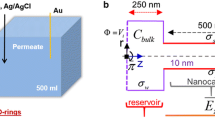
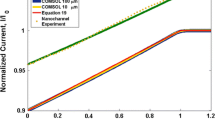
Abstract
Species transport in nanocapillary membrane systems has engaged considerable research interest, presenting technological challenges and opportunities, while exhibiting significant deviations from conventionally well understood bulk behavior in microfluidics. Nonlinear electrokinetic effects and surface charge of materials, along with geometric considerations, dominate the phenomena in structures with characteristic lengths below 100 nm. Consequently, these methods have enabled 3D micro- and nanofluidic hybrid systems with high-chemical selectivity for precise manipulation of mass-limited quantities of analytes. In this review, we present an overview of both fundamental developments and applications of these unique nanocapillary systems, identifying forces that govern ion and particle transport, and surveying applications in separation, sensing, mixing, and chemical reactions. All of these developments are oriented toward adding important functionality in micro-total analysis systems.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adiga SP, Jin CM, Curtiss LA, Monteiro-Riviere NA, Narayan RJ (2009) Nanoporous membranes for medical and biological applications. WIREs Nanomed Nanobiotechnol 1:568–581
Agerbaek M, Keiding K (1995) Streaming potential during cake filtration of slightly compressible particles. J Colloid Interface Sci 169:255–342
Ali M, Tahir MN, Siwy ZS, Neumann R, Tremel W, Ensinger W (2011) Hydrogen peroxide sensing with horseradish peroxidase-modified polymer single conical nanochannels. Anal Chem 83:1673–1680
Bohn PW (2009) Nanoscale control and manipulation of molecular transport in chemical analysis. Annu Rev Anal Chem 2:279–296
Boukany PE, Morss A, Liao W, Henslee B, Jung H, Zhang X, Yu B, Wang X, Wu Y, Li L, Gao K, Hu X, Zhao X, Hemminger O, Lu W, Lafyatis GP, Lee LJ (2011) Nanochannel electroporation delivers precise amounts of biomolecules into living cells. Nat Nanotechnol 6:747–754
Bowski L, Saini R, Ryu D, Vieth W (1971) Kinetic modeling of hydrolysis of sucrose by invertase. Biotechnol Bioeng 13:641–656
Burgmayer P, Murray RW (1982) An ion gate membrane: electrochemical control of ion permeability through a membrane with an embedded electrode. J Am Chem Soc 4:6139–6140
Burgreen D, Nakache F (1964) Electrokinetic flow in ultrafine capillary slits. J Phys Chem 68:1084–1091
Buyukserin F, Kohli P, Wirtz M, Martin C (2007) Electroactive nanotube membranes and redox-gating. Small 3:266–270
Cannon DM Jr, Kuo T-C, Bohn PW, Sweedler JV (2003) Nanocapillary array interconnects for gated analyte injections and electrophoretic separations in multilayer microfluidic architectures. Anal Chem 75:2224–2230
Cervera J, Patricio R, Manzanares JA, Mafe S (2010) Incorporating ionic size in the transport equations for charged nanopores. Microfluid Nanofluid 9:41–53
Chang I-H, Tulock JJ, Liu J, Cannon DM Jr, Bohn PW, Sweedler JV, Cropeck DM (2005) Miniaturized lead sensor based on lead-specific DNAzyme in a nanocapillary interconnected microfluidic device. Environ Sci Technol 39:3756–3761
Chatterjee AN, Cannon DM Jr, Gatimu EN, Sweedler JV, Aluru NR, Bohn PW (2005) Modeling and simulation of ionic currents in three-dimensional microfluidic devices with nanofluidic interconnects. J Nanopart Res 7:507–516
Chowdiah P, Wasan D, Gidaspow D (1983) On the interpretation of streaming potential data in nonaqueous media. Colloids Surf 7:291–299
Chun K-Y, Stroeve P (2002) Protein transport in nanoporous membranes modified with self-assembled monolayers of functionalized thiols. Langmuir 18:4653–4658
