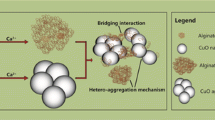
Abstract
The stability of engineered nanoparticles in natural aquatic systems is of high interest for environmental risk assessment since an already important quantity of these reactive species is entering aquatic systems. In the present study, an important issue is addressed by investigating (i) the influence of divalent cations and water hardness (Mg2+ and Ca2+) in agglomerate formation and (ii) alginate concentration effect on the stability TiO2 agglomerates formed in environmental freshwater conditions (pH and total hardness) representative of Lake Geneva, France/Switzerland. Our results indicate that the presence of alginate at typical natural organic matter concentration strongly modifies the stability of TiO2 nanoparticle agglomerates by inducing their partial disagglomeration. Significant TiO2 nanoparticles redispersion and formation of small fragments are expected to be induced by alginate adsorbed layer formed at the nanoparticle surfaces within the agglomerates.
Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Auffan M, Rose J, Bottero J-Y, Lowry GV, Jolivet J-P, Wiesner MR (2009) Towards a definition of inorganic nanoparticles from an environmental, health and safety perspective. Nat Nanotechnol 4(10):634–641. doi:10.1038/nnano.2009.242
Baalousha M (2009) Aggregation and disaggregation of iron oxide nanoparticles: influence of particle concentration, pH and natural organic matter. Sci Total Environ 407(6):2093–2101. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.11.022
Baalousha M, Manciulea A, Cumberland S, Kendall K, Lead JR (2008) Aggregation and surface properties of iron oxide nanoparticles: influence of pH and natural organic matter. Environ Toxicol Chem 27(9):1875–1882. doi:10.1897/07-559.1
Baalousha M, Nur Y, Römer I, Tejamaya M, Lead JR (2013) Effect of monovalent and divalent cations, anions and fulvic acid on aggregation of citrate-coated silver nanoparticles. Sci Total Environ 454–455 (0):119–131. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.02.093
Batley GE, Kirby JK, McLaughlin MJ (2013) Fate and risks of nanomaterials in aquatic and terrestrial environments. Acc Chem Res 46(3):854–862. doi:10.1021/ar2003368
Bernhardt H, Hoyer O, Schell H, Lusse B (1985) Reaction-mechanisms involved in the influence of algogenic organic-matter on flocculation. Zeitschrift Fur Wasser Und Abwasser Forschung-Journal for Water and Wastewater Research 18(1):18–30
Carnal F, Stoll S (2011) Adsorption of weak polyelectrolytes on charged nanoparticles. Impact of salt valency, pH, and nanoparticle charge density. Monte Carlo simulations. J Phys Chem B 115(42):12007–12018. doi:10.1021/jp205616e
Chen X, Mao SS (2007) Titanium dioxide nanomaterials: synthesis, properties, modifications, and applications. Chem Rev 107(7):2891–2959. doi:10.1021/cr0500535
Chen KL, Mylon SE, Elimelech M (2006) Aggregation kinetics of alginate-coated hematite nanoparticles in monovalent and divalent electrolytes. Environ Sci Technol 40(5):1516–1523. doi:10.1021/es0518068
Chowdhury I, Hong Y, Honda RJ, Walker SL (2011) Mechanisms of TiO2 nanoparticle transport in porous media: role of solution chemistry, nanoparticle concentration, and flow rate. J Colloid Interface Sci 360(2):548–555. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2011.04.111
Christian P, Von der Kammer F, Baalousha M, Hofmann T (2008) Nanoparticles: structure, properties, preparation and behaviour in environmental media. Ecotoxicology 17(5):326–343. doi:10.1007/s10646-008-0213-1
Dai HJ (2002) Carbon nanotubes: synthesis, integration, and properties. Acc Chem Res 35(12):1035–1044. doi:10.1021/ar0101640
Domingos RF, Tufenkji N, Wilkinson KJ (2009) Aggregation of titanium dioxide nanoparticles: role of a fulvic acid. Environ Sci Technol 43(5):1282–1286. doi:10.1021/es8023594
Domingos RF, Peyrot C, Wilkinson KJ (2010) Aggregation of titanium dioxide nanoparticles: role of calcium and phosphate. Environ Chem 7(1):61–66. doi:10.1071/en09110
