Abstract
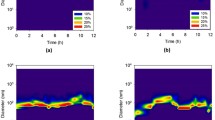
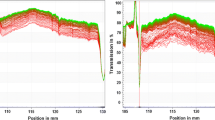
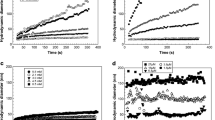
The predictable significant increase in manufacture and use of engineered nanoparticles (ENPs) will cause their inevitable release into environment, and the potential harmful effects of ENPs have been confirmed. As representative ENPs, sedimentation behavior of nano-titanium dioxide (n-TiO2) should be better understood to control its environmental risk. In this study, an experimental methodology was established to set the sampling area and sampling time of n-TiO2 sedimentation. In addition, we defined a quasi-stable state and a precise index, i.e., sedimentation efficiency (SE) at this state, to describe the n-TiO2 sedimentation behavior. Both alternative concentration determination and conventional size measurement were applied to evaluate the sedimentation behavior of n-TiO2 with fulvic acid. Results showed that the sedimentation behavior described by SE was more precise and in disagreement with those predicted by particle size. Moreover, sedimentation experiments with salicylic acid (SA), under an electric field and different water temperatures or with sulfosalicylic acid under light irradiation were also performed. When the total organic carbon concentration of SA, the voltage of working electrodes, and water temperature increased, or the wavelength of light source decreased, the SE of n-TiO2 increased and n-TiO2 showed a tendency to settle in water. These findings might be important for deepening the understanding of n-TiO2 environmental behavior and exploring sedimentation behavior of other ENPs.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Badawy A, Luxton T, Silva R, Scheckel K, Suidan M, Tolaymat T (2010) Impact of environmental conditions (pH, IS, and electrolyte type) on the surface charge and aggregation of silver nanoparticles suspensions. Environ Sci Technol 44(4):1260–1266
Bello Lamo M, Williams P, Reece P, Lumpkin G, Sheppard L (2014) Study of gamma irradiation effect on commercial TiO2 photocatalyst. Appl Radiat Isot 89:25–29
Bhatkhande D, Pangarkar V, Beenackers A (2002) Photocatalytic degradation for environmental applications: a review. J Chem Technol Biot 77(1):102–116
Block I, Scheffold F (2010) Modulated 3D cross-correlation light scattering: improving turbid sample characterization. Rev Sci Instrum 81(12):123107
Braun J, Baidins A, Marganski R (1992) TiO2 pigment technology: a review. Prog Org Coat 20(2):105–138
Bushell G, Yan Y, Woodfield D, Raper J, Amal R (2002) On techniques for the measurement of the mass fractal dimension of aggregates. Adv Colloid Interfac 95(1):1–50
Chen K, Elimelech M (2007) Influence of humic acid on the aggregation kinetics of fullerene (C60) nanoparticles in monovalent and divalent electrolyte solutions. J Colloid Interface Sci 309(1):126–134
Chen X, Mao S (2009) Titanium dioxide nanomaterials: synthesis, properties, modifications, and applications. Chem Rev 107(7):2891–2959
Chowdhury I, Cwiertny D, Walker S (2012) Combined factors influencing the aggregation and deposition of nano-TiO2 in the presence of humic acid and bacteria. Environ Sci Technol 46(13):6668–6676
Colvin VL (2003) The potential environmental impact of engineered nanomaterials. Nat Biotechnol 21(10):1166–1170
Deonarine A, Lau B, Aiken G, Ryan J, Hsu-Kim H (2011) Effects of humic substances on precipitation and aggregation of zinc sulfide nanoparticles. Environ Sci Technol 45(8):3217–3223
Domingos R, Tufenkji N, Wilkinson K (2009) Aggregation of titanium dioxide nanoparticles: role of a fulvic acid. Environ Sci Technol 43(5):1282–1286
French R, Jacobson A, Kim B, Isley S, Penn R, Baveye P (2009) Influence of IS, pH, and cation valence on aggregation kinetics of titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Environ Sci Technol 43(5):1354–1359
Gaya U, Abdullah A (2008) Heterogeneous photocatalytic degradation of organic contaminants over titanium dioxide: a review of fundamentals, progress and problems. J Photoch Photobio C 9(1):1–12
