Abstract
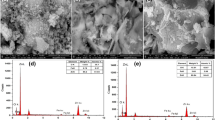
Zinc sulfide nanoparticles (particles size range 10–20 nm) and nanorods (particles size range 20–35 nm) were prepared through a hydrothermal method. The influence of surface defects and lattice strain on the optical, dielectric, and electrical transport properties was investigated. The spectral shifts and modification in bandgap are explained based on effective mass approximation model. Photoluminescence and ESR studies clearly showed the presence of large density of surface defects in the samples. The Raman spectra were thoroughly studied using the Gaussian confinement model. Dielectric studies using impedance and electric modulus spectroscopy showed enhanced grain boundary conductivity. Both nanoparticles and nanorods were found to exhibit Cole–Cole type dielectric relaxation. The enhanced ac electrical conductivities observed in both the nanostructures were successfully explained using the correlated barrier hopping model. Parameters like hopping time, barrier width, and defect densities were calculated.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad M, Rafiq MA, Hasan MM (2013) Transport characteristics and colossal dielectric response of cadmium sulfide nanoparticles. J Appl Phys 114:133702–133708
Arguello CA, Rousseau DL, Porto SPS (1968) First-order Raman effect in wurtzite-type crystals. Phys Rev 181:1351–1363
Balandin A, Wang KL, Kouklin N, Sandyopadhyay S (2000) Raman spectroscopy of electrochemically self-assembled CdS quantum dots. Appl Phys Lett 76:137–139
Bhattacharjee B, Hs C, Lu I (2006) Multicolor luminescence of undoped zinc sulfide nanocrystalline thin films at room temperature. Thin Solid Films 514:132–137
Biju V, Abdulkhadar M (2001) AC conductivity of nanostructured nickel oxide. J Mater Sci 36:5779–5787
Bonato C, Ding D, Gudat J, Thon S, Kim H, Petroff PM, Exter MPV, Bouwmeester D (2009) Tuning micropillar cavity birefringence by laser induced surface defects. Appl Phys Lett 95:251104
Brada Y (1989) Electrical conductivity of ZnS crystals: ZnS crystals as quasi-one-dimensional conductors. Phys Rev B 39:7645–7652
Brafman O, Mitra SS (1968) Raman effect in wurtzite- and zinc-blende-type ZnS single crystals. Phys Rev 171:931–934
Cassina V, Gerosa L, Podesta` A, Ferrari G, Sampietro M, Fiorentini F, Mazza T, Lenardi C, P P (2009) Nanoscale electrical properties of cluster-assembled palladium oxide thin films. Phys Rev B 79:115422–115429
Chandran A, Samuel SM, Koshy J, George KC (2011a) Correlated barrier hopping in CdS nanoparticles and nanowires. J Appl Phys 109:84314–84319
Chandran A, Samuel SM, Koshy J, George KC (2011b) Dielectric relaxation behavior of CdS nanoparticles and nanowires. J Mater Sci 46:4646–4653
Cheng YC, Jin CQ, Gao F, Wu XL, Zong W, Li SH, Chu PK (2009) Raman scattering study of zinc blende and wurtzite ZnS. J Appl Phys 106:123505–123509
Chiang YM, Lavik EB, Kosacki I, Tuller HL, Ying JY (1996) Defect and transport properties of nanocrystalline CeO2−x . Appl Phys Lett 69:185–187
Chihara H, Nakamura N, Hellwege KH, Hellwege AM (1987) Landolt-Börnstein: numerical data and functional relationships in science and technology, vol 22. Springer, Berlin
Coe S, Woo W, Bawendi M, Bulovic V (2002) Electroluminescence from single monolayers of nanocrystals in molecular organic devices. Nature 420:800–803
