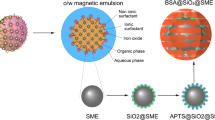
Abstract
In the present work, biocompatible superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles coated by mesoporous silica were used as drug nanocarriers for doxorubicin (Dox; an anticancer drug) delivery. In biological media, the interaction of protein corona layer with the surface of nanoparticles is inevitable. For this reason, we studied the effect of protein corona on drug release from magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MMSNs) in human plasma medium. Besides, we used hydrophilic and biocompatible polymer, polyethylene glycol (PEG), to decrease protein corona effects. The results showed the increased Dox release from PEGylated MMSNs compared with bare MMSNs. This result indicated that the coating of PEG reduced the wrapping of the protein corona around the nanoparticles. This phenomenon caused increase in Dox release.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal P, Hall JB, McLeland CB, Dobrovolskaia MA, McNeil SE (2009) Nanoparticle interaction with plasma proteins as it relates to particle biodistribution, biocompatibility and therapeutic efficacy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 61:428–437
Angelos S, Choi E, Vögtle F, De Cola L, Zink JI (2007) Photo-driven expulsion of molecules from mesostructured silica nanoparticles. J Phys Chem C 111:6589–6592
Baeza A, Guisasola E, Ruiz-Hernández E, Vallet-Regí M (2012) Magnetically triggered multi-drug release by hybrid mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Chem Mater 24:517–524
Behzadi S, Serpooshan V, Sakhtianchi R, Müller B, Landfester K, Crespy D, Mahmoudi M (2014) Protein corona change the drug release profile of nanocarriers: the ignored factor at the nanobio interface. Colloids Surf B 23:143–149
Berry CC, Wells S, Charles S, Curtis ASG (2003) Dextran and albumin derivatised iron oxide nanoparticles: influence on fibroblasts in vitro. Biomaterials 24:4551–4557
Chen F, Bu W, Chen Y, Fan Y, He Q, Zhu M, Liu X, Zhou L, Zhang S, Peng W, Shi J (2009) A Sub-50-nm monosized superparamagnetic Fe3O4@SiO2T2-weighted MRI contrast agent: highly reproducible synthesis of uniform single-loaded core–shell nanostructures. Chem–An Asian J 4:1809–1816
Chen Y, Chen H, Zeng D, Tian Y, Chen F, Feng J, Shi J (2010) Core/shell structured hollow mesoporous nanocapsules: a potential platform for simultaneous cell imaging and anticancer drug delivery. ACS Nano 4:6001–6013
Chen X, Gambhir SS, Cheon J (2011) Theranostic Nanomedicine. Acc Chem Res 44:841
de Almeida MPS, Caiado KL, Sartoratto PPC, Cintra e Silva DO, Pereira AR, Morais PC (2010) Preparation and size-modulation of silica-coated maghemite nanoparticles. J Alloy Compd 500:149–152
Dobson J (2005) Gene therapy progress and prospects: magnetic nanoparticle-based gene delivery. Gene Ther 13:283–287
Du L, Liao S, Khatib HA, Stoddart JF, Zink JI (2009) Controlled-access hollow mechanized silica nanocontainers. J Am Chem Soc 131:15136–15142
Garcia MP, Miranda Parca R, Braun Chaves S, Paulino Silva L, Djalma Santos A, Guerrero Marques Lacava Z, César Morais P, Azevedo RB (2005) Morphological analysis of mouse lungs after treatment with magnetite-based magnetic fluid stabilized with DMSA. J Magn Magn Mater 293:277–282
Gref R, Minamitake Y, Peracchia MT, Trubetskoy V, Torchilin V, Langer R (1994) Biodegradable long-circulating polymeric nanospheres. Science 263:1600–1603
Gref R, Luck M, Quellec P, Marchand M, Dellacherie E, Harnisch S, Blunk T, Muller RH (2000) ‘Stealth’ corona–core nanoparticles surface modified by polyethylene glycol (PEG): influences of the corona (PEG chain length and surface density) and of the core composition on phagocytic uptake and plasma protein adsorption. Colloids Surf B 18:301–313