Gómez-Merino A, Rubio-Hernández F, Velázquez-Navarro J, Aguiar J, Jiménez-Agredanoa C (2015) Study of the aggregation state of anatase water nanofluids using rheological and DLS methods. Ceram Int 40:14045–14050
Grillo R, Rosa A, Fraceto L (2015) Engineered nanoparticles and organic matter: a review of the state-of-the-art. Chemosphere 119:608–619
Guo Y, Cheng C, Wang J, Wang Z, Jin X, Li K, Kang P, Gao J (2011) Detection of reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated by TiO2(R), TiO2(R/A) and TiO2(A) under ultrasonic and solar light irradiation and application in degradation of organic dyes. J Hazard Mater 192:786–793
He G, Liu H, Chen R, Wang C (2013) Transport behavior of engineered nanosized photocatalytic materials in water. J Nanomater. doi:10.1155/2013/856387
Johnson R, Johnson G, Nurmi J, Tratnyek P (2009) Natural organic matter enhanced mobility of nano zerovalent iron. Environ Sci Technol 43(14):5455–5460
Keller A, Wang H, Zhou D, Lenihan H, Cherr G, Cardinale B, Miller R, Ji Z (2010) Stability and aggregation of metal oxide nanoparticles in natural aqueous matrices. Environ Sci Technol 44(6):1962–1967
Klaine S, Alvarez P, Batley G, Fernandes T, Handy R, Lyon D, Mahendra S, McLaughlin M, Lead J (2008) Nanomaterials in the environment: behavior, fate, bioavailability, and effects. Environ Toxicol Chem 27(9):1825–1851
Klimkevicius V, Graule T, Makuska R (2015) Effect of structure of cationic comb copolymers on their adsorption and stabilization of titania nanoparticles. Langmuir 31:2074–2083
Kralchevska R, Milanova M, Tsvetkov M, Dimitrov D, Todorovsky D (2012) Influence of gamma-irradiation on the photocatalytic activity of Degussa P25 TiO2. J Mater Sci 47:4936–4945
Lead J, Wilkinson K (2006) Aquatic colloids and nanoparticles: current knowledge and future trends. Environ Chem 3(3):159–171
Li S, Zheng F, Cai S, Liang W, Li Y (2013) A visible light assisted photocatalytic system for determination of chemical oxygen demand using 5-sulfosalicylic acid in situ surface modified titanium dioxide. Sens Acutat B 188:280–285
Liu X, Chen G, Su C (2011) Effects of material properties on sedimentation and aggregation of titanium dioxide nanoparticles of anatase and rutile in the aqueous phase. J Colloid Interface Sci 363:84–91
Liu W, Sun W, Borthwick A, Ni J (2013) Comparison on aggregation and sedimentation of titanium dioxide, titanate nanotubes and titanate nanotubes-TiO2: influence of pH, ionic strength and natural organic matter. Colloid Surf A 434:319–328
Loosli F, Le Coustumer P, Stoll S (2015a) Effect of electrolyte valency, alginate concentration and pH on engineered TiO2 nanoparticle stability in aqueous solution. Sci Total Environ 535:28–34
Loosli F, Vitorazi L, Berret J, Stoll S (2015b) Towards a better understanding on agglomeration mechanisms and thermodynamic properties of TiO2 nanoparticles interacting with natural organic matter. Water Res 80:139–148
Mitrano D, Motellier S, Clavaguera S, Nowack B (2015) Review of nanomaterial aging and transformations through the life cycle of nano-enhanced products. Environ Int 77:132–147
Navarro E, Baun A, Behra R, Hartmann NB, Filser J, Miao AJ, Quigg A, Santschi PH, Sigg L (2008) Environmental behavior and ecotoxicity of engineered nanoparticles to algae, plants, and fungi. Ecotoxicology 17(5):372–386
Nel A, Xia T, Mädler L, Li N (2006) Toxic potential of materials at the nanolevel. Science 311(5761):622–627
Nowack B, Bucheli TD (2007) Occurrence, behavior and effects of nanoparticles in the environment. Environ Pollut 150(1):5–22
Othman S, Rashid S, Ghazi T, Abdullah N (2012) Dispersion and stabilization of photocatalytic TiO2 nanoparticles in aqueous suspension for coatings applications. J Nanomater. doi:10.1155/2012/718214
Ottofuelling S, von der Kammer F, Hofmann T (2011) Commercial titanium dioxide nanoparticles in both natural and synthetic water: comprehensive multidimensional testing and prediction of aggregation behavior. Environ Sci Technol 45(23):10045–10052
Pettibone J, Cwiertny D, Scherer M, Grassian V (2008) Adsorption of organic acids on TiO2 nanoparticles: effects of pH, nanoparticle size, and nanoparticle aggregation. Langmuir 24(13):6659–6667