Chun K-Y, Mafe S, Ramirez P, Stroeve P (2006) Protein transport through gold-coated, charged nanopores: Effects of applied voltage. Chem Phys Lett 418:561–564
Conlisk AT (2005) The Debye-Huckel approximation: Its use in describing electroosmotic flow in micro- and nanochannels. Eletrophoresis 26:1896–1912
Conlisk AT (2012) Essentials of micro- and nanofluidics: with applications to the biological and chemical sciences. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Conlisk AT, McFerran J, Zheng Z, Hansford D (2002) Mass transfer and flow in electrically charged micro- and nano-channels. Anal Chem 74:2139–2150
Conlisk AT, Kumar A, Rampersaud A (2007) Ionic and biomolecular transport in nanochannels. Nanoscale Microscale Thermophys Eng 11:177–199
Contento NM, Branagan SP, Bohn PW (2011) Electrolysis in nanochannels for in situ reagent generation in confined geometries. Lab Chip 11:3634–3641
Daiguji H, Oka Y, Shirono K (2005) Nanofluidic diode and bipolar transistor. Nano Lett 5:2274–2280
Datta S, Conlisk AT, Kanani DM, Zydney AL, Fissell WH, Roy S (2010) Characterizing the surface charge of synthetic nanomembranes by the streaming potential method. J Colloid Interface Sci 348:85–95
Dhathathreyan A (2011) Real-time monitoring of invertase activity immobilized in nanoporous aluminum oxide. J Phys Chem B 115:6678–6682
Fa K, Tulock JJ, Sweedler JV, Bohn PW (2005) Profiling pH gradients across nanocapillary array membranes connecting microfluidic channels. J Am Chem Soc 127:13928–13933
Fievet P, Szymczyk A, Aoubiza B, Pagetti J (2000) Evaluation of three methods for the characterisation of the membrane-solution interface: streaming potential, membrane potential and electrolyte conductivity inside pores. J Membr Sci 168:87–100
Flachsbart BR, Wong K, Iannacone JM, Abante EN, Vlach RI, Rauchfuss PA, Bohn PW, Sweedler JV, Shannon MA (2006) Design and fabrication of a multilayered polymer microfluidic chip with nanofluidic interconnects via adhesive contact printing. Lab Chip 6:667–674
Gong M, Flachsbart BR, Shannon MA, Bohn PW, Sweedler JV (2008a) Fluidic communication between multiple vertically segregated microfluidic channels connected by nanocapillary array membranes. Electrophoresis 29:1237–1244
Gong M, Kim BY, Flachsbart BR, Shannon MA, Bohn PW, Sweedler JV (2008b) An on-chip fluorogenic enzyme assay using a multilayer microchip interconnected with a nanocapillary array membrane. IEEE Sens J 8:601–607
Han J, Fu J, Schoch RB (2008) Molecular sieving using nanofilters: past, present and future. Lab Chip 8:23–33
He Y, Gillespie D, Boda D, Vlassiouk I, Eisenberg RS, Siwy ZS (2009) Tuning transport properties of nanofluidic devices with local charge inversion. J Am Chem Soc 131:5194–5202
Huang S, Yin Y (2006) Transport and separation of small organic molecules through nanotubules. Anal Sci 22:1005–1009
Huisman IH, Pradanos P, Calvo JI, Hernandez A (2000) Electroviscous effects, streaming potential, and zeta potential in polycarbonate track-etched membranes. J Membr Sci 178:79–92
Hulteen JC, Jirage KB, Martin CR (1998) Introducing chemical transport selectivity into gold nanotubule membranes. J Am Chem Soc 120:6603–6604
Jagerszki G, Gyurcsanyi R, Hofler L, Pretsch E (2007) Hybridization-modulated ion fluxes through peptide-nucleic-acid-functionalized gold nanotubes. A new approach to quantitative label-free DNA analysis. Nano Lett 7:1609–1612
Jirage KB, Hulteen JC, Martin CR (1999) Effect of thiol chemisorption on the transport properties of gold nanotubule membranes. Anal Chem 71:4913–4918
