Abstract
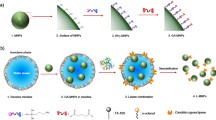
We present a new approach for the fabrication of magnetic thermoresponsive polymer microcapsules with mobile magnetic spherical cores. The microcontainers form fried-egg-like structures with a polymer shell layer of 50 nm due to the existence of hollow cavities. The microcontainers undergo a temperature-induced volume phase transition upon changing the temperature and present an impressive magnetic response. The magnetic saturation of these smart microcontainers (42 emu/g) is high enough to meet most requirements of bioapplications. To further investigate the potential application of these smart microcontainers in biotechnology, Candida rugosa lipase was selected for the enzyme immobilization process. The immobilized lipase exhibited excellent thermal stability and reusability in comparison with the free enzyme. The adsorption/release of the lipase from the microcontainers can be controlled by the environmental temperature and magnetic force, thus, offering new potential applications such as in controlled drug delivery, bioseparation, and catalysis.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bae Y, Fukushima S, Harada A, Kataoka K (2003) Design of environment-sensitive supramolecular assemblies for intracellular drug delivery: polymeric micelles that are responsive to intracellular pH change. Angew Chem Int Ed 42(38):4640–4643
Bilalis P, Chatzipavlidis A, Tziveleka LA, Boukos N, Kordas G (2012a) Nanodesigned magnetic polymer containers for dual stimuli actuated drug controlled release and magnetic hyperthermia mediation. J Mater Chem 22(27):13451–13454
Bilalis P, Efthimiadou EK, Chatzipavlidis A, Boukos N, Kordas GC (2012b) Multi-responsive polymeric microcontainers for potential biomedical applications: synthesis and functionality evaluation. Polym Int 61(6):888–894
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72(1):248–254
Carregal-Romero S, Buurma NJ, Pérez-Juste J, Liz-Marzán LM, Hervés P (2010) Catalysis by Au@ pNIPAM nanocomposites: effect of the cross-linking density. Chem Mater 22(10):3051–3059
Chang B, Sha X, Guo J, Jiao YF, Wang CC, Yang WL (2011) Thermo and pH dual responsive, polymer shell coated, magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles for controlled drug release. J Mater Chem 21(25):9239–9247
Chen JP, Su DR (2001) Latex particles with thermo-flocculation and magnetic properties for immobilization of α-chymotrypsin. Biotechnol Prog 17(2):369–375
Chen LB, Zhang F, Wang CC (2009) Rational synthesis of magnetic thermosensitive microcontainers as targeting drug carriers. Small 5(5):621–628
Chen J, Liu M, Chen C, Gong HH, Gao CM (2011) Synthesis and characterization of silica nanoparticles with well-defined thermoresponsive PNIPAM via a combination of RAFT and click chemistry. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 3(8):3215–3223
Deng YH, Yang WL, Wang CC, Fu SK (2003) A novel approach for preparation of thermoresponsive polymer magnetic microspheres with core-shell structure. Adv Mater 15(20):1729–1732
Deng H, Li X, Peng Q, Wang X, Chen JP, Li YD (2005) Monodisperse magnetic single-crystal ferrite microspheres. Angew Chem 117(18):2842–2845
Dubbert J, Honold T, Pedersen JS, Radulescu A, Drechsler M, Karg M, Richtering W (2014) How hollow are thermoresponsive hollow nanogels? Macromolecules 47:8700–8708
Gao H, Yang W, Min K, Zha LS, Wang CC, Fu SK (2005) Thermosensitive poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) nanocapsules with controlled permeability. Polymer 46(4):1087–1093
Hou C, Zhu H, Wu DM, Li YJ, Hou K, Jiang Y, Li YF (2014) Immobilized lipase on macroporous polystyrene modified by PAMAM-dendrimer and their enzymatic hydrolysis. Process Biochem 49:244–249
Khosroshahi ME, Ghazanfari L (2012) Synthesis and functionalization of SiO2 coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles with amine groups based on self-assembly. Mater Sci Eng, C 32(5):1043–1049
Lei L, Liu X, Li YF, Cui YJ, Yang Y, Qin GR (2011) Study on synthesis of poly (GMA)-grafted Fe3O4/SiOX magnetic nanoparticles using atom transfer radical polymerization and their application for lipase immobilization. Mater Chem Phys 125:866–871
Li P, Zhu AM, Liu QL, Zhang QG (2008) Fe3O4/poly (N-isopropylacrylamide)/chitosan composite microspheres with multiresponsive properties. Ind Eng Chem Res 47(20):7700–7706