Guedes MHA, Sadeghiani N, Peixoto DLG, Coelho JP, Barbosa LS, Azevedo RB, Kückelhaus S, Da Silva MDF, Morais PC, Lacava ZGM (2005) Effects of AC magnetic field and carboxymethyldextran-coated magnetite nanoparticles on mice peritoneal cells. J Magn Magn Mater 293:283–286
Gupta A, Curtis A (2004a) Surface modified superparamagnetic nanoparticles for drug delivery: interaction studies with human fibroblasts in culture. J Mater Sci Mater Med 15:493–496
Gupta AK, Curtis ASG (2004b) Lactoferrin and ceruloplasmin derivatized superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for targeting cell surface receptors. Biomaterials 25:3029–3040
Gupta AK, Gupta M (2005) Synthesis and surface engineering of iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Biomaterials 26:3995–4021
Harris JM, Martin NE, Modi M (2001) Pegylation: a novel process for modifying pharmacokinetics. Clin Pharmacokinet 40:539–551
Jokerst JV, Gambhir SS (2011) Molecular imaging with theranostic nanoparticles. Acc Chem Res 44:1050–1060
Kim J, Lee JE, Lee J, Yu JH, Kim BC, An K, Hwang Y, Shin C-H, Park J-G, Kim J, Hyeon T (2005) Magnetic fluorescent delivery vehicle using uniform mesoporous silica spheres embedded with monodisperse magnetic and semiconductor nanocrystals. J Am Chem Soc 128:688–689
Kim J, Kim HS, Lee N, Kim T, Kim H, Yu T, Song IC, Moon WK, Hyeon T (2008) Multifunctional uniform nanoparticles composed of a magnetite nanocrystal core and a mesoporous silica shell for magnetic resonance and fluorescence imaging and for drug delivery. Angew Chem Int Ed 47:8438–8441
Krotz F, Wit CD, Sohn H-Y, Zahler S, Gloe T, Pohl U, Plank C (2003) Magnetofection[mdash] A highly efficient tool for antisense oligonucleotide delivery in vitro and in vivo. Mol Ther 7:700–710
Lammers T, Aime S, Hennink WE, Storm G, Kiessling F (2011) Theranostic nanomedicine. Acc Chem Res 44:1029–1038
Lee JE, Lee N, Kim T, Kim J, Hyeon T (2011) Multifunctional mesoporous silica nanocomposite nanoparticles for theranostic applications. Acc Chem Res 44:893–902
Lele BS, Kulkarni MG (1998) Single step room temperature oxidation of poly(ethylene glycol) to poly(oxyethylene)-dicarboxylic acid. J Appl Polym Sci 70:883–890
Leung KCF, Nguyen TD, Stoddart JF, Zink JI (2006) Supramolecular nanovalves controlled by proton abstraction and competitive binding. Chem Mater 18:5919–5928
Ling Y, Wei K, Luo Y, Gao X, Zhong S (2011) Dual docetaxel/superparamagnetic iron oxide loaded nanoparticles for both targeting magnetic resonance imaging and cancer therapy. Biomaterials 32:7139–7150
Liong M, Lu J, Kovochich M, Xia T, Ruehm SG, Nel AE, Tamanoi F, Zink JI (2008) Multifunctional inorganic nanoparticles for imaging,targeting, and drug delivery. ACS Nano 2:889–896
Lu J, Liong M, Zink JI, Tamanoi F (2007) Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a delivery system for hydrophobic anticancer drugs. Small 3:1341–1346
Mahmoudi M, Simchi A, Imani M, Milani AS, Stroeve P (2008) Optimal design and characterization of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles coated with polyvinyl alcohol for targeted delivery and imaging. J Phys Chem B 112:14470–14481
Mahmoudi M, Shokrgozar MA, Simchi A, Imani M, Milani AS, Stroeve P, Vali H, Hafeli UO, Bonakdar S (2009a) Multiphysics flow modeling and in vitro toxicity of iron oxide nanoparticles coated with poly(vinyl alcohol). J Phys Chem C 113:2322–2331
