Abstract
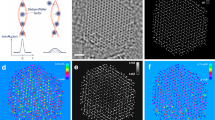
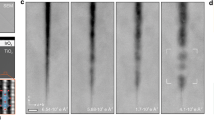
Direct atomic imaging of ultrasmall nanoclusters in three-dimension is challenging, not only because of the low signal to noise ratio, but also of the cluster–probe interaction that is often uncharacterized. Here, we report a study of Au nanoclusters (~3 nm) supported on MgO(100) surface using aberration-corrected scanning transmission electron microscopy. By applying the model-based method on successively acquired images, the number of atoms in the projected atomic columns of a cluster was analyzed, allowing for the reconstruction of its 3D structures. It is found that the total number of atoms within the cluster fluctuated under the intense electron beam and the cluster became strongly elongated along the e-beam illumination direction. This study highlights the importance of atom counting with single atom sensitivity. The reported approach is particularly useful in dealing with practical difficulties associated with the characterization of ultrasmall clusters.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajayan PM, Marks LD (1989a) Experimental-evidence for quasimelting in small particles. Phys Rev Lett 63(3):279–282
Ajayan PM, Marks LD (1989b) Evidence for sinking of small particles into substrates and implications for heterogeneous catalysis. Nature 338(6211):139–141
Barnard AS, Young NP, Kirkland AI, van Huis MA, Xu H (2009) Nanogold: a quantitative phase map. ACS Nano 3(6):1431–1436
Bruma A, Negreiros FR, Xie S, Tsukuda R, Johnston RL, Fortunelli A, Li ZY (2013) Direct atomic imaging and density functional theory study of the Au24Pd1 cluster catalyst. Nanoscale. doi:10.1039/C3NR01852K
Cuenya BR (2010) Synthesis and catalytic properties of metal nanoparticles: size, shape, support, composition, and oxidation state effects. Thin Solid Films 518(12):3127–3150
den Dekker AJ, Van Aert S, van den Bos A, Van Dyck D (2005) Maximum likelihood estimation of structure parameters from high resolution electron microscopy images. Part i: a theoretical framework. Ultramicroscopy 104(2):83–106
Freund HJ (2002) Clusters and islands on oxides: from catalysis via electronics and magnetism to optics. Surf Sci 500(1–3):271–299
Goris B, Van den Bals S, Broek W, Carbo-Argibay E, Gomes-Grana S, Liz-Marzan LM, Van Tendeloo G (2012) Atomic-scale determination of surface facets in gold nanorods. Nat Mater 11:930–935
Han Y, He DS, Liu Y, Xie S, Tsukuda T, Li ZY (2012) Size and shape of nanoclusters: single-shot imaging approach. Small 8(15):2361–2364
Hartel P, Rose H, Dinges C (1996) Conditions and reasons for incoherent imaging in STEM. Ultramicroscopy 63(2):93–114
Haruta M (2004) Gold as a novel catalyst in the 21st century: preparation, working mechanism and applications. Gold Bull 37(1–2):27–36
Henry CR (2005) Morphology of supported nanoparticles. Prog Surf Sci 80(3–4):92–116
Iijima S, Ichihashi T (1986) Structural instability of ultrafine particles of metals. Phys Rev Lett 56(6):616–619
Jones L, Nellist PD (2013) Identifying and correcting scan noise and drift in the scanning transmission electron microscope. Microsc Microanal 2013:1–11
Krivanek OL, Chisholm MF, Nicolosi V, Pennycook TJ, Corbin GJ, Dellby N, Murfitt MF, Own CS, Szilagyi ZS, Oxley MP, Pantelides ST, Pennycook SJ (2010) Atom-by-atom structural and chemical analysis by annular dark-field electron microscopy. Nature 464(7288):571–574
LeBeau JM, Stemmer S (2008) Experimental quantification of annular dark-field images in scanning transmission electron microscopy. Ultramicroscopy 108(12):1653–1658