French RA, Jacobson AR, Kim B, Isley SL, Penn RL, Baveye PC (2009) Influence of ionic strength, pH, and cation valence on aggregation kinetics of titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Environ Sci Technol 43(5):1354–1359. doi:10.1021/es802628n
Gallego-Urrea JA, Perez Holmberg J, Hassellov M (2014) Influence of different types of natural organic matter on titania nanoparticle stability: effects of counter ion concentration and pH. Environ Sci: Nano. doi:10.1039/c3en00106g
Gottschalk F, Sonderer T, Scholz RW, Nowack B (2009) Modeled environmental concentrations of engineered nanomaterials (TiO2, ZnO, Ag, CNT, Fullerenes) for different regions. Environ Sci Technol 43(24):9216–9222. doi:10.1021/es9015553
Graham ND, Stoll S, Loizeau J-L (2014) Colloid characterization at the sediment-water interface of Vidy Bay, Lake Geneva. Fundam Appl Limnol 184(2):87–100. doi:10.1127/1863-9135/2014/0591
Grant GT, Morris ER, Rees DA, Smith PJC, Thom D (1973) Biological interactions between polysaccharides and divalent cations–Egg-Box model. FEBS Lett 32(1):195–198. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(73)80770-7
Gregor JE, Fenton E, Brokenshire G, vanden Brink P, Osullivan B (1996) Interactions of calcium and aluminium ions with alginate. Water Res 30(6):1319–1324. doi:10.1016/0043-1354(95)00194-8
Guzman KAD, Finnegan MP, Banfield JF (2006) Influence of surface potential on aggregation and transport of titania nanoparticles. Environ Sci Technol 40(24):7688–7693. doi:10.1021/es060847g
Handy RD, Owen R, Valsami-Jones E (2008) The ecotoxicology of nanoparticles and nanomaterials: current status, knowledge gaps, challenges, and future needs. Ecotoxicology 17(5):315–325. doi:10.1007/s10646-008-0206-0
Helgerud T, Gåserød O, Fjæreide T, Andersen PO, Larsen CK (2009) Alginates. In: Imeson A (ed) Food stabilisers, thickeners and gelling agents. Wiley-Blackwell, Oxford. doi:10.1002/9781444314724.ch4
Horst A, Ji Z, Holden P (2012) Nanoparticle dispersion in environmentally relevant culture media: a TiO2 case study and considerations for a general approach. J Nanopart Res 14(8):1–14. doi:10.1007/s11051-012-1014-2
Hyung H, Fortner JD, Hughes JB, Kim J-H (2007) Natural organic matter stabilizes carbon nanotubes in the aqueous phase. Environ Sci Technol 41(1):179–184. doi:10.1021/es061817g
Jain PK, Huang X, El-Sayed IH, El-Sayed MA (2008) Noble metals on the nanoscale: optical and photothermal properties and some applications in imaging, sensing, biology, and medicine. Acc Chem Res 41(12):1578–1586. doi:10.1021/ar7002804
Ju-Nam Y, Lead JR (2008) Manufactured nanoparticles: an overview of their chemistry, interactions and potential environmental implications. Sci Total Environ 400(1–3):396–414. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.06.042
Klaine SJ, Alvarez PJJ, Batley GE, Fernandes TF, Handy RD, Lyon DY, Mahendra S, McLaughlin MJ, Lead JR (2008) Nanomaterials in the environment: behavior, fate, bioavailability, and effects. Environ Toxicol Chem 27(9):1825–1851. doi:10.1897/08-090.1
Kunhi Mouvenchery Y, Kucerik J, Diehl D, Schaumann GE (2012) Cation-mediated cross-linking in natural organic matter: a review. Rev Environ Sci Bio-Technol 11(1):41–54. doi:10.1007/s11157-011-9258-3
Lee KY, Mooney DJ (2012) Alginate: properties and biomedical applications. Prog Polym Sci 37(1):106–126. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2011.06.003
Lee S, Kim K, Shon HK, Kim S, Cho J (2011) Biotoxicity of nanoparticles: effect of natural organic matter. J Nanopart Res 13(7):3051–3061. doi:10.1007/s11051-010-0204-z
Li L, Fang Y, Vreeker R, Appelqvist I (2007) Reexamining the egg-box model in calcium-alginate gels with X-ray diffraction. Biomacromolecules 8(2):464–468. doi:10.1021/bm060550a
Liu Z, Jiao Y, Wang Y, Zhou C, Zhang Z (2008) Polysaccharides-based nanoparticles as drug delivery systems. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 60(15):1650–1662. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2008.09.001
Liu X, Wazne M, Han Y, Christodoulatos C, Jasinkiewicz KL (2010) Effects of natural organic matter on aggregation kinetics of boron nanoparticles in monovalent and divalent electrolytes. J Colloid Interface Sci 348(1):101–107. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2010.04.036
