Abstract
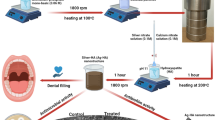
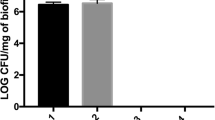
The antibacterial activity of zinc oxide (ZnO) and the strengthening of hydroxylapatite whiskers (HAPws) have been widely studied and applied. However, the antibacterial properties of ZnO–HAPws have scarcely been researched. The aim of this study was to further investigate several types of nano-ZnO morphologies of ZnO–HAPws that were prepared using the sol–gel method at different pondus hydrogenii (pH) values and temperatures. The four morphologies of ZnO–HAPws that were investigated here were granule, triangle, short rod and disc type, and these morphologies were investigated at 70 °C at pH 6.4, 37 °C at pH 6.6, 70 °C at pH 6.6 and 70 °C at pH 6.6, respectively. Next, the antibacterial activity of ZnO–HAPw was compared to that of nano-ZnO, commercially available ZnO and tetrapod-like ZnO whiskers (T-ZnOw) with six bacteria that are associated with oral infections: Streptococcus mutans, Lactobacillus casei, Candida albicans, Actinomyces viscosus, Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. The results of examinations of the minimal inhibitory concentrations (MICs) and minimal bactericidal concentrations (MBCs) showed that the antibacterial activity of ZnO–HAPw exceeded that of the commercially available ZnO and T-ZnOw. Additionally, analysis of variance (ANOVA) analysis of the MBCs revealed that the four tested antibacterial agents had significantly different effects on S. mutans (F = 8.940; P = 0.006), S. aureus (F = 6.924; P = 0.013) and E. coli (F = 4.468; P = 0.04). ANOVA analyses of the MICs revealed that the four tested antibacterial agents had significantly different effects on S. mutans (F = 6.183; P = 0.018), A. viscosus (F = 4.531; P = 0.039) and S. aureus (F = 18.976; P = 0.001).






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amornpitoksuk P, Suwanboon S, Sangkanu S, Sukhoom A, Wudtipan J, Srijan K (2011) Synthesis, photocatalytic and antibacterial activities of ZnO particles modified by diblock copolymer. Powder Technol 212(3):432–438
Aydin Sevinç B, Hanley L (2010) Antibacterial activity of dental composites containing zinc oxide nanoparticles. J Biomed Mater Res B 94(1):22–31
Brayner R, Ferrari-Illiou R, Briviois N, Djediat S, Benedetti MF, Fievet F (2006) Toxicological impact studies based on Escherichia coli bacteria in ultrafine ZnO nanoparticles colloidal medium. Nano Lett 6(4):866–870
Choi SH, Kim EG, Park JN, An KJ, Lee NY, Kim SC, Hyeon T (2005) Large-scale synthesis of hexagonal pyramid-shaped ZnO nanocrystals from thermolysis of Zn–oleate complex. J Phys Chem B 109(31):14792–14794
Fang M, Chen JH, Xl Wu, Yang PH, Hildebrand HF (2006) Antibacterial activities of inorganic agents on six bacteria associated with oral infections by two susceptibility tests. Int J Antimicrob Agents 27(6):513–517
Fu G, Vary PS, Lin CT (2005) Anatase TiO2 nanocomposites for antimicrobial coatings. J Phys Chem 109(18):8889–8898
Guggenheim B, Giertsen E, Schupbach P, Shapiro S (2001) Validation of an in vitro biofilm model of supragingival plaque. J Dent Res 80(1):363–370
Jiang XP, Liu YZ, Gao YG, Zhang XJ, Shi LH (2010) Preparation of one-dimensional nanostructured ZnO. Particuology 8(4):383–385
Katsuhiko A, Takeshi K, Takahiro T, Anezka L, Petr S (2002) Nonlinear viscoelasticity of silicone carbide whisker-filled liquid crystalline polymer melts. Polym Polym Compos 10(5):361–373
Kawashita M, Toda S, Kim HM, Kokubo T, Masuda N (2003) Preparation of antibacterial silver-doped silica glass microspheres. J Biomed Mater Res A 66(2):266–274
Lei H, Xu T, Gao CT (2010) Characterization of the dispersion of tetrapod-like nano-ZnO whiskers in acrylic resin and properties of the nano-composite coating system. J Coat Technol Res 7(1):91–97
Li J, Srinivasan S, He GN, Kang JK, Wu ST, Ponce FA (2008) Synthesis and luminescence properties of ZnO nanostructures produced by the sol–gel method. J Cryst Growth 310(3):599–603
