Abstract
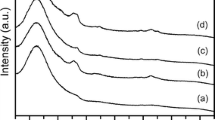
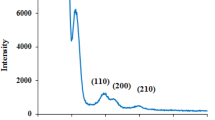
The electronics industry is one of the world’s fastest growing manufacturing industries. However, e-waste has become a serious pollution problem. This study reports the recovery of e-waste for preparing valuable MCM-48 and ordered mesoporous carbon for the first time. Specifically, this study adopts an alkali-extracted method to obtain sodium silicate precursors from electronic packaging resin ash. The influence of synthesis variables such as gelation pH, neutral/cationic surfactant ratio, hydrothermal treatment temperature, and calcination temperature on the mesophase of MCM-48 materials is investigated. Experimental results confirm that well-ordered cubic MCM-48 materials were synthesized in strongly acidic and strongly basic media. The resulting mesoporous silica had a high surface area of 1,317 m2/g, mean pore size of about 3.0 nm, and a high purity of 99.87 wt%. Ordered mesoporous carbon with high surface area (1,715 m2/g) and uniform pore size of CMK-1 type was successfully prepared by impregnating MCM-48 template using the resin waste. The carbon structure was sensitive to the sulfuric acid concentration and carbonization temperature. Converting e-waste into MCM-48 materials not only eliminates the disposal problem of e-waste, but also transforms industrial waste into a useful nanomaterial.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhagiyalakshmi M, Yun LJ, Anuradha R, Jang HT (2010a) Utilization of rice husk ash as silica source for the synthesis of mesoporous silicas and their application to CO2 adsorption through TREN/TEPA grafting. J Hazard Mater 175:928–938
Bhagiyalakshmi M, Lee JY, Jang HT (2010b) Synthesis of mesoporous magnesium oxide: Its application to CO2 chemisorption. Int J Greenh Gas Control 4:51–56
Brinker CJ, Scherer GW (1990) Applications. In: Sol–gel science, the physics and chemistry of sol–gel processing. Academic Press, Inc., San Diego
Chandrasekar G, Ahn WS (2008) Synthesis of cubic mesoporous silica and carbon using fly ash. J Non-Cryst Solids 354:4027–4030
Chen D, Bi X, Liu M, Huang B, Sheng G, Fu J (2011) Phase partitioning, concentration variation and risk assessment of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in the atmosphere of an e-waste recycling site. Chemosphere 82:1246–1252
Cui J, Zhang L (2008) Metallurgical recovery of metals from electronic waste: a review. J Hazard Mater 158:228–256
Dai M, Song L, LaBelle JT, Vogt BD (2011) Ordered mesoporous carbon composite films containing cobalt oxide and vanadia for electrochemical applications. Chem Mater 23:2869–2878
Doyle A, Hodnett BK (2003) Stability of MCM-48 in aqueous solution as a function of pH. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 63:53–57
Doyle AM, Ahmed E, Hodnett BK (2006) The evolution of phases during the synthesis of the organically modified catalyst support MCM-48. Catal Today 116:50–55
Han S, Xu J, Hou W, Yu X, Wang Y (2004) Synthesis of high-quality MCM-48 mesoporous silica using gemini surfactant dimethylene-1,2-bis(dodecyldimethylammonium bromide). J Phys Chem B 108:15043–15048
Hao GP, Li WC, Wang S, Zhang S, Lu AH (2010) Tubular structured ordered mesoporous carbon as an efficient sorbent for the removal of dyes from aqueous solutions. Carbon 48:3330–3339
Hussain M, Ihm SK (2009) Synthesis, characterization, and hydrodesulfurization activity of new mesoporous carbon supported transition metal sulfide catalysts. Ind Eng Chem Res 48:698–707
Jang HT, Park YK, Ko YS, Lee JY, Margandan B (2009) Highly siliceous MCM-48 from rice husk ash for CO2 adsorption. Int J Greenh Gas Control 3:545–549
Joo SH, Jun S, Ryoo R (2001) Synthesis of ordered mesoporous carbon molecular sieves CMK-1. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 44–45:153–158
Kaneda M, Tsubakiyama T, Carlsson A, Sakamoto Y, Ohsuna T, Terasaki O, Joo SH, Ryoo R (2002) Structural study of mesoporous MCM-48