LeBeau JM, Findlay SD, Allen LJ, Stemmer S (2008) Quantitative atomic resolution scanning transmission electron microscopy. Phys Rev Lett 100:206101
LeBeau JM, Findlay SD, Allen LJ, Stemmer S (2010) Standardless atom counting in scanning transmission electron microscopy. Nano Lett 10(11):4405–4408
Li ZY, Young NP, Di Vece M, Palomba S, Palmer RE, Bleloch AL, Curley BC, Johnston RL, Jiang J, Yuan J (2008) Three-dimensional atomic-scale structure of size-selected gold nanoclusters. Nature 451(7174):46–48
Liu Y, Jia CJ, Yamasaki J, Terasaki O, Schuth F (2010) Highly active iron oxide supported gold catalysts for CO oxidation: how small must the gold nanoparticles be? Angew Chem Int Ed 49(33):5771–5775
Lopez N, Janssens TVW, Clausen BS, Xu Y, Mavrikakis M, Bligaard T, Norskov JK (2004) On the origin of the catalytic activity of gold nanoparticles for low-temperature CO oxidation. J Catal 223(1):232–235
Marks LD (1994) Experimental studies of small-particle structures. Rep Prog Phys 57(6):603–649
McLachlan G, Peel D (2000) Finite mixture models. Wiley, New York
Nellist PD, Pennycook SJ (2000) The principles and interpretation of annular dark-field Z-contrast imaging. Adv Imaging Electron Phys 113:147–203
Pearmain D, Park SJ, Wang ZW, Abdela A, Palmer, Li ZY (2013) Size and shape of industrial Pd catalyst particles using size-selected clusters as mass standards. Appl Phys Lett 102(16):163103
Peng LM, Ren G, Ddarev SL, Whelan MJ (1996) Debye–Waller factors and absorptive scattering factors of elemental cyrstals. Acta Cryst A52:456–470
Smith DJ, Petfordlong AK, Wallenberg LR, Bovin JO (1986) Dynamic atomic-level rearrangements in small gold particles. Science 233(4766):872–875
Turner PS, Bullough TJ, Devenish RW, Maher DM, Humphreys CJ (1990) Nanometer hole formation in MgO using electron-beams. Phil Mag Lett 61(4):181–193
Van Aert S, den Dekker AJ, van den Bos A, Van Dyck D, Chen JH (2005) Maximum likelihood estimation of structure parameters from high resolution electron microscopy images. Part ii: a practical example. Ultramicroscopy 104(2):107–125
Van Aert S, Batenburg KJ, Rossell MD, Erni R, Van Tendeloo G (2011) Three-dimensional atomic imaging of crystalline nanoparticles. Nature 470(7334):372–375
Van Aert S, De Backer A, Martinez GT, Goris B, Bals S, Van Tendeloo G (2013) Procedure to count atoms with trustworthy single-atom sensitivity. Phys Rev B 87:064107
Young NP, Li ZY, Chen Y, Palomba S, Di Vece M, Palmer RE (2008) Weighing supported nanoparticles: size-selected clusters as mass standards in nanometrology. Phys Rev Lett 101(24):246103
Zhou W, Wachs IE, Kiely CJ (2012) Nanostructural and chemical characterization of supported metal oxide catalysts by aberration corrected analytical electron microscopy. Curr Opin Solid State Mat Sci 16(1):10–22
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the financial support from the EPSRC UK (Grant Number EP/G070326/1). The STEM instrument employed in this research was funded through the Birmingham Science City project “Creating and Characterising Next Generation Advanced Materials” by AWM and ERDF. DSH would like to thank the University of Birmingham and the China Scholarship Council for providing the PhD scholarship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Special Issue Editors: Juan Manuel Rojo, Vasileios Koutsos
This article is part of the topical collection on Nanostructured Materials 2012
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, Y., He, D.S. & Li, Z.Y. Direct observation of dynamic events of Au clusters on MgO(100) by HAADF-STEM. J Nanopart Res 15, 1941 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-1941-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-1941-6