Liu X, Wazne M, Chou T, Xiao R, Xu S (2011) Influence of Ca2+ and Suwannee River Humic Acid on aggregation of silicon nanoparticles in aqueous media. Water Res 45(1):105–112. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2010.08.022
Liu W-S, Peng Y-H, Shiung C-E, Shih Y-h (2012) The effect of cations on the aggregation of commercial ZnO nanoparticle suspension. J Nanopart Res 14(12):1–10. doi:10.1007/s11051-012-1259-9
Loosli F, Le Coustumer P, Stoll S (2013) TiO2 nanoparticles aggregation and disaggregation in presence of alginate and Suwannee River humic acids. pH and concentration effects on nanoparticle stability. Water Res 47(16):6052–6063. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2013.07.021
Loosli F, Le Coustumer P, Stoll S (2014) Effect of natural organic matter on the disagglomeration of manufactured TiO2 nanoparticles. Environ Sci: Nano 1:154–160
Morris ER, Rees DA, Thom D, Boyd J (1978) Chiroptical and stoichiometric evidence of a specific, primary dimerization process in alginate gelation. Carbohydr Res 66:145–154. doi:10.1016/s0008-6215(00)83247-4
Ohshima H (1995a) Electrophoresis of soft particles. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 62(2–3):189–235. doi:10.1016/0001-8686(95)00279-y
Ohshima H (1995b) Electrophoretic mobility of soft particles. Colloids Surf a-Physicochem Eng Asp 103(3):249–255. doi:10.1016/0927-7757(95)03293-m
Palomino D, Stoll S (2013) Fulvic acids concentration and pH influence on the stability of hematite nanoparticles in aquatic systems. J Nanopart Res 15(2):1–8. doi:10.1007/s11051-013-1428-5
Parks GA (1965) Isoelectric points of solid oxides solid hydroxides and aqueous hydroxo complex systems. Chem Rev 65(2):177. doi:10.1021/cr60234a002
Pefferkorn E (1995) The role of polyelectrolytes in the stabilization and destabilization of colloids. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 56:33–104. doi:10.1016/0001-8686(94)00230-a
Saif M, Aboul-Fotouh SMK, El-Molla SA, Ibrahim MM, Ismail LFM (2012) Improvement of the structural, morphology, and optical properties of TiO2 for solar treatment of industrial wastewater. J Nanopart Res. doi:10.1007/s11051-012-1227-4
Seitz F, Bundschuh M, Dabrunz A, Bandow N, Schaumann GE, Schulz R (2012) Titanium dioxide nanoparticles detoxify pirimicarb under UV irradiation at ambient intensities. Environ Toxicol Chem 31(3):518–523. doi:10.1002/etc.1715
Shih Y, Zhuang C, Peng Y, Lin C, Tseng Y (2012a) The effect of inorganic ions on the aggregation kinetics of lab-made TiO2 nanoparticles in water. Sci Total Environ 435:446–452. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.06.076
Shih Y, Zhuang C, Tso C, Lin C (2012b) The effect of electrolytes on the aggregation kinetics of titanium dioxide nanoparticle aggregates. J Nanopart Res 14(8):1–11. doi:10.1007/s11051-012-0924-3
von Moos N, Slaveykova VI (2014) Oxidative stress induced by inorganic nanoparticles in bacteria and aquatic microalgae - state of the art and knowledge gaps. Nanotoxicology 8(6):605–630. doi:10.3109/17435390.2013.809810
Weir A, Westerhoff P, Fabricius L, Hristovski K, von Goetz N (2012) Titanium dioxide nanoparticles in food and personal care products. Environ Sci Technol 46(4):2242–2250. doi:10.1021/es204168d
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the financial support received from the Swiss National Foundation, project numbers 200020_152847 and 200021_135240. The work leading to these results has also received funding from the European Union Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007–2013) under agreement no. NMP4-LA-2013-310451 (NanoMILE).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Loosli, F., Le Coustumer, P. & Stoll, S. Impact of alginate concentration on the stability of agglomerates made of TiO2 engineered nanoparticles: Water hardness and pH effects. J Nanopart Res 17, 44 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-015-2863-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-015-2863-2