Abstract
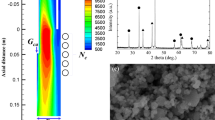
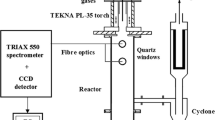
Boron-rich compounds of AlB12 and AlB10 nanoparticles were synthesized by a radiofrequency thermal plasma. Aluminum and boron raw powders were evaporated in virtue of high enthalpy of the thermal plasma in upstream region, followed by the formation of aluminum boride nanoparticles in the tail region of plasma flame with rapid quenching. A high production rate of aluminum boride was confirmed by the X-ray diffraction measurement in the case of high input power, high boron content in raw material and helium inner gas. Polyhedral nanoparticles of 20.8 nm in mean size were observed by a transmission electron microscope. In the raw powder mixture of aluminum, titanium, and boron, titanium-boride nanoparticles were synthesized preferentially, because the Gibbs free energy for the boridation of titanium is lower than that of aluminum. Since the nucleation temperature of boron is higher than that of aluminum, the condensation of metal monomers onto boron nuclei results in the formation of boron-rich aluminum boride nanoparticles.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albert B, Hillebrecht H (2009) Boron: elementary challenge for experimenters and theoreticians. Angew Chem Int Ed 48:8640–8668. doi:10.1002/anie.200903246
Artamonov AY, Bezykornov AI, Ivanov AN (1966) Abrasive power of refractory compounds. Powder Metall Met Ceram 5:722–725. doi:10.1007/BF00774099
Bale CW, Chartrand P, Degterov SA, Eriksson G, Hack K, Mahfoud RB, Melançon J, Pelton AD, Petersen S (2002) FactSage thermochemical software and databases. Calphad 26:189–228. doi:10.1016/j.calphad.2008.09.009
Boulos MI (1991) Thermal plasma processing. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci 19:1078–1089. doi:10.1109/27.125032
Cheng Y, Watanabe T (2011) Synthesis of titanium boride nanoparticles by induction thermal plasmas. J Chem Eng Jpn 44:583–589. doi:10.1252/jcej.10we328
Cheng Y, Shigeta M, Choi S, Watanbe T (2012) Formation mechanism of titanium boride nanoparticles by RF induction thermal plasma. Chem Eng J 183:483–491. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2011.12.040
Girshick SL, Chiu C-P (1990) Kinetic nucleation theory: a new expression for the rate of homogeneous nucleation from an ideal supersaturated vapor. J Chem Phys 93:1273–1277. doi:10.1063/1.459191
Girshick SL, Chiu C-P, AcMurry PH (1990) Time-dependent aerosol models and homogeneous nucleation rates. Aerosol Sci Technol 13:465–477. doi:10.1080/02786829008959461
Higashi I (2000) Crystal chemistry of α-AlB12 and γ-AlB12. J Solid State Chem 154:168–176. doi:10.1006/jssc.2000.8831
Higashi I, Kobayshi M, Takahashi Y, Okada S, Hamano K (1990) Crystal growth of icosahedral B12 compounds from high-temperature metal solutions. J Cryst Growth 99:998–1004. doi:10.1016/S0022-0248(08)80070-X
Huang JY, Ishigaki T, Tanaka T, Horiuchi S (1998) Morphology and microstructure investigations of YB66 nano-particles prepared by plasma chemical process. J Mater Sci 33:4141–4145. doi:10.1023/A:1004453103149
Imai Y, Mukaida M, Ueda M, Watanabe A (2001) Screening of the possible boron-based n-type thermoelectric conversion materials on the basis of the calculated densities of states of metal borides and doped β-boron. Intermetallics 9:721–734. doi:10.1016/S0966-9795(01)00060-7
Kanatzidis MG, Pöttgen R, Jeitschko WT (2005) The Metal flux: a preparative tool for the exploration of intermetallic compounds. Angew Chem Int Ed 44:6996–7023. doi:10.1002/anie.200462170
Kruis FE, Fissan H, Peled A (1998) Synthesis of nanoparticles in the gas phase for electronic, optical and magnetic applications—a review. J Aerosol Sci 29:511–535. doi:10.1016/S0021-8502(97)10032-5
Mann BS (1999) Solid-particle erosion and protective layers for steam turbine blading. Wear 224:8–12. doi:10.1016/S0043-1648(98)00305-6
Munro RG (2000) Material properties of titanium diboride. J Res Natl Inst Stand Technol 105:709–720. doi:10.6028/jres.105.057
Murphy AB (1997) Transport coefficient of helium and argon–helium plasmas. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci 25:809–814. doi:10.1109/27.649574
Murphy AB (2001) Thermal plasmas in gas mixtures. J Phys D 34:R151–R173. doi:10.1088/0022-3727/34/20/201
Shigeta M, Watanabe T (2005) Numerical analysis for co-condensation processes in silicide nanoparticle synthesis using induction thermal plasmas at atmospheric pressure conditions. J Mater Res 20:2801–2811. doi:10.1557/JMR.2005.0351
Swihart MT (2003) Vapor-phase synthesis of nanoparticles. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 8:127–133. doi:10.1016/S1359-0294(03).00007-4
Tromp HJ, Gelderen PV, Kelly PJ, Brocks G, Bobbert PA (2001) CaB6: a new semiconducting material for spin electronics. Phys Rev Lett 87:016401. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.87.016401
Watanabe T, Fujiwara K (2004) Nucleation and growth of oxide nanoparticles prepared by induction thermal plasmas. Chem Eng Commun 191:1343–1361. doi:10.1080/00986440490464264
Watanabe T, Ibe T, Abe Y, Ishii Y, Adachi K (2004) Nucleation mechanism of boride nanoparticles in induction thermal plasmas. Trans Mater Res Soc Jpn 29:3407–3410
Werheit H (1995) Boron-rich solids: a chance for high-efficiency high-temperature thermoelectric energy conversion. Mater Sci Eng B 29:228–232. doi:10.1016/0921-5107(94)04023-W
Xu TT, Zheng JG, Nicholls AW, Stankovich S, Piner RD, Ruoff RS (2004) Single-crystal calcium hexaboride nanowires: synthesis and characterization. Nano Lett 4:2051–2055. doi:10.1021/nl0486620
Yuan Y, Zhang L, Liang L, He K, Liu R, Min G (2011) A solid-state reaction route to prepare LaB6 nanocrystals in vacuum. Ceram Int 37:2891–2896. doi:10.1016/j.ceramint.2011.03.073
Zhang H, Zhang Q, Tang J, Qin LC (2005) Single-crystalline LaB6 nanowires. J Am Chem Soc 127:2862–2863. doi:10.1021/ja043512c
Zhao X, Min G (2009) Low temperature synthesis of BaB6 nanometer powders. Int J Mod Phys B 23:1553–1558. doi:10.1142/S0217979209061251
Zhou S, Zhang J, Liu D, Lin Z, Huang Q, Bao L, Ma R, Wei Y (2010) Synthesis and properties of nanostructured dense LaB6 cathodes by arc plasma and reactive spark plasma sintering. Acta Mater 58:4978–4985. doi:10.1016/j.actamat.2010.05.031
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, S., Matsuo, J., Cheng, Y. et al. Preparation of boron-rich aluminum boride nanoparticles by RF thermal plasma. J Nanopart Res 15, 1820 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-1820-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-1820-1