Li Q, Zhang L, Bai L, Zhang ZB, Zhu J, Zhou NC, Cheng ZP, Zhu XL (2011) Multistimuli-responsive hybrid nanoparticles with magnetic core and thermoresponsive fluorescence-labeled shell via surface-initiated RAFT polymerization. Soft Matter 7(15):6958–6966
Liu X, Lei L, Li YF, Zhu H, Cui YJ, Hu HY (2011) Preparation of carriers based on magnetic nanoparticles grafted polymer and immobilization for lipase. Biochem Eng J 56(3):142–149
Luo B, Song XJ, Zhang F, Xia A, Yang WL, Hu JH, Wang CC (2009) Multi-functional thermosensitive composite microspheres with high magnetic susceptibility based on magnetite colloidal nanoparticle clusters. Langmuir 26(3):1674–1679
Qin L, He XW, Yuan X, Li WY, Zhang YK (2011) Molecularly imprinted beads with double thermosensitive gates for selective recognition of proteins. Anal Bioanal Chem 399(10):3375–3385
Qu L, Shi G (2004) Hollow microstructures of polypyrrole doped by poly (styrene sulfonic acid). J Polym Sci, Part A 42(13):3170–3177
Shamim N, Hong L, Hidajat K, Uddin MS (2007) Thermosensitive polymer coated nanomagnetic particles for separation of bio-molecules. Sep Purif Technol 53(2):164–170
Shchukin DG, Möhwald H (2005) Urea photosynthesis inside polyelectrolyte capsules: effect of confined media. Langmuir 21(12):5582–5587
Stöber W, Fink A, Bohn E (1968) Controlled growth of monodisperse silica spheres in the micron size range. J Colloid Interface Sci 26(1):62–69
Tong W, Song X, Gao C (2012) Layer-by-layer assembly of microcapsules and their biomedical applications. Chem Soc Rev 41(18):6103–6124
Wang HD, Chu LY, Yu XQ, Xie R, Yang M, Xu D, Zhang J, Lin H (2007) Thermosensitive affinity behavior of poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogels with β-cyclodextrin moieties. Ind Eng Chem Res 46(5):1511–1518
Wang JZ, Zhao GH, Li YF, Liu X, Hou PP (2013) Reversible immobilization of glucoamylase onto magnetic chitosan nanocarriers. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(2):681–692
Ward MA, Georgiou TK (2011) Thermoresponsive polymers for biomedical applications. Polymers 3(3):1215–1242
Wu T, Zhang YF, Wang XF, Liu SY (2007) Fabrication of hybrid silica nanoparticles densely grafted with thermoresponsive poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) brushes of controlled thickness via surface-initiated atom transfer radical polymerization. Chem Mater 20(1):101–109
Wu F, Li Q, Zhang X, Liu L, Wu SX, Sun DP, Li FS (2012) Fabrication and characterization of thermo-sensitive magnetic polymer composite nanoparticles. J Magn Magn Mater 324(7):1326–1330
Xie W, Ma N (2010) Enzymatic transesterification of soybean oil by using immobilized lipase on magnetic nano-particles. Biomass Bioenergy 34(6):890–896
Xu SF, Lu HZ, Zheng XW, Chen LX (2013) Stimuli-responsive molecularly imprinted polymers: versatile functional materials. J Mater Chem C 1(29):4406–4422
Zhang F, Wang CC (2008) Preparation of thermoresponsive core-shell polymeric microspheres and hollow PNIPAM microgels. Colloid Polym Sci 286(8–9):889–895
Zhang F, Wang CC (2009) Preparation of P(NIPAM-co-AA) microcontainers surface-anchored with magnetic nanoparticles. Langmuir 25(14):8255–8262
Zhao GH, Li YF, Wang JZ, Zhu H (2011) Reversible immobilization of glucoamylase onto magnetic carbon nanotubes functionalized with dendrimer. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 91(3):591–601
Zhu H, Hou C, Li YJ, Zhao GH, Liu X, Hou K, Li YF (2013) One-pot solvothermal synthesis of highly water-dispersible size-tunable functionalized magnetite nanocrystal clusters for lipase immobilization. Chem Asian J 8(7):1447–1454
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the financial supports from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21374045, 21301081), the scientific research ability training of under-graduate students majoring in chemistry by the two patterns based on the tutorial system and top students (J1103307) and the Opening Foundation of State Key Laboratory of Applied Organic Chemistry (SKLAOC-2009-35).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Zhao, G., Wang, X. et al. Synthesis of magnetic thermosensitive microcontainers for enzyme immobilization. J Nanopart Res 17, 224 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-015-2986-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-015-2986-5