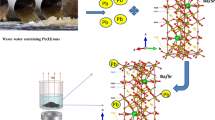
Abstract
Nanoscale magnetite (Fe3O4) (<15 nm) is known to remove arsenic efficiently but is very difficult to separate or require high magnetic fields to separate out from the waste water after treatment. Anisotropic hexagonal ferrite (BaFe12O19, BHF) is a well-known permanent magnet (i.e., fridge magnets) and attractive due to its low cost in making large quantities. BHF offers a viable alternative to magnetite nanocrystals for arsenic removal since it features surfaces similar to iron oxides but with much enhanced magnetism. Herein, we employ BHF nanocrystalline materials for the first time in arsenic removal from wastewater. Our results show better (75 %) arsenic removal than magnetite of the similar sizes. The BHF nanoparticles, 6.06 ± 0.52 nm synthesized by thermolysis method at 320 °C do not show hexagonal phase, however, subsequent annealing at 750 °C produced pure hexagonal BHF in >200 nm assemblies. By using BHF, we demonstrate that nanoparticle removal is more efficient and fixed bed type cartridge applications are more possible.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acharyya SK, Chatraborty P, Lahiri S, Raymahashay BC, Guha S, Bhowmik A (1999) Arsenic poisoning in the Ganges delta. Nature 401:545–546
Bao N, Shen L, Wang Y, Padhan P, Gupta A (2007) A facile thermolysis route to monodisperse ferrite nanocrystals. J Am Chem Soc 129:12374–12375
Beker U, Cumbal L, Duranoglu D, Kucuk I, Sengupta AK (2010) Preparation of Fe oxide nanoparticles for environmental applications: arsenic removal. Environ Geochem Health 32:291–296
Bhakat PB, Gupta AK, Ayoob S, Kundu S (2006) Investigations on arsenic(V) removal by modified calcined bauxite. Colloids Surf A 281:237–245
Biswas BK, Inoue J, Inoue K, Ghimire KN, Harada H, Ohto K, Kawakita H (2008) Adsorptive removal of As(V) and As(III) from water by a Zr(IV)-loaded orange waste gel. J Hazard Mater 154:1066–1074
Borah D, Satokawa S, Kato S, Kojima T (2009) Sorption of As(V) from aqueous solution using acid modified carbon black. J Hazard Mater 162:1269–1277
Cumbal L, Greenleaf J, Leun D, SenGupta AK (2003) Polymer supported inorganic nanoparticles: characterization and environmental applications. React Funct Polym 54:167–180
Hessien MM, Rashad MM, El-Barawy K (2008) Controlling the composition and magnetic properties of strontium hexaferrite synthesized by co-precipitation method. J Magn Magn Mater 320:336–343
Hyeon T, Chung Y, Park J, Lee SS, Kim Y-W, Park BH (2002) Synthesis of highly crystalline and monodisperse cobalt ferrite nanocrystals. J Phys Chem B 106:6831–6833
Junliang L, Yanwei Z, Cuijing G, Wei Z, Xiaowei Y (2010) One-step synthesis of barium hexaferrite nano-powders via microwave-assisted sol–gel auto-combustion. J Eur Ceram Soc 30:993–997
Kwon SG, Hyeon T (2008) Colloidal chemical synthesis and formation kinetics of uniformly sized nanocrystals of metals, oxides, and chalcogenides. Acc Chem Res 41(12):1696–1709
Li Z, Beachner R, McManama Z, Hanlie H (2007) Sorption of arsenic by surfactant-modified zeolite and kaolinite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 105:291–297
Lim S-F, Zheng Y-M, Paul Chen J (2009) Organic arsenic adsorption onto a magnetic sorbent. Langmuir 25(9):4973–4978
Mayo JT, Yavuz C, Yean S, Cong L, Shipley H, Yu W, Falkner J, Kan A, Tomson M, Colvin VL (2007) The effect of nanocrystalline magnetite size on arsenic removal. Sci Technol Adv Mater 8:71–75
Mohan D, Pittman CU Jr (2007) Arsenic removal from water/wastewater using adsorbents—a critical review. J Hazard Mater 142(1–2):1–53