Mahmoudi M, Simchi A, Imani M, Häfeli UO (2009b) Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles with rigid cross-linked polyethylene glycol fumarate coating for application in imaging and drug delivery. J Phys Chem C 113:8124–8131
Mahmoudi M, Hosseinkhani H, Hosseinkhani M, Boutry S, Simchi A, Journeay WS, Subramani K, Laurent S (2010a) Magnetic resonance imaging tracking of stem cells in vivo using iron oxide nanoparticles as a tool for the advancement of clinical regenerative medicine. Chem Rev 111:253–280
Mahmoudi M, Simchi A, Imani M, Stroeve P, Sohrabi A (2010b) Templated growth of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles by temperature programming in the presence of poly(vinyl alcohol). Thin Solid Films 518:4281–4289
Mahmoudi M, Sant S, Wang B, Laurent S, Sen T (2011a) Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs): development, surface modification and applications in chemotherapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 63:24–46
Mahmoudi M, Sant S, Wang B, Laurent S, Sen T (2011b) Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs): development, surface modification and applications in chemotherapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 63:24–46
Mahmoudi M, Abdelmonem AM, Behzadi S, Clement JH, Dutz S, Ejtehadi MR, Hartmann R, Kantner K, Linne U, Maffre P, Metzler S, Moghadam MK, Pfeiffer C, Rezaei M, Ruiz-Lozano P, Serpooshan V, Shokrgozar MA, Nienhaus GU, Parak WJ (2013a) Temperature: the “ignored” factor at the nanobio interface. ACS Nano 7:6555–6562
Mahmoudi M, Lohse SE, Murphy CJ, Fathizadeh A, Montazeri A, Suslick KS (2013b) Variation of protein corona composition of gold nanoparticles following plasmonic heating. Nano Lett 14:6–12
Mirshafiee V, Mahmoudi M, Lou K, Cheng J, Kraft ML (2013) Protein corona significantly reduces active targeting yield. Chem Comm 49:2557–2559
Moghimi SM, Hunter AC, Murray JC (2001) Long-circulating and target-specific nanoparticles: theory to practice. Pharmacol Rev 53:283–318
Nguyen TD, Tseng H-R, Celestre PC, Flood AH, Liu Y, Stoddart JF, Zink JI (2005) A reversible molecular valve. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:10029–10034
Nguyen TD, Leung KCF, Liong M, Pentecost CD, Stoddart JF, Zink JI (2006) Construction of a pH-Driven supramolecular nanovalve. Org Lett 8:3363–3366
Nguyen TD, Leung KCF, Liong M, Liu Y, Stoddart JF, Zink JI (2007) Versatile supramolecular nanovalves reconfigured for light activation. Adv Funct Mater 17:2101–2110
Niu D, Ma Z, Li Y, Shi J (2010) Synthesis of core—shell structured dual-mesoporous silica spheres with tunable pore size and controllable shell thickness. J Am Chem Soc 132:15144–15147
Owens DE, Peppas NA (2006) Opsonization, biodistribution, and pharmacokinetics of polymeric nanoparticles. Int J Pharm 307:93–102
Paciotti GF, Myer L, Weinreich D, Goia D, Pavel N, McLaughlin RE, Tamarkin L (2004) Colloidal gold: a novel nanoparticle vector for tumor directed drug delivery. Drug Deliv. 11:169–183
Park J, An K, Hwang Y, Park J-G, Noh H-J, Kim J-Y, Park J-H, Hwang N-M, Hyeon T (2004) Ultra-large-scale syntheses of monodisperse nanocrystals. Nat Mater 3:891–895
Peracchia MT, Fattal E, Desmaele D, Besnard M, Noel JP, Gomis JM, Appel M, Portilho FA, Estevanato LLC, Miranda-Vilela AL, Almeida-Santos MFM, de Oliveira-Cavalcanti CE, Lacava BM, Simioni AR, Tedesco AC, Morais PC, Lacava ZGM (2011) Investigation of a magnetohyperthermia system efficacy. J Appl Phys 109:07B307
Prokopowicz M, Przyjazny AJ (2007) Synthesis of sol-gel mesoporous silica materials providing a slow release of doxorubicin. Microencapsulation 24:694