Karnik R, Fan R, Yue M, Li D, Yang P, Majumdar A (2005) Electrostatic control of ions and molecules in nanofluidic transistors. Nano Lett 5:943–948
Karnik R, Castelino K, Majumdar A (2006) Field-effect control of protein transport in a nanofluidic transistor circuit. Appl Phys Lett 88:123114
Kemery PJ, Steehler JK, Bohn PW (1998) Electric field mediated transport in nanometer diameter channels. Langmuir 14:2884–2889
Khandurina J, Jacobson SC, Waters LC, Foote RS, Ramsey JM (1999) Microfabricated porous membrane structure for sample concentration and electrophoretic analysis. Anal Chem 71:1815–1819
Kim BY, Swearingen CB, Ho JA, Romanova EV, Bohn PW, Sweedler JV (2007) Direct immobilization of Fab’ in nanocapillaries for manipulating mass-limited samples. J Am Chem Soc 129:7620–7626
Kim BY, Yang J, Gong M, Flachsbart BR, Shannon MA, Bohn PW, Sweedler JV (2009) Multidimensional separation of chiral amino acid mixtures in a multilayered three-dimensional hybrid microfluidic/nanofluidic device. Anal Chem 81:2715–2722
Kim S, Ko S, Kang K, Han J (2010) Direct seawater desalination by ion concentration polarization. Nat Nanotechnol 5:297–301
Kohli P, Harrell CC, Cao Z, Gasparac R, Tan W, Martin CR (2004) DNA-functionalized nanotube membranes with single-base mismatch selectivity. Science 305:984–986
Ku J-R, Lai S-M, Ileri N, Ramirez P, Mafe S, Stroeve P (2007) pH and ionic strength effects on amino acid transport through Au-nanotubule membranes charged with self-assembled monolayers. J Phys Chem C 111:2965–2973
Kuo T-C, Sloan LA, Sweedler JV, Bohn PW (2001) Manipulating molecular transport through nanoporous membranes by control of electrokinetic flow- effect of surface charge density and Debye length. Langmuir 17:6298–6303
Kuo T-C, Cannon DM Jr, Chen Y, Tulock JJ, Shannon MA, Sweedler JV, Bohn PW (2003a) Gateable nanofluidic interconnects for multilayered microfluidic separation systems. Anal Chem 75:1861–1867
Kuo T-C, Cannon DM Jr, Shannon MA, Bohn PW, Sweedler JV (2003b) Hybrid three-dimensional nanofluidic/microfluidic devices using molecular gates. Sens Actuators, A 102:223–233
Kuo T-C, Kim H-K, Cannon DM Jr, Shannon MA, Sweedler JV, Bohn PW (2004) Nanocapillary arrays effect mixing and reaction in multilayer fluidic structures. Angew Chem 116:1898–1901
Lee SB, Martin CR (2002) Electromodulated molecular transport in gold-nanotube membranes. J Am Chem Soc 124:11850–11851
Lokuge I, Wang X, Bohn PW (2007) Temperature-controlled flow switching in nanocapillary array membranes mediated by poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) polymer brushes grafted by atom transfer radical polymerization. Langmuir 23:305–311
Lu Y, Liu J (2006) Functional DNA nanotechnology: emerging applications of DNAzymes and aptamers. Curr Opin Biotechnol 17:580–588
Martin CR, Nishizawa M, Jirage K, Kang MS, Lee SB (2001a) Controlling ion-transport selectivity in gold nanotubule membranes. Adv Mater 13:1351–1362
Martin CR, Nishizawa M, Jirage K, Kang M (2001b) Investigations of the transport properties of gold nanotubule membranes. J Phys Chem B 105:1925–1934
Mulero R, Prabhu AS, Freedman KJ, Kim MJ (2010) Nanopore-based devices for bioanalytical applications. JALA 15:243–252
Nam S-W, Rooks MJ, Kim K-B, Rossnagel SM (2009) Ionic field effect transistors with sub-10 nm multiple nanopores. Nano Lett 9:2044–2048
Napoli M, Eijkel J, Pennathur S (2010) Nanofluidic technology for biomolecule applications: a critical review. Lab Chip 10:957–985
Nishizawa M, Menon VP, Martin CR (1995) Metal nanotubule membranes with electrochemically switchable ion-transport selectivity. Science 268:700–702