Cole KS, Cole RH (1941) Dispersion and absorption in dielectrics. I alternating current characteristics. J Chem Phys 9:341–351
Denzler D, Olschewski M, Sattler K (1998) Luminescence studies of localized gap states in colloidal ZnS nanocrystals. J Appl Phys 84:2841–2845
Derlet PM, Petegem SV, Swygenhoven HV (2005) Calculation of X-ray spectra for nanocrystalline materials. Phys Rev B 71:24114–24121
Dutta A, Sinha TP (2007) Dielectric relaxation and electronic structure of Ca(Fe1/2Sb1/2)O3. Phys Rev B 76:155113–155119
Einevoll GH (1991) Confinement of excitons in quantum dots. Phys Rev B 45:3410–3417
Elliott SR (1977) A theory of ac conduction in chalcogenide glasses. Philos Mag 36:1291–1304
Fang X, Zhai T, Gautam UK, Li L, Wu L, Bando Y, Golberg D (2011) ZnS nanostructures: from synthesis to applications. Prog Mater Sci 56:175–287
George KC, Kurien S, Mathew J, Sebastian S, Potty SN (2006) Dielectric behavior and ac electrical conductivity of nanocrystalline nickel aluminate. Mater Chem Phys 98:470–476
Goswami N, Sen P (2007) Photoluminescent properties of ZnS nanoparticles prepared by electro-explosion of Zn wires. J Nanopart Res 9:513–517
Hudlikar M, Joglekar S, Dhaygude M, Kodam K (2012) Latex-mediated synthesis of ZnS nanoparticles: green synthesis approach. J Nanopart Res 14:865–870
Iza DC, Rojas DM, Jia Q, Swartzentruber B, Driscoll JLM (2012) Tuning of defects in ZnO nanorod arrays used in bulk heterojunction solar cells. Nanoscale Res Lett 7:655–662
Jacob J, Khadar MA (2010) Investigation of mixed spinel structure of nanostructured nickel ferrite. J Appl Phys 107:114310–114319
Junkermeier CE, Lewis JP (2009) Amorphous nature of small CdS nanoparticles: molecular dynamics simulations. Phys Rev B 79:125323–125330
Kao KC (2004) Dielectric phenomena in solids. Elsevier Academic Press, London
Kasai PH, Otomo Y (1962) Electron paramagnetic resonance studies of the ZnS-A and -B centers. J Chem Phys 37:1263–1275
Khan N, Li J (2006) Effects of compressive strain on optical properties of InxGa1 − xN/GaN quantum wells. Appl Phys Lett 89:151916(1)–151916(3)
Limaye MV, Gokhale S, Acharya SA, Kulkarni SK (2008) Template-free ZnS nanorod synthesis by microwave irradiation. Nanotechnology 19:415602
Lippens PE, Lannoo M (1989) Calculation of the band gap for small CdS and ZnS crystallites. Phys Rev B 39:10935–10942
Lunkenheimer P, Loidl A, Ottermannand CR, Bange K (1991) Correlated barrier hopping in NiO films. Phys Rev B 44:5927–5930
Prabhu RR, Khadar MA (2008) Study of optical phonon modes of CdS nanoparticles using Raman spectroscopy. Bull Mater Sci 31:511–515
Qin W, Szpunar JA (2005) Origin of lattice strain in nanocrystalline materials. Philos Mag Lett 85:649–656
Raymond O, Font R, Suárez-Almodover N, Portelles J, Siqueiros JM (2005) Frequency-temperature response of ferroelectromagnetic Pb(Fe1/2Nb1/2)O3 ceramics obtained by different precursors. Part II. Impedance spectroscopy characterization. J Appl Phys 97:84108–84115
Ritcher H, Wang ZP, Lay L (1981) The one phonon Raman spectrum in microcrystalline silicon. Solid State Commun 39:625–629
Savitha T, Selvasekarapandian S, Ramya CS, Bhuvaneswari MS, Angelo PC (2007) Electrical conduction and relaxation mechanism in Li2AlZr[PO4]3. J Mater Sci 42:5470–5475
Sayer M, Mansingh M, Webb JB, Noad J (1978) Long-range potential centres in disordered solids. J Phys C 11:315–329
