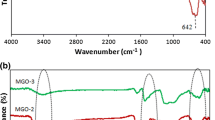
Abstract
Nanocatalysts are frequently connected to magnetic nanoparticles. These composites are easy to be retrieved from the reaction system under a magnetic field because of their magnetic properties. Magnetic separation is particularly promising in industry since it can solve many issues present in filtration, centrifugation, or gravitation separation. Herein, a facile method to prepare bismuth and Fe3O4 nanoparticles loaded on reduced graphene oxide magnetic hybrids (Bi-Fe3O4@RGO) using soluble starch as a dispersant is demonstrated. The magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles were synthesized by the co-precipitation of Fe2+ and Fe3+ ions, and Bi nanoparticles were fabricated by the redox reactions between sodium borohydride and ammonium bismuth citrate in the presence of soluble starch. Transmission electron microscopy images demonstrate that the average diameter of the Fe3O4 nanoparticles is about 5 nm and the diameters of Bi nanoparticles range from 10 to 20 nm. The magnetic Bi-Fe3O4@RGO hybrids exhibit high catalytic activity in the reduction of 4-nitrophenol (4-NP) to 4-aminophenol (4-AP) by NaBH4 with a first-order rate constant (K) of 0.00808 s−1 and is magnetically recyclable for at least five cycles. This strategy provides an efficient and recyclable catalyst for the use in environmental protection applications.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balandin AA, Ghosh S, Bao W et al (2008) Superior thermal conductivity of single-layer graphene. Nano Lett 8:902–907
Berger P, Adelman NB, Beckman KJ et al (1999) Preparation and properties of an aqueous ferrofluid. J Chem Educ 76:943–948
Bhimarasetti G, Sunkara MK (2005) Synthesis of sub-20-nm-sized bismuth 1-D structures using gallium-bismuth systems. J Phys Chem B 109:16219–16222
Bodaghi H, Mostofi Y, Oromiehie A, Ghanbarzadeh B, Hagh ZG (2015) Synthesis of clay–TiO2 nanocomposite thin films with barrier and photocatalytic properties for food packaging application. J Appl Polym Sci 132:41764–41771
Cai HD, Li KG, Shen MW et al (2012) Facile assembly of Fe3O4@Au nanocomposite particles for dual mode magnetic resonance and computed tomography imaging applications. J Mater Chem 22:15110–15120
Carotenuto G, Hison CL, Capezzuto F et al (2009) Synthesis and thermoelectric characterisation of bismuth nanoparticles. J Nanopart Res 11:1729–1738
Chang YC, Chen DH (2009) Catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol by magnetically recoverable Au nanocatalyst. J Hazard Mater 165:664–669
Chen JL, Cheng G, Li ZG, Miao FJ, Cui XQ, Zheng WT (2012a) Ultrafine Au nanodots on graphene oxide for catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol. NANO 8:13500341–13500348
Chen S, Zhang HY, Wu LY et al (2012b) Controllable synthesis of supported Cu-M (M = Pt, Pd, Ru, Rh) bimetal nanocatalysts and their catalytic performances. J Mater Chem 22:9117–9122
Chen Q, Li KG, Wen SH et al (2013) Targeted CT/MR dual mode imaging of tumors using multifunctional dendrimer-entrapped gold nanoparticles. Biomaterials 34:5200–5209
Deshmukh SP, Dhokale RK, Yadav HM et al (2013) Titania–supported silver nanoparticles: an efficient and reusable catalyst for reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Appl Surf Sci 273:676–683
Gong JL, Wang B, Zeng GM et al (2009) Removal of cationic dyes from aqueous solution using magnetic multi-wall carbon nanotube nanocomposite as adsorbent. J Hazard Mater 164:1517–1522
Heremans JP, Thrush CM, Morelli DT, Wu MC (2002) Thermoelectric power of bismuth nanocomposites. Phys Rev Lett 88:216801–216804
Hossain M, Su M (2012) Nanoparticle location and material-dependent dose enhancement in X-ray radiation therapy. J Phys Chem C 116:23047–23052
Hu R, Dai SY, Shao DD et al (2015) Efficient removal of phenol and aniline from aqueous solutions using graphene oxide/polypyrrole composites. J Mol Liq 203:80–89
Hummers W, Offeman R (1958) Preparation of graphitic oxide. J Am Chem Soc 80:1339
Kidwai M, Bansal V, Saxena A, Aerry S, Mozumdar S (2006) Cu-Nanoparticles: efficient catalysts for the oxidative cyclization of Schiffs’ bases. Tetrahedron Lett 47:8049–8053
Lee SJ, Jung JJ, Kim MA, Kim YR, Park JK (2012) Synthesis of highly stable graphite-encapsulated metal (Fe Co, and Ni) nanoparticles. J Mater Sci 47:8112–8117
Lin G, Tan DZ, Luo FF et al (2011) Linear and nonlinear optical properties of glasses doped with Bi nanoparticles. J Non-Cryst Solids 357:2312–2315
Lu WS, Shen YH, Xie AJ, Zhang WQ (2010) Green synthesis and characterization of superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles. J Magn Magn Mater 322:1828–1833
Ma DC, Zhao JZ, Zhao Y et al (2012) Synthesis of bismuth nanoparticles and self-assembled nanobelts by a simple aqueous route in basic solution. Colloids Surf A 395:276–283
Masazumi T, Kenichi K, Atsushi S, Kenichi S (2012) Volcano-curves for dehydrogenation of 2-propanol and hydrogenation of nitrobenzene by SiO2-supported metal nanoparticles catalysts as described in terms of a d-band model. ACS Catal 2:1904–1909