Patel HA, Bajaj HC, Jasra RV (2008) Synthesis of Pd and Rh metal nanoparticles in the interlayer space of organically modified montmorillonite. J Nanopart Res 10:625–632
Pena ME, Korfiatis GP, Patel M, Lippincott L, Meng X (2005) Adsorption of As(V) and As(III) by nanocrystalline, Titanium dioxide. Water Res 39:2327–2337
Phu ND, Phong PC, Chau N, Luong NH, Hoang LH, Hai NH (2009) Arsenic removal from water by magnetic Fe1−xCoxFe2O4 and Fe1−yNiyFe2O4 nanoparticles. J Exp Nanosci 4(3):253–258
Ranjan D, Talat M, Hasan SH (2009) Biosorption of arsenic from aqueous solution using agricultural residue ‘rice polish’. J Hazard Mater 166:1050–1059
Sharma VK, Sohn M (2009) Aquatic arsenic: toxicity, speciation, transformations, and remediation. Environ Int 35:743–759
Shipley HJ, Engates KE, Guettner AM (2011) Study of iron oxide nanoparticles in soil for remediation of arsenic. J Nanopart Res 13:2387–2397
Tang W, Li Q, Li C, Gao S, Shang JK (2011) Ultrafine α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles grown in confinement of in situ self-formed ‘‘cage’’ and their superior adsorption performance on arsenic(III). J Nanopart Res 13:2641–2651
Tucek J, Zboril R, Namai A, Ohkoshi S (2010) ε-Fe2O3: an advanced nanomaterial exhibiting giant coercive field, millimeter-wave ferromagnetic resonance, and magnetoelectric coupling. Chem Mater 22:6483–6505
Yavuz CT, Mayo JT, Yu WW, Prakash A, Falkner JC, Yean S, Cong L, Shipley HJ, Kan A, Tomson M, Natelson D, Colvin VL (2006) Low-field magnetic separation of monodisperse Fe3O4 nanocrystals. Science 314:964–967
Yavuz CT, Prakash A, Mayo JT, Colvin VL (2009) Magnetic separations: from steel plants to biotechnology. Chem Eng Sci 64:2510–2521
Yavuz CT, Mayo JT, Suchecki C, Wang J, Ellsworth AZ, D’Couto H, Quevedo E, Prakash A, Gonzalez L, Nguyen C, Kelty C, Colvin VL (2010) Pollution magnet: nano-magnetite for arsenic removal from drinking water. Environ Geochem Health 32:327–334
Yean S, Cong L, Yavuz CT, Mayo JT, Yu WW, Colvin VL, Tomson MB (2005) Effect of magnetite particle size on adsorption and desorption of arsenite and arsenate. J Mater Res 20(12):3255–3264
Zeng H, Li J, Liu JP, Wang ZL, Sun S (2002) Exchange-coupled nanocomposite magnets by nanoparticles self-assembly. Nature 420:395–398
Zhao X, Wang J, Wub F, Wang T, Cai Y, Shi Y, Jiang G (2010) Removal of fluoride from aqueous media by Fe3O4@Al(OH)3 magnetic nanoparticles. J Hazard Mater 173:102–109
Zhao X, Guo X, Yang Z, Liu H, Qian Q (2011) Phase-controlled preparation of iron (oxyhydr)oxide nanocrystallines for heavy metal removal. J Nanopart Res 13:2853–2864
Acknowledgments
This study is supported by KAIST EEWS Initiative 2011–2013 for the development of enhanced water treatment technologies by nanoscale ferrites and their carbon assemblies. This work was also supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea Grant funded by the Korean Government (MEST) (NRF-2012-C1AAA001-M1A2A2026588).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Special Issue Editors: Mamadou Diallo, Neil Fromer, Myung S. Jhon
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Nanotechnology for Sustainable Development
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patel, H.A., Byun, J. & Yavuz, C.T. Arsenic removal by magnetic nanocrystalline barium hexaferrite. J Nanopart Res 14, 881 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-012-0881-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-012-0881-x