Nystrom M, Lindstrom M, Matthiasson E (1989) Streaming potential as a tool in the characterization of ultrafiltration membranes. Colloids Surf 36:297–312
Oukhaled A, Cressiot B, Bacri L, Pastoriza-Gallego M, Betton J-M, Bourhis E, Jede R, Gierak J, Auvray L, Pelta J (2011) Dynamics of completely unfolded and native proteins through solid-state nanopores as a function of electric driving force. ACS Nano 5:3628–3638
Pardon G, van der Wijngaart W (2011) Electrostatic gating of ion and molecule transport through a nanochannel-array membrane. Proc IEEE Solid-State Sens Actuators Microsyst Conf (Transducers) Beijing, China, pp 1610-1613
Perera DNT, Ito T (2010) Cyclic voltammetry on recessed nanodisk-array electrodes prepared from track-etched polycarbonate membranes with 10-nm diameter pores. Analyst 135:172–176
Piruska A, Branagan SP, Cropek DM, Sweedler JV, Bohn PW (2008) Electrokinetically driven fluidic transport in integrated three-dimensional microfluidic devices incorporating gold-coated nanocapillary array membranes. Lab Chip 8:1625–1631
Piruska A, Branagan SP, Minnis AB, Wang Z, Cropeck DM, Sweedler JV, Bohn PW (2010a) Electrokinetic control of fluid transport in gold-coated nanocapillary array membranes in hybrid nanofluidic-microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 10:1237–1244
Piruska A, Gong M, Sweedler JV, Bohn PW (2010b) Nanofluidics in chemical analysis. Chem Soc Rev 39:1060–1072
Plecis A, Schoch RB, Renaud P (2005) Ionic transport phenomena in nanofluidics: experimental and theoretical study of the exclusion-enrichment effect on a chip. Nano Lett 5:1147–1155
Powell MR, Cleary L, Davenport M, Shea KJ, Siwy ZS (2011) Electric-field-induced wetting and dewetting in single hydrophobic nanopores. Nat Nanotechnol 6:798–802
Prakash S, Yeom J, Jin N, Adesida I, Shannon MA (2007) Characterization of ionic transport at the nanoscale. Proc ASME IMECE, N: J Nanoeng Nanosyst 220:45–52
Prakash S, Piruska A, Gatimu EN, Bohn PW, Sweedler JV, Shannon MA (2008) Nanofluidics: Systems and Applications. IEEE Sens J 8:441–450
Prakash S, Karacor M, Benerjee S (2009) Surface modification in microsystems and nanosystems. Surf Sci Rep 64:233–254
Prakash S, Pinti M, Bellman K (2012a) Variable cross-section nanopores fabricated in silicon nitride membranes using a transmission electron microscope. J Micromech Microeng in press
Prakash S, Pinti M, Bhushan B (2012b) Theory, fabrication and applications of microfluidic and nanofluidic biosensors. Philos Trans R Soc London, Ser A 370:2269–2303
Qiao R, Aluru N (2003) Ion concentration and velocity in nanochannel electroosmotic flows. J Chem Phys 118:4692–4701
Qiao R, Aluru N (2004) Charge inversion and flow reversal in a nanochannel electroosmotic flow. Phys Rev Lett 92:198301
Qiao R, Georgiadis J, Aluru N (2006) Differential ion transport induced electroosmosis and internal recirculation in heterogeneous osmosis membranes. Nano Lett 6:995–999
Renkin E (1954) Filtration, diffusion, and molecular sieving through porous cellulose membranes. J Gen Physiol 38:225–243
Rice C, Whitehead R (1965) Electrokinetic flow in a narrow cylindrical capillary. J Phys Chem 69:4017–4024
Sadr R, Yoda M, Gnanaprakasam P, Conlisk AT (2006) Velocity measurements inside the diffuse electric double layer in electro-osmotic flow. Appl Phys Lett 89:044103
Schasfoort RB, Schlautmann S, Hendrikse J, van den Berg A (1999) Field-effect flow control for microfabricated fluidic networks. Science 286:942–944
Schibel AE, Heider EC, Harris JM, White HS (2011) Fluorescence microscopy of the pressure-dependent structure of lipid bilayers suspended across conical nanopores. J Am Chem Soc 133:7810–7815
