Abstract
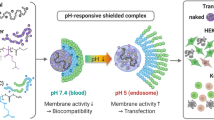
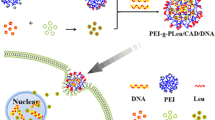
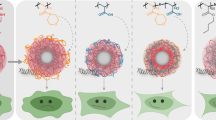
The objective of the present work was to develop new cationic nanoparticles (cNPs) with amphiphilic cationic copolymers for the delivery of plasmid DNA (pDNA). Cationic copolymers were built on the synthesis of quaternary ammonium salt compounds from diethylenetriamine (DETA) to include the positively charged head group and amphiphilic multi-grafts. PLGA-phe-PEG-qDETA (PPD), phe-PEG-qDETA-PLGA (PDP), and PLGA-phe-PEG-qDETA-PLGA (PPDP) cationic copolymers were created by this moiety of DETA quaternary ammonium, heterobifunctional polyethylene glycol (COOH-PEG-NH2), phenylalanine (phe), and poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA). These new cNPs were prepared by the water miscible solvent displacement method. They exhibit good pDNA binding ability, as shown in a retardation assay that occurred at a particle size of ~217 nm. The zeta potential was approximately +21 mV when the cNP concentration was 25 mg/ml. The new cNPs also have a better buffering capacity than PLGA NPs. However, the pDNA binding ability was demonstrated starting at a weight ratio of approximately 6.25 cNPs/pDNA. Gene transfection results showed that these cNPs had transfection effects similar to those of Lipofectamine 2000 in 293T cells. Furthermore, cNPs can also transfect human adipose-derived stem cells. The results indicate that the newly developed cNP is a promising candidate for a novel gene delivery vehicle.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambegia E, Ansell S, Cullis P, Heyes J, Palmer L, MacLachlan I (2005) Stabilized plasmid-lipid particles containing PEG-diacylglycerols exhibit extended circulation lifetimes and tumor selective gene expression. Biochim Biophys Acta 1669(2):155–163
Ando S, Putnam D, Pack DW, Langer R (1999) PLGA microspheres containing plasmid DNA: preservation of supercoiled DNA via cryopreparation and carbohydrate stabilization. J Pharm Sci 88(1):126–130
Antipina MN, Dobner B, Konovalov OV, Shapovalov VL, Brezesinski G (2007) Investigation of the protonation state of novel cationic lipids designed for gene transfection. J Phys Chem B 111(49):13845–13850
Banerjee SR, Levadala MK, Lazarova N, Wei L, Valliant JF, Stephenson KA, Babich JW, Maresca KP, Zubieta J (2002) Bifunctional single amino acid chelates for labeling of biomolecules with the [Tc(CO)(3)](+) and [Re(CO)(3)](+) cores. Crystal and molecular structures of [ReBr(CO)(3)(H(2)NCH(2)C(5)H(4)N)], [Re(CO)(3)[(C(5)H(4)NCH(2))(2)NH]]Br, [Re(CO)(3)[(C(5)H(4)NCH(2))(2)NCH(2)CO(2)H]]Br, [Re(CO)(3)[X(Y)NCH(2)CO(2)CH(2)CH(3)]]Br (X = Y = 2-pyridylmethyl; X = 2-pyridylmethyl, Y = 2-(1-methylimidazolyl)methyl; X = Y = 2-(1-methylimidazolyl)methyl), [ReBr(CO)(3)[(C(5)H(4)NCH(2))NH(CH(2)C(4)H(3)S)]], and [Re(CO)(3)[(C(5)H(4)NCH(2))N(CH(2)C(4)H(3)S)(CH(2)CO(2))]]. Inorg Chem 41(24):6417–6425
Bivas-Benita M, Romeijn S, Junginger HE, Borchard G (2004) PLGA–PEI nanoparticles for gene delivery to pulmonary epithelium. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 58(1):1–6
Boddu S, Vaishya R, Jwala J, Vadlapudi A, Pal D, Mitra A (2012) Preparation and characterization of folate conjugated nanoparticles of doxorubicin using PLGA-PEG-FOL polymer. Med Chem 2:068–075
Boussif O, Lezoualc’h F, Zanta MA, Mergny MD, Scherman D, Demeneix B, Behr JP (1995) A versatile vector for gene and oligonucleotide transfer into cells in culture and in vivo: polyethylenimine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92(16):7297–7301
Capan Y, Woo BH, Gebrekidan S, Ahmed S, DeLuca PP (1999) Preparation and characterization of poly(d,l-lactide-co-glycolide) microspheres for controlled release of poly(l-lysine) complexed plasmid DNA. Pharm Res 16(4):509–513
Cheng TL, Cheng CM, Chen BM, Tsao DA, Chuang KH, Hsiao SW, Lin YH, Roffler SR (2005) Monoclonal antibody-based quantitation of poly(ethylene glycol)-derivatized proteins, liposomes, and nanoparticles. Bioconjug Chem 16(5):1225–1231