Mohamed MM, Al-Sharif MS (2012) One pot synthesis of silver nanoparticles supported on TiO2 using hybrid polymers as template and its efficient catalysis for the reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Mater Chem Phys 136:528–537
Nemanashi M, Meijboom R (2013) Synthesis and characterization of Cu, Ag and Au dendrimer-encapsulated nanoparticles and their application in the reduction of 4-nitrophenol to 4-aminophenol. J Colloid Interface Sci 389:260–262
Novoselov KS, Geim AK, Morozov SV et al (2005) Two-dimensional gas of massless Dirac fermions in grapheme. Nature 438:197–200
Park S, Kang K, Han WQ, Vogt T (2005) Generation and photocatalytic activities of Bi@Bi2O3 microspheres. J Alloy Comp 400:88–91
Stankovich S, Dikin DA, Dommett GHB et al (2006) Graphene-based composite materials. Nature 442:282–286
Tahir M, Amin NS (2015) Indium-doped TiO2 nanoparticles for photocatalytic CO2 reductionwith H2O vapors to CH4. Appl Catal B 162:98–109
Udayabhaskar R, Mangalaraja RV, Manikandan D, Arjunan V, Karthikeyan B (2012) Room temperature synthesis and optical studies on Ag and Au mixed nanocomposite polyvinylpyrrolidone polymer films. Spectrochim Acta Part A 99:69–73
Vadivel S, Kamalakannan VP, Keerthi Balasubramanian N (2014) D-Pencillamine assisted microwave synthesis of Bi2S3 microflowers/RGO composites for photocatalytic degradation—A facile green approach. Ceram Int 40:14051–14060
Wang FD, Buhro WE (2010) An easy shortcut synthesis of size-controlled bismuth nanoparticles and their use in the SLS growth of high-quality colloidal cadmium selenide quantum wires. Small 6:573–581
Wang J, Song DQ, Zhang H et al (2013) Studies of Fe3O4/Ag/Au composites for immunoassay based on surface plasmon resonance biosensor. Colloids Surf B 102:165–170
Wu JL, Shen XP, Jiang L, Wang K, Chen KM (2010) Solvothermal synthesis and characterization of sandwich-like graphene/ZnO nanocomposites. Appl Surf Sci 256:2826–2830
Wunder S, Polzer F, Lu Y, Mei Y, Ballauff M (2010) Kinetic analysis of catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol by metallic nanoparticles immobilized in spherical polyelectrolyte brushes. J Phys Chem C 114:8814–8821
Xia FL, Xu XY, Li XC, Zhang L, Wang W, Liu Y, Gao JP (2014) Preparation of bismuth nanoparticles in aqueous solution and its catalytic performance for the reduction of 4–nitrophenol. Ind Eng Chem Res 53:10576–10582
Xing HB, Su LB, Jiang XB et al (2014) Mid-infrared luminescence of Bi–Te series single crystals. Opt Mater 36:1982–1985
Xu R, Bi HP, He GY, Zhu JW, Chen HQ (2014a) Synthesis of Cu-Fe3O4@graphene composite: a magnetically separable and efficient catalyst for the reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Mater Res Bull 57:190–196
Xu XY, Wu T, Xia FL et al (2014b) Redox reaction between graphene oxide and In powder to prepare In2O3/reduced graphene oxide hybrids for supercapacitors. J Power Sources 266:282–290
Yang FY, Liu K, Hong K, Reich DH, Searson PC, Chien CL (1999) Large magnetoresistance of electrodeposited single-crystal bismuth thin films. Science 284:1335–13357
Yang GW, Gao GY, Wang C, Xu CL, Li HL (2008) Controllable deposition of Ag nanoparticles on carbon nanotubes as a catalyst for hydrazine oxidation. Carbon 46:747–752
Ye L, Li ZH (2014) Rapid microwave-assisted syntheses of reduced grapheme oxide (RGO)/ZnIn2S4 microspheres as superior noble-metal-free photocatalyst for hydrogen volution sunder visible light. Appl Catal B 160(161):552–557
Zhang Y, Tan YW, Stormer HL, Kim P (2005) Experimental observation of the quantum Hall effect and Berry’s phase in grapheme. Nature 438:201–204
Zhang PP, Zhang XX, Sun HX et al (2009) Pd–CNT-catalyzed ligandless and additive-free heterogeneous Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling of arylbromides. Tetrahedron Lett 50:4455–4458
Zhang S, Shao YY, Liao HG et al (2011) Graphene decorated with Pt Au alloy nanoparticles: facile synthesis and promising application for formic acid oxidation. Chem Mater 23:1079–1081
Zhang YL, Yan WW, Sun ZM, Li XC, Gao JP (2014) Fabrication of magnetically recyclable Ag/Cu@Fe3O4 nanoparticles with excellent catalytic activity for p-nitrophenol reduction. Rsc Advances 72:38040-38047Zhang ZM, Zhao CJ, Min SD, Qian XZ (2014) A facile one-step route to RGO/Ni3S2 for high-performance super capacitors. Electrochim Acta 144:100–110
Zhao ZW, Liu J, Cui FY, Feng H, Zhang LL (2012) One pot synthesis of tunable Fe3O4–MnO2 core–shell nanoplates and their applications for water purification. J Mater Chem 22:9052–9057
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51202158, 21074089, and 21276181).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Xia, F., Li, X. et al. Fabrication of Bi-Fe3O4@RGO hybrids and their catalytic performance for the reduction of 4-nitrophenol. J Nanopart Res 17, 436 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-015-3230-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-015-3230-z