Schoch RB, Han J, Renaud P (2008) Transport phenomena in nanofluidics. Rev Mod Phys 80:839–883
Shannon MA, Flachsbart BR, Iannacone JM, Wong K, Cannon Jr DM, Fa K, Sweedler JV, Bohn PW (2005) Nanofluidic interconnects within a multilayer microfluidic chip for attomolar biochemical analysis and molecular manipulation. Proc 3rd Ann IEEE Int EMBS Special Topic Conf Microtechnol Medicine Biology Kahuhu, pp 257-259
Shannon MA, Bohn PW, Elimelech M, Georgiadis JG, Marinas BJ (2008) Science and technology for water purification in the coming decades. Nature 452:301–310
Sparreboom W, van den Berg A, Eijkel J (2009) Principles and applications of nanofluidic transport. Nat Nanotechnol 4:713–720
Sparreboom W, van den Berg A, Eijkel J (2010) Transport in nanofluidic systems: a review of theory and applications. New J Phys 12:015004
Szymczyk A, Aoubiza B, Fievet P, Pagetti J (1999) Electrokinetic phenomena in homogeneous cylindrical pores. J Colloid Interface Sci 216:285–296
Talaga DS, Li J (2009) Single-Molecule Protein Unfolding in Solid State Nanopores. J Am Chem Soc 131:9287–9297
Tulock JJ, Shannon MA, Bohn PW, Sweedler JV (2004) Microfluidic Separation and Gateable Fraction Collection for Mass-Limited Samples. Anal Chem 76:6419–6425
Vitarelli M, Prakash S, Talaga D (2011) Determining nanocapillary geometry from electrochemical impedance spectroscopy using a variable topology network circuit model. Anal Chem 83:533–541
Vlassiouk I, Siwy ZS (2007) Nanofluidic diode. Nano Lett 7:552–556
Wang Y-C, Stevens A, Han J (2005) Million-fold preconcentration of proteins and peptides by nanofluidic filter. Anal Chem 77:4293–4299
Wang Z, King TL, Branagan SP, Bohn PW (2009) Enzymatic activity of surface-immobilized horseradish peroxidase confined to micrometer- to nanometer-scale structures in nanocapillary array membranes. Analyst 134:851–859
Wernette DP, Swearingen CB, Cropek DM, Lu Y, Sweedler JV, Bohn PW (2006) Incorporation of a DNAzyme into Au-coated nanocapillary array membranes with an internal standard for Pb(II) sensing. Analyst 131:41–47
Yan R, Liang W, Fan R, Yang P (2009) Nanofluidic diodes based on nanotube heterojunctions. Nano Lett 9:3820–3825
Zhang Y, Timperman AT (2003) Integration of nanocapillary arrays into microfluidic devices for use as analyte concentrators. Analyst 128:537–542
Acknowledgments
Mark Shannon and Vikhram Swaminathan acknowledge support through WaterCAMPWS, Center for Advanced Materials for the Purification of Water with Systems, a US National Science Foundation funded Science and Technology Center under contract CTS-0120978, and the US Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency under grant W911NF-09-C-0079. The portion of this study conducted at the University of Notre Dame was supported by the US National Science Foundation under grants DBI 0852741 and CBET 0120978, by the US Department of Energy Office of Basic Energy Sciences DE FG02 07ER15851, and by the US Army Corps of Engineers contract W9132-10-0010. Shaurya Prakash and Marie Pinti acknowledge partial support through the US Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency grant W911NF-09-C-0079.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Special Issue Editors: Mamadou Diallo, Neil Fromer, Myung S. Jhon
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Nanotechnology for Sustainable Development
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Swaminathan, V.V., Gibson, L.R., Pinti, M. et al. Ionic transport in nanocapillary membrane systems. J Nanopart Res 14, 951 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-012-0951-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-012-0951-0