds through the Financial Agreement POSDRU/159/1.5/S/132397.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mîndrilă, I., Buteică, S.A., Mihaiescu, D.E. et al. Fe3O4/salicylic acid nanoparticles versatility in magnetic mediated vascular nanoblockage. J Nanopart Res 18, 10 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-015-3318-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-015-3318-5