Liu B, Zeng HC (2003) Hydrothermal synthesis of ZnO nanorods in the diameter regime of 50 nm. J Am Chem Soc 125:4430–4431
Mao LQ, Li QL, Dang HX, Zhang ZJ (2005) Synthesis of nanocrystalline TiO2 with high photoactivity and large specific surface area at low temperature. Mater Res Bull 40(2):201–208
Nishioka M, Nishimura T, Ookubo A, Taya M (2003) Improved bactericidal activity of silver-loaded zirconium phosphate in the presence of Cl− by combining with hydroxyapatite. Biotechnol Lett 25(15):1263–1266
Paillet M, Dufresne A (2001) Chitin whisker reinforced thermoplastic nanocomposites. Macromolecules 34(19):6527–6530
Park WI, Kim DH, Jung SW, Yi GC (2002) Metalorganic vapor-phase epitaxial growth of vertically well-aligned ZnO nanorods. Appl Phys Lett 80(22):4232–4234
Sherman RG, Prusinski L, Ravenel MC, Joralmon RA (2002) Oral candidosis. Quintessence Int 33(521):532
Tjong SC, Meng YZ (1998) Morphology and performance of potassium titanate whisker-reinforced polypropylene composites. J Appl Polym Sci 70(3):431–439
Vafaee M, Ghamsari MS (2007) Preparation and characterization of ZnO nanoparticles by a novel sol–gel route. Mater Lett 61(14):3265–3268
Vayssieres L, Keis K, Lindquist SE, Hagfeldt A (2001) Purpose-built anisotropic metal oxide material: 3D highly oriented microrod array of ZnO. J Phys Chem B 105(17):3350–3352
Wahab R, Mishra A, Yun S, Kim YS, Shin HS (2010) Antibacterial activity of ZnO nanoparticles prepared via non-hydrolytic solution route. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 87(5):1917–1925
Wang YW, Zhang LD, Wang GZ, Peng XS, Chu ZQ, Liang CH (2002) Catalytic growth of semiconducting zinc oxide nanowires and their photoluminescence properties. J Cryst Growth 234(1):171–175
Xie J, Li P, Wang YJ, Wei Y (2008) Synthesis of ZnO whiskers with different aspect ratios by a facile solution route. Phys Status Solidi A 205(7):1560–1565
Xie J, Li P, Li YT, Wang YJ, Wei Y (2009a) Morphology control of ZnO particles via aqueous solution route at low temperature. Mater Chem Phys 114(2):943–947
Xie J, Li P, Wang YJ, Wei Y (2009b) Synthesis of needle- and flower-like ZnO microstructures by a simple aqueous solution route. J Phys Chem Solids 70(1):112–116
Xie J, Li P, Wang YJ, Wei Y (2011) Simple fabrication and photocatalytic activity of ZnO particles with different morphologies. Powder Technol 207(1):140–144
Xu CK, Xu GD, Liu YK, Wang GH (2002a) A simple and novel route for the preparation of ZnO nanorods. Solid State Commun 122(3):175–179
Xu HHK, Quinn JB, Smith DT, Antonucci JM, Schumacher GE, Eichmiller FC (2002b) Dental resin composites containing silica-fused whiskers-effects of whisker-to-silica ratio on fracture toughness and indentation properties. Biomaterials 23(3):735–742
Xu HHK, Quinn JB, Smith DT, Giuseppetti AA, Eichmiller FC (2003) Effects of different whiskers on the reinforcement of dental resin composites. Dent Mater 19(5):359–367
Yamamoto O, Komatsu M, Sawai J, Nakagawa ZE (2004) Effect of lattice constant of zinc oxide on antibacterial characteristics. J Mater Sci Mater Med 15(8):847–851
Yang H, Wang K, Ding X, Zhou G, Ge M (2002) Study on relationship between antibacterial property and silver ions in inorganic antibacterial powders. J Chin Ceram Soc 30(5):585–588
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully thank Professor Minghua Huang for assistance with the studies and Yongshun Cui and Jia Chen for assistance with the HAPw (Biological Engineering Materials Laboratory of Kunming University of Science and Technology). This project was supported by a Grant (No. 81260272) from the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, J., Liu, W., Zhang, W. et al. Nano-ZnO/ZnO–HAPw prepared via sol–gel method and antibacterial activities of inorganic agents on six bacteria associated with oral infections. J Nanopart Res 16, 2658 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-014-2658-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-014-2658-x