Abstract
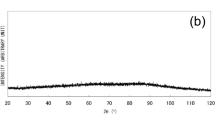
A simple method to precipitate nanoparticles of iron phosphate with acid character has been developed in which the control of pH allows to obtain amorphous nanoparticles. The acid aging of the precipitated amorphous nanoparticles favored the P–O bond strength that contributes to the surface reordering, the surface roughness and the increase of the phosphate acid character. The thermal behavior of the acid iron phosphate nanoparticles has been also studied and the phosphate polymerization at 400 °C produces strong compacts of amorphous nanoparticles with interconnected porosity.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boonchom B, Danvirutai C (2007) Thermal decomposition kinetics of FePO4·3H2O precursor to synthesize spherical nanoparticles FePO4. Ind Eng Chem Res 46:9071–9076. doi:10.1021/ie071107z
Boonchom B, Youngme S, Maensiri S, Danvirutai C (2008) Nanocrystalline serrabrancaite (MnPO4·H2O) prepared by a simple precipitation route at low temperature. J Alloys Compd 454:78–82. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2006.12.064
Boonchom B, Baitahe R, Joungmunkong Z, Vittayakorn N (2010) Grass blade-like microparticle MnPO4·H2O prepared by a simple precipitation at room temperature. Powder Technol 203:310–314. doi:10.1016/j.powtec.2010.05.022
Burrel LS, Johnston CT, Schulze D, Klein J, White JL, Hem SL (2001) Aluminum phosphate adjuvants prepared by precipitation at constant pH. Part I: composition and structure. Vaccine 19:275–281
Fergus JW (2010) Recent developments in cathode materials for lithium ion batteries. J Power Sources 195:939–954. doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2009.08.089
Kang B, Ceder G (2009) Battery materials for ultrafast charging and discharging. Nature 458:190–193. doi:10.1038/nature07853
Lagno F, Demopoulos GP (2005) Synthesis of hydrated aluminum phosphate, AlPO4·1.5H2O (AlPO4–H3), by controlled reactive crystallization in sulfate media. Ind Eng Chem Res 44:8033–8038. doi:10.1021/ie0505559
Laoutid F, Bonnaud L, Alexandre M, Lopez-Cuesta JM, Dubois Ph (2009) New prospects in flame retardant polymer materials: from fundamentals to nanocomposites. Mater Sci Eng R 63:100–125
Lynn AK, Bonfield W (2005) A novel method for the simultaneous, titrant-free control of pH and calcium phosphate mass yield. Acc Chem Res 38:202–207
Wang M, Xue Y, Zhang K, Zhang Y (2011) Synthesis of FePO4·2H2O nanoplates and their usage for fabricating superior high-rate performance LiFePO4. Electrochim Acta 56:4294–4298
Padhi AK, Nanjundaswamy KS, Masquelier C, Okada S, Goodenough JB (1997) Effect of structure on the Fe3+/Fe2+ redox couple in iron phosphates. J Electrochem Soc 144:1609–1613
Prosini PP, Lisi M, Scaccia S, Carewska M, Cardellini F, Pasquali M (2002) Synthesis and characterization of amorphous hydrated FePO4 and Its electrode performance in lithium batteries. J Electrochem Soc 149:A297. doi:10.1149/1.1435359
Ray NH (1979) The structure and properties of inorganic polymeric phosphates. Br Polym J 11:163–177. doi:10.1002/pi.4980110402
Rodríguez-Paéz J, Caballero AC, Villegas M, Moure C, Durán P, Fernández JF (2001) Controlled precipitation methods: formation mechanism of ZnO nanoparticles. J Eur Ceram Soc 21:925–930. doi:10.1016/S0955-2219(00)00283-1
Scaccia S, Carewska M, Prosini PP (2004) Thermoanalytical study of iron(III) phosphate obtained by homogeneous precipitation from different media. Thermochim Acta 413:81–86. doi:10.1016/j.tca.2003.10.024
Shi Z, Attia A, Ye W, Wang Q, Li Y, Yang Y (2008) Synthesis, characterization and electrochemical performance of mesoporous FePO4 as cathode material for rechargeable lithium batteries. Electrochim Acta 53:2665–2673. doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2007.06.079
Socrates G (2001) Infrared and Raman characteristic group frequencies: tables and charts. Wiley, Chichester
Song Y, Zavalij PY, Suzuki M, Whittingham MS (2002) New iron(III) phosphate phases: crystal structure and electrochemical and magnetic properties. Inorg Chem 41:5778–5786
Zhang L, Schlesinger ME, Brow RK (2011) Phase equilibria in the Fe2O3–P2O5 system. J Am Ceram Soc 94:1605–1610. doi:10.1111/j.1551-2916.2010.04287.x
Zhang Y, Du P, Huo Qing, Li Wang, Ai Zhang, Song Y, Lv Y, Li G (2012) Advances in new cathode material LiFePO4 for lithium-ion batteries. Synth Met 162:1315–1326. doi:10.1016/j.synthmet.2012.04.025
Acknowledgments
This work has been financially supported under contract by MAT2010-21088-C03-01. E. Palacios acknowledges the financial support of the JAE (CSIC) fellowship program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Palacios, E., Leret, P., Fernández, J.F. et al. Synthesis of amorphous acid iron phosphate nanoparticles. J Nanopart Res 14, 1131 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-012-1131-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-012-1131-y