Pfaff G, Reynders P (1999) Angle-dependent optical effects deriving from submicron structures of films and pigments. Chem Rev 99(7):1963–1982
Phenrat T, Saleh N, Sirk K, Tilton R, Lowry G (2007) Aggregation and sedimentation of aqueous nanoscale zerovalent iron dispersions. Environ Sci Technol 41(1):284–290
Schätzel K (1991) Suppression of multiple scattering by photon cross-correlation techniques. J Mod Optic 38(9):1849–1865
Schaumann G, Philippe A, Bundschuh M, Metreveli G, Klitzke S, Rakcheev D, Grün A, Kumahor S, Kühn M, Baumann T, Lang F, Manz W, Schulz R, Vogel H (2015) Understanding the fate and biological effects of Ag- and TiO2-nanoparticles in the environment: the quest for advanced analytics and interdisciplinary concepts. Sci Total Environ 535:3–19
Shen M, Yin Y, Booth A, Liu J (2015) Effects of molecular weight-dependent physicochemical heterogeneity of natural organic matter on the aggregation of fullerene nanoparticles in mono- and di-valent electrolyte solutions. Water Res 71:11–20
Tian X, Wu F, Xing B, Lin D (2010) Fate and transport of engineered nanomaterials in the environment. J Environ Qual 39(6):1896–1908
Topuz E, Traber J, Sigg L, Talinli I (2015) Agglomeration of Ag and TiO2 nanoparticles in surface and wastewater: role of calcium ions and of organic carbon fractions. Environ Pollut 204:313–323
Urban C, Schurtenberger P (1998) Characterization of turbid colloidal suspensions using light scattering techniques combined with cross-correlation methods. J Colloid Interface Sci 207(1):150–158
Wang C, Zhang X, Liu H, Li X, Li W, Xu H (2009) Reaction kinetics of photocatalytic degradation of sulfosalicylic acid using TiO2 microspheres. J Hazard Mater 163:1101–1106
Weir A, Westerhoff P, Fabricius L, Hristovski K, von Goetz N (2012) Titanium dioxide nanoparticles in food and personal care products. Environ Sci Technol 46(4):2242–2250
Wiesner M, Lowry G, Alvarez P, Dionysiou D, Biswas P (2006) Assessing the risks of manufactured nanomaterials. Environ Sci Technol 40(14):4336–4345
Yang Y, Kelkar A, Zhu X, Bai G, Ng H, Corti D, Franses E (2015) Effect of sodium dodecylsulfate monomers and micelles on the stability of aqueous dispersions of titanium dioxide pigment nanoparticles against agglomeration and sedimentation. J Colloid Interface Sci 450:434–445
Yu J, Jaroniec M, Yu H, Fan W (2012) Synthesis, characterization, properties, and applications of nanosized photocatalytic materials. J Nanomater. doi:10.1155/2012/783686
Zhang Y, Chen Y, Westerhoff P, Hristovski K, Crittenden J (2008) Stability of commercial metal oxide nanoparticles in water. Water Res 42(8–9):2204–2212
Zhang Y, Chen Y, Westerhoff P, Crittenden J (2009) Impact of natural organic matter and divalent cations on the stability of aqueous nanoparticles. Water Res 43(17):4249–4257
Zhu M, Wang H, Keller A, Wang T, Li F (2014) The effect of humic acid on the aggregation of titanium dioxide nanoparticles under different pH and ionic strengths. Sci Total Environ 487:375–380
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21067004, 51378494, and 51378316), Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Committee Program (JCYJ20130331151242230), and One Hundred Talents Program, CAS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11051_2015_3250_MOESM1_ESM.doc
Supplementary material 1. Additional information contains the characterization of n-TiO2, the analysis of FA, the detection method of n-TiO2 mass concentration, the detection method of SSA, the schematic of n-TiO2 sedimentation experiments under an electric field and light irradiation as well as the statistical analysis and data of n-TiO2 sedimentation experiments (DOC 5158 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, G., Chen, R., Lu, S. et al. Alternative assessment of nano-TiO2 sedimentation under different conditions based on sedimentation efficiency at quasi-stable state. J Nanopart Res 17, 454 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-015-3250-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-015-3250-8