Rosenholm JM, Meinander A, Peuhu E, Niemi R, Eriksson JE, Sahlgren C, Lindén M (2008) Targeting of porous hybrid silica nanoparticles to cancer cells. ACS Nano 3:197–206
Rosenholm JM, Peuhu E, Eriksson JE, Sahlgren C, Lindén M (2009) Targeted intracellular delivery of hydrophobic agents using mesoporous hybrid silica nanoparticles as carrier systems. Nano Lett 9:3308–3311
Salvati A, Pitek AS, Monopoli MP, Prapainop K, Bombelli FB, Hristov DR, Kelly PM, Aberg C, Mahon E, Dawson KA (2013) Transferrin-functionalized nanoparticles lose their targeting capabilities when a biomolecule corona adsorbs on the surface. Nat Nano 8:137–143
Sartoratto PPC, Caiado KL, Pedroza RC, da Silva SW, Morais PC (2007) The thermal stability of maghemite-silica nanocomposites: an investigation using X-ray diffraction and Raman spectroscopy. J Alloy Compd 434–435:650–654
Shen S, Gu T, Mao D, Xiao X, Yuan P, Yu M, Xia L, Ji Q, Meng L, Song W, Yu C, Lu G (2011) Synthesis of nonspherical mesoporous silica ellipsoids with tunable aspect ratios for magnetic assisted assembly and gene delivery. Chem Mater 24:230–235
Singh N, Karambelkar A, Gu L, Lin K, Miller JS, Chen CS, Sailor MJ, Bhatia SN (2011) Bioresponsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles for triggered drug release. J Am Chem Soc 133:19582–19585
Slowing II, Vivero-Escoto JL, Wu C-W, Lin VSY (2011) Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as controlled release drug delivery and gene transfection carriers. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 60:1278–1288
Stein A, Melde BJ, Schroden RC (2011) Hybrid inorganic-organic mesoporous silicates—nanoscopic reactors coming of age. Adv Mater 12:1403–1419
Taylor KML, Kim JS, Rieter WJ, An H, Lin W, Lin W (2008) Mesoporous silica nanospheres as highly efficient MRI contrast agents. J Am Chem Soc 130:2154–2155
Thomas CR, Ferris DP, Lee J-H, Choi E, Cho MH, Kim ES, Stoddart JF, Shin J-S, Cheon J, Zink JI (2010) Noninvasive remote-controlled release of drug molecules in vitro using magnetic actuation of mechanized nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 132:10623–10625
Vallet-Regí M, Balas F, Arcos D (2007) Mesoporous materials for drug delivery. Angew Chem Int Ed 46:7548–7558
Xenariou S, Griesenbach U, Ferrari S, Dean P, Scheule RK, Cheng SH, Geddes DM, Plank C, Alton EWFW (2006) Using magnetic forces to enhance non-viral gene transfer to airway epithelium in vivo. Gene Ther 13:1545–1552
Xie J, Liu G, Eden HS, Ai H, Chen X (2011) Surface-engineered magnetic nanoparticle platforms for cancer imaging and therapy. Acc Chem Res 44:883–892
Yoo D, Lee J-H, Shin T-H, Cheon J (2011) Theranostic magnetic nanoparticles. Acc Chem Res 44:863–874
Zhao Y-L, Stoddart JF (2009) Azobenzene-based light-responsive hydrogel system. Langmuir 25:8442–8446
Zhao Y-L, Li Z, Kabehie S, Botros YY, Stoddart JF, Zink JI (2010) pH-operated nanopistons on the surfaces of mesoporous silica nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 132:13016–13025
Zhu C-L, Lu C-H, Song X-Y, Yang H-H, Wang X-R (2011) Bioresponsive controlled release using mesoporous silica nanoparticles capped with aptamer-based molecular gate. J Am Chem Soc 133:1278–1281
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pourjavadi, A., Tehrani, Z.M. & Mahmoudi, N. The effect of protein corona on doxorubicin release from the magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles with polyethylene glycol coating. J Nanopart Res 17, 197 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-015-3008-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-015-3008-3