Cheng J, Teply BA, Sherifi I, Sung J, Luther G, Gu FX, Levy-Nissenbaum E, Radovic-Moreno AF, Langer R, Farokhzad OC (2007) Formulation of functionalized PLGA–PEG nanoparticles for in vivo targeted drug delivery. Biomaterials 28(5):869–876
Desai MP, Labhasetwar V, Amidon GL, Levy RJ (1996) Gastrointestinal uptake of biodegradable microparticles: effect of particle size. Pharm Res 13(12):1838–1845
Duncan R (2006) Polymer conjugates as anticancer nanomedicines. Nat Rev Cancer 6(9):688–701
Florence AT, Hillery AM, Hussain N, Jani PU (1995) Nanoparticles as carriers for oral peptide absorption—studies on particle uptake and fate. J Controlled Release 36(1–2):39–46
Gao X, Kim KS, Liu D (2007) Nonviral gene delivery: what we know and what is next. AAPS J 9(1):E92–E104
Harush-Frenkel O, Rozentur E, Benita S, Altschuler Y (2008) Surface charge of nanoparticles determines their endocytic and transcytotic pathway in polarized MDCK cells. Biomacromolecules 9(2):435–443
Ho ML, Fu YC, Wang GJ, Chen HT, Chang JK, Tsai TH, Wang CK (2008) Controlled release carrier of BSA made by W/O/W emulsion method containing PLGA and hydroxyapatite. J Controlled Release 128(2):142–148
Huang Z, Li W, MacKay JA, Szoka FC Jr (2005) Thiocholesterol-based lipids for ordered assembly of bioresponsive gene carriers. Mol Ther 11(3):409–417
Jang JH, Lim KI, Schaffer DV (2007) Library selection and directed evolution approaches to engineering targeted viral vectors. Biotechnol Bioeng 98(3):515–524
Kang SW, Lim HW, Seo SW, Jeon O, Lee M, Kim BS (2008) Nanosphere-mediated delivery of vascular endothelial growth factor gene for therapeutic angiogenesis in mouse ischemic limbs. Biomaterials 29(8):1109–1117
Kim YH, Gihm SH, Park CR, Lee KY, Kim TW, Kwon IC, Chung H, Jeong SY (2001) Structural characteristics of size-controlled self-aggregates of deoxycholic acid-modified chitosan and their application as a DNA delivery carrier. Bioconjug Chem 12(6):932–938
Kodama K, Katayama Y, Shoji Y, Nakashima H (2006) The features and shortcomings for gene delivery of current non-viral carriers. Curr Med Chem 13(18):2155–2161
Labhasetwar V, Song C, Humphrey W, Shebuski R, Levy RJ (1998) Arterial uptake of biodegradable nanoparticles: effect of surface modifications. J Pharm Sci 87(10):1229–1234
Li SD, Huang L (2006) Gene therapy progress and prospects: non-viral gene therapy by systemic delivery. Gene Ther 13(18):1313–1319
Li Z, Ning W, Wang J, Choi A, Lee PY, Tyagi P, Huang L (2003) Controlled gene delivery system based on thermosensitive biodegradable hydrogel. Pharm Res 20(6):884–888
Lim YB, Choi YH, Park JS (1999) A self-destroying polycationic polymer: biodegradable poly(4-hydroxy-l-proline ester). J Am Chem Soc 121(24):5633–5639
Locatelli E, Franchini MC (2012) Biodegradable PLGA-b-PEG polymeric nanoparticles: synthesis, properties, and nanomedical applications as drug delivery system. J Nanopart Res 14(12):1316–1333
MacLaughlin FC, Mumper RJ, Wang J, Tagliaferri JM, Gill I, Hinchcliffe M, Rolland AP (1998) Chitosan and depolymerized chitosan oligomers as condensing carriers for in vivo plasmid delivery. J Controlled Release 56(1–3):259–272
Mateos-Timoneda MA, Lok MC, Hennink WE, Feijen J, Engbersen JF (2008) Poly(amido amine)s as gene delivery vectors: effects of quaternary nicotinamide moieties in the side chains. Chem Med Chem 3(3):478–486
Nie H, Ho ML, Wang CK, Wang CH, Fu YC (2009) BMP-2 plasmid loaded PLGA/HAp composite scaffolds for treatment of bone defects in nude mice. Biomaterials 30(5):892–901
Ohlfest JR, Lobitz PD, Perkinson SG, Largaespada DA (2004) Integration and long-term expression in xenografted human glioblastoma cells using a plasmid-based transposon system. Mol Ther 10(2):260–268
Ohlfest JR, Freese AB, Largaespada DA (2005) Nonviral vectors for cancer gene therapy: prospects for integrating vectors and combination therapies. Curr Gene Ther 5(6):629–641
Palmer DH, Young LS, Mautner V (2006) Cancer gene-therapy: clinical trials. Trends Biotechnol 24(2):76–82
Pamujula S, Graves RA, Moiseyev R, Bostanian LA, Kishore V, Mandal TK (2008) Preparation of polylactide-co-glycolide and chitosan hybrid microcapsules of amifostine using coaxial ultrasonic atomizer with solvent evaporation. J Pharm Pharmacol 60(3):283–289