Schroer P, Kruger P, Pollmann J (1993) First-principles calculation of the electronic structure of the wurtzite semiconductors ZnO and ZnS. Phys Rev B 47:6971–6980
Serrano J, Cantarero A, Cardona M, Garro N, Lauck R, Tallman RE, Ritter TM, Weinstein BA (2004) Raman scattering in β-ZnS. Phys Rev B 69:14301–14311
Shalish I, Temkin H, Narayanamurti V (2004) Size-dependent surface luminescence in ZnO nanowires. Phys Rev B 69:245401–245404
Shevarenkov DN, Shchurov AF (2006) Dielectric properties of polycrystalline ZnS. Semiconductors 40:33–35
Shimakawa K (1982) On the temperature dependence of AC conduction in chalcogenide glasses. Philos Mag B 46:123–135
Smith AM, Mohs AM, Nie S (2009) Tuning the optical and electronic properties of colloidal nanocrystals by lattice strain. Nat Nanotechnol 4:56–63
Sural M, Ghosh A (1998) Electrical conductivity and conductivity relaxation in ZrF4–BaF2–YF3–LiF glasses. J Phys 10:10577–10586
Suresh S (2013) Synthesis, structural and dielectric properties of zinc sulfide nanoparticles. Int J Phys Sci 8:1121–1127
Unlu H, Horing NJM (2013) Low dimensional semiconductor structures: characterization, modeling and applications. Springer, Berlin
Veena GE, Malini KA, Sakthi Kumar D, Yoshida Y, Al-Omari IA, Saravanan S, Anantharaman MR (2009) On the dielectric dispersion and absorption in nanosized manganese zinc mixed ferrites. J Phys Condens Matter 21:146006–146017
Vij DR, Singh N (1998) Luminescence and related properties of II–VI semiconductors. Nova Science Publishers Inc, New York
Voon LCLY, Willatzen M (2009) The K–p method: electronic properties of semiconductors. Springer, Berlin
Wang C, Ao Y, Wang P, Hou J, Qian J, Zhang S (2010) Controlled synthesis in large-scale of CdS mesospheres and photocatalytic activity. Mater Lett 64:439–441
Xiao Q, Xiao C, Ouyang L (2008) Strong enhancement of band-edge photoluminescence in CdS nanocrystals prepared by one-step aqueous synthesis method. J Lumin 128:1942–1947
Xu XJ, Feil GT, HuiYu W, WeiWang X, Chen L, Zhang LD (2006) Preparation and formation mechanism of ZnS semiconductor nanowires made by the electrochemical deposition method. Nanotechnology 17:426–429
Yang H, Shen C, Song N, Wang Y, Yang T, Gao H, Cheng H (2010a) Facile synthesis of hollow nano-spheres and hemispheres of cobalt by polyol reduction. Nanotechnology 21:375602–375606
Yang Y, Yu SF, Yan J, Zhang LD (2010b) Random lasing action from randomly assembled ZnS nanosheets. Nanoscale Res Lett 5:809–812
Zhao YH, Zhang K, Lu K (1997) Structure characteristics of nanocrystalline element selenium with different grain sizes. Phys Rev B 56:14322–14329
Zhu Z, Ouyang G, Yang G (2010) Bandgap shift in SnO2 nanostructures induced by lattice strain and coordination imperfection. J Appl Phys 108:83511–83514
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank STIC (Cochin), IUC-DAE consortium for scientific research (INDORE), and the central instrumentation facility (SB College) for the analyses carried out.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chandran, A., George, K.C. Defect induced modifications in the optical, dielectric, and transport properties of hydrothermally prepared ZnS nanoparticles and nanorods. J Nanopart Res 16, 2238 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-2238-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-2238-5