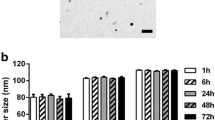
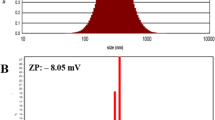
Abstract
Lysosomal TLR-9 is stimulated in A549 lung epithelial cells through administration of nanoparticles (NPs) either based on γ-Fe2O3 or MnO. Synthetic single-stranded immunostimulatory CpG-oligodeoxynucleotides (CpG-ODN) are covalently attached to fluorescently labelled γ-Fe2O3- and MnO-NPs in order to monitor the impact of TLR-9 activation on motility and cell morphology employing time-resolved impedance spectroscopy. In contrast to cytotoxic MnO-based particles, particles made from Fe2O3 are non-toxic carriers for pathogen-mimicking CpG-ODNs, which efficiently stimulate endogenous TLR-9, resulting in enhanced micromotility and a loss of barrier properties. Compared to neat CpG-ODNs administered in the absence of particles, the nucleotides displayed by NPs are found to be considerably more efficient in stimulating A549 cells attributed to a larger local concentration of ligands on the particles’ surface. The study shows that particle-based CpG-ODNs added to tumour cells increase their motility even further and therefore might also enhance their invasiveness and metastatic potential, foiling the original strategy of immunotherapy.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akira S, Takeda K, Kaisho T (2001) Toll-like receptors: critical proteins linking innate and acquired immunity. Nat Immunol 2(8):675–680
Choi JY, Lee SH, Na HB, An K, Hyeon T, Seo TS (2010) In vitro cytotoxicity screening of water-dispersible metal oxide nanoparticles in human cell lines. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 33(1):21–30. doi:10.1007/s00449-009-0354-5
Droemann D, Albrecht D, Gerdes J, Ulmer AJ, Branscheid D, Vollmer E, Dalhoff K, Zabel P, Goldmann T (2005) Human lung cancer cells express functionally active toll-like receptor 9. Respir Res 6:1
Giaever I, Keese CR (1989) Fractal motion of mammalian-cells. Physica D 38(1–3):128–133
Giaever I, Keese CR (1991) Micromotion of mammalian cells measured electrically. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88(17):7896–7900
Horner AA, Takabaysahi K, Zubeldia JM, Raz E (2002) Immunostimulatory DNA-based therapeutics for experimental and clinical allergy. Allergy 57(Suppl 72):24–29
Klinman DM (2004) Immunotherapeutic uses of CpG oligodeoxynucleotides. Nat Rev Immunol 4(4):249–259
Krieg AM (2002) CPG motifs in bacterial dna and their immune effects*. Annu Rev Immunol 20(1):709–760. doi:10.1146/annurev.immunol.20.100301.064842
Lo C-M, Ferrier J (1998) Impedance analysis of fibroblastic cell layers measured by electric cell-substrate impedance sensing. Phys Rev E 57(6):6982
Lo CM, Keese CR, Giaever I (1995) Impedance analysis of MDCK cells measured by electric cell-substrate impedance sensing. Biophys J 69(6):2800–2807
Minelli C, Lowe SB, Stevens MM (2010) Engineering nanocomposite materials for cancer therapy. Small 6(21):2336–2357. doi:10.1002/smll.201000523
Murphy K, Travers P, Walport M, Janeway C (2008) Janeway’s immunobiology, 7th edn. Garland Science, New York
Park J, An K, Hwang Y, Park J, Noh H, Kim J, Park J, Hwang N, Hyeon T (2004) Ultra-large-scale syntheses of monodisperse nanocrystals. Nat Mater 3:891–895. doi:10.1038/nmat1251
Ren T, Xu L, Jiao S, Wang Y, Cai Y, Liang Y, Zhou Y, Zhou H, Wen Z (2009) TLR9 signaling promotes tumor progression of human lung cancer cell in vivo. Pathol Oncol Res 15(4):623–630. doi:10.1007/s12253-009-9162-0
Schladt TD, Graf T, Tremel W (2009) Synthesis and characterization of monodisperse manganese oxide nanoparticlesâ—evaluation of the nucleation and growth mechanism. Chem Mater 21(14):3183–3190. doi:10.1021/cm900663t
Schladt TD, Shukoor MI, Schneider K, Tahir MN, Natalio F, Ament I, Becker J, Jochum FD, Weber S, Köhler O, Theato P, Schreiber LM, Sönnichsen C, Schröder HC, Müller WEG, Tremel W (2010) Au@MnO-“nanoblumen”—hybrid-nanokomposite zur selektiven dualen funktionalisierung und bildgebung. Angew Chem 122(23):4068–4072. doi:10.1002/ange.200906689
Schneider D, Janshoff A (2012) Inhibition of actin dynamics during epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 419:221–225. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.01.151
Schneider D, Tarantola M, Janshoff A (2011) Dynamics of TGF-β induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition monitored by electric cell-substrate impedance sensing. Biochim Biophys Acta 1813(12):2099–2107
Shukoor MI, Natalio F, Tahir MN, Wiens M, Tarantola M, Therese HA, Barz M, Weber S, Terekhov M, Schröder HC, Müller WEG, Janshoff A, Theato P, Zentel R, Schreiber LM, Tremel W (2009) Pathogen-mimicking MnO nanoparticles for selective activation of the TLR9 pathway and imaging of cancer cells. Adv Funct Mater 19(23):3717–3725. doi:10.1002/adfm.200900635
Takeda K, Akira S (2004) TLR signaling pathways. Semin Immunol 16(1):3–9
Tarantola M, Schneider D, Sunnick E, Adam H, Pierrat S, Rosman C, Breus V, Sönnichsen C, Basché T, Wegener J, Janshoff A (2009) Cytotoxicity of metal and semiconductor nanoparticles indicated by cellular micromotility. ACS Nano 3:213–222
Wang AZ, Langer R, Farokhzad OC (2012) Nanoparticle delivery of cancer drugs. Annu Rev Med 63(63):185–198. doi:10.1146/annurev-med-040210-162544
Wegener J, Keese CR, Giaever I (2000) Electric cell-substrate impedance sensing (ECIS) as a noninvasive means to monitor the kinetics of cell spreading to artificial surfaces. Exp Cell Res 259(1):158–166. doi:10.1006/excr.2000.4919
Xu CJ, Xu KM, Gu HW, Zheng RK, Liu H, Zhang XX, Guo ZH, Xu B (2004) Dopamine as a robust anchor to immobilize functional molecules on the iron oxide shell of magnetic nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 126(32):9938–9939. doi:10.1021/Ja0464802
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Patrick Theato and Florian D. Jochum for preparation of the polymer for coating the particles. We thank Anja Herdlitschke and Angela Rübeling for cell preparation. Financial support was provided by SPP1313 ‘Bionanoresponse’, Boehringer Ingelheim Fonds (J.R., University of Goettingen), Dorothea Schloezer fellowship (A.P., University of Goettingen), POLYMAT (K.K., University of Mainz) and the Carl-Zeiss Foundation (T.D.S.). I.S. acknowledges a ‘Fonds der Chemischen Industrie VCI’ Fellowship and is a recipient of a fellowship through the Excellence Initiative (DFG/GSC 266).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rother, J., Pietuch, A., Koll, K. et al. Enhanced motility of alveolar cancer cells induced by CpG-ODN-functionalized nanoparticles. J Nanopart Res 15, 2107 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-2107-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-2107-2