Peetla C, Labhasetwar V (2009) Effect of molecular structure of cationic surfactants on biophysical interactions of surfactant-modified nanoparticles with a model membrane and cellular uptake. Langmuir 25(4):2369–2377
Peracchia MT, Harnisch S, Pinto-Alphandary H, Gulik A, Dedieu JC, Desmaele D, d’Angelo J, Muller RH, Couvreur P (1999) Visualization of in vitro protein-rejecting properties of PEGylated stealth polycyanoacrylate nanoparticles. Biomaterials 20(14):1269–1275
Perumal OP, Inapagolla R, Kannan S, Kannan RM (2008) The effect of surface functionality on cellular trafficking of dendrimers. Biomaterials 29(24–25):3469–3476
Petros RA, DeSimone JM (2010) Strategies in the design of nanoparticles for therapeutic applications. Nat Rev Drug Discov 9(8):615–627
Piest M, Engbersen JF (2010) Effects of charge density and hydrophobicity of poly(amido amine)s for non-viral gene delivery. J Controlled Release 148(1):83–90
Prabha S, Labhasetwar V (2004) Nanoparticle-mediated wild-type p53 gene delivery results in sustained antiproliferative activity in breast cancer cells. Mol Pharm 1(3):211–219
Prabha S, Zhou WZ, Panyam J, Labhasetwar V (2002) Size-dependency of nanoparticle-mediated gene transfection: studies with fractionated nanoparticles. Int J Pharm 244(1–2):105–115
Qaddoumi MG, Ueda H, Yang J, Davda J, Labhasetwar V, Lee VH (2004) The characteristics and mechanisms of uptake of PLGA nanoparticles in rabbit conjunctival epithelial cell layers. Pharm Res 21(4):641–648
Rabinovich-Guilatt L, Couvreur P, Lambert G, Dubernet C (2004) Cationic vectors in ocular drug delivery. J Drug Target 12(9–10):623–633
Singh M, Briones M, Ott G, O’Hagan D (2000) Cationic microparticles: a potent delivery system for DNA vaccines. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(2):811–816
Son S, Kim WJ (2009) Biodegradable nanoparticles modified by branched polyethyleneimine for plasmid DNA delivery. Biomaterials 31(1):133–143
Song LY, Ahkong QF, Rong Q, Wang Z, Ansell S, Hope MJ, Mui B (2002) Characterization of the inhibitory effect of PEG–lipid conjugates on the intracellular delivery of plasmid and antisense DNA mediated by cationic lipid liposomes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1558(1):1–13
van den Berg JH, Oosterhuis K, Hennink WE, Storm G, van der Aa LJ, Engbersen JF, Haanen JB, Beijnen JH, Schumacher TN, Nuijen B (2009) Shielding the cationic charge of nanoparticle-formulated dermal DNA vaccines is essential for antigen expression and immunogenicity. J Controlled Release 141(2):234–240
Vercauteren D, Rejman J, Martens TF, Demeester J, De Smedt SC, Braeckmans K (2012) On the cellular processing of non-viral nanomedicines for nucleic acid delivery: mechanisms and methods. J Controlled Release 161(2):566–581
Verma IM, Somia N (1997) Gene therapy—promises, problems and prospects. Nature 389(6648):239–242
Wang CK, Ho ML, Wang GJ, Chang JK, Chen CH, Fu YC, Fu HH (2009) Controlled-release of rhBMP-2 carriers in the regeneration of osteonecrotic bone. Biomaterials 30(25):4178–4186
Wetzer B, Byk G, Frederic M, Airiau M, Blanche F, Pitard B, Scherman D (2001) Reducible cationic lipids for gene transfer. Biochem J 356(Pt 3):747–756
Yue ZG, Wei W, Lv PP, Yue H, Wang LY, Su ZG, Ma GH (2011) Surface charge affects cellular uptake and intracellular trafficking of chitosan-based nanoparticles. Biomacromolecules 12(7):2440–2446
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support for this research by the Ministry of Economic Affairs, and National Science Council in Taiwan under the Grant Numbers 100-EC-17-A-19-S1-176, NSC 99-2628-E-037-003, and the Kaohsiung Medical University Hospital (KMUH99-9R36, KMUH100-0R40), respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Yan-Hsung Wang and Yin-Chih Fu contributed equally to this study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, YH., Fu, YC., Chiu, HC. et al. Cationic nanoparticles with quaternary ammonium-functionalized PLGA–PEG-based copolymers for potent gene transfection. J Nanopart Res 15, 2077 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-2077-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-2077-4