Abstract
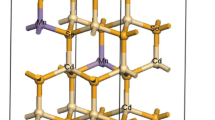
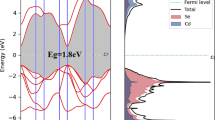
The spin-polarization and magnetic coupling of N-doped CdS nanowires (NWs) with a diameter size of 12.33 Ǻ have been investigated through first-principles calculations. The doped N prefers surface S sites and leads to a half-metallic property. The magnetic interaction between the nearest and the next-nearest N dopants results in a strong ferromagnetic (FM) coupling, while, when the distance between N dopants is larger than 8.0 Ǻ, the ground state of the system tends to be paramagnetic. Also, a nitrogen concentration threshold to produce the FM order is estimated to be 8.3 %. The results of incorporation of N dopants to CdS NWs pave a promising way to realize potential applications in spintronics.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Awschalom D, Flatté ME (2007) Chanllenges for semiconductor spintronics. Nat Phys 3:153–159
Bao NN, Fan HM, Ding J, Yi JB (2011) Room temperature ferromagnetism in N-doped rutile TiO2 films. J Appl Phys 109:07C3021–07C3023
Coey JMD, Chamber SA (2008) Oxide dilute magnetic semiconductors-fact or fiction? MRS Bull 33:1053–1058
Hong NH, Song JH, Raghavender AT, Asaeda T, Kurisu M (2011) Ferromagnetism in C-doped SnO2 thin films. Appl Phys Lett 99:0525051–0525053
Kim JY, Park JH, Park BG, Noh HJ, Oh SJ, Yang JS, Kim DH, Bu SD, Noh TW, Lin HJ, Hsieh HH, Chen CT (2003) Ferromagnetism induced by clustered co in co-doped anatase TiO2 thin films. Phys Rev Lett 90:0174011–0174014
Kresse G, Furthmuller J (1996a) Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set. Phys Rev B 54:11169–11186
Kresse G, Furthmuller J (1996b) Efficiency of ab initio total energy calculations for metals and semiconductors using a plane-wave basis set. Comput Mater Sci 6:15–50
Kresse G, Joubert D (1999) From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented-wave method. Phys Rev B 59:1758–1775
Kudrnovsky J, Turek I, Drchal V, Maca F, Weinberger P, Bruno P (2004) Exchange interactions in III-V and group-IV diluted magnetic semiconductors. Phys Rev B 69:1152081–11520811
Lin Y, Song J, Ding Y, Lu S, Wang ZL (2008) Piezoelectric nanogenerator using CdS nanowires. Appl Phys Lett 92:0221051–0221053
Maca F, Kudrnovsky J, Drchal V, Bouzerar G (2008) Magnetism without magnetic impurities in ZrO2 oxide. Appl Phys Lett 92:2125031–2125033
Monkhorst HJ, Pack JD (1976) Special points for Brillouin-zone integrations Phys. Rev B 13:5188–5192
Pan H, Yi JB, Shen L, Wu RQ, Yang JH, Lin JY, Feng YP, Ding J, Van LH, Yin JH (2007) Room-temperature ferromagnetism in carbon-doped ZnO. Phys Rev Lett 99:1272011–1272014
Pan H, Feng Y, Wu Q, Huang Z, Lin J (2008) Magnetic properties of carbon doped CdS: a first-principles and Monte Carlo study. Phys Rev B 77:1252111–1252114
Slipukhina I, Mavropoulos P, Blugel S, Lezaic M (2011) FerromagneticSpin coupling of 2p impurities in band insulators stabilized by an intersite coulomb interaction: nitrogen-doped MgO. Phys Rev Lett 107:1372031–1372035
Song J, Zhou J, Wang ZL (2006) Piezoelectric and semiconducting coupled power generating process of a single ZnO Belt/Wire. a technology for harvesting electricity from the environment. Nano Lett 6:1656–1662
Tan X, Chen C, Jin K, Luo B (2011) Room-temperature ferromagnetism in nitrogen-doped BaTiO3. J Alloys Compd 509:L311–L313
Wang ZL, Song J (2006) Piezoelectric nanogenerators based on zincoxide nanowire arrays. Science 312:242–246
Wang XD, Song J, Liu J, Wang ZL (2007) Direct-current nanogenerator driven by ultrasonic waves. Science 316:102–105
Wang Q, Sun Q, Jena P (2009) N-doped ZnO thin films and nanowires: energetics, impurity distribution and magnetism. New J Phys 11:0630351–06303514
Wen QY, Zhang HW, Yang QH, Gu DE, Li YX, Liu YL, Shen J, Xiao JQ (2009) Magnetic characteristics of carbon-doped nanocrystalline TiO2. IEEE Trans Magn 45:4096–4099
Yang K, Dai Y, Huang B, Whangbo MH (2008) On the possibility of ferromagnetism in carbon-doped anatase TiO2. Appl Phys Lett 93:1325071–1325073
Zhang CW, Yan SS (2009) First-principles study on ferromagnetism in Mg-doped SnO2. Appl Phys Lett 95:2321081–2321083
Zhang CW, Wang PJ, Su Y (2010) First-principles study on ferromagnetism in nitrogen-doped CdO. Phys Lett A 374:1889–1892
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 61076088 and 11274143), and Technological Development Program in Shandong Province Education Department (Grant No. J10LA16).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, Fb., Zhang, Cw., Yan, Ss. et al. Manipulation of half-metallicity and ferromagnetism in N-doped CdS nanowire. J Nanopart Res 15, 1647 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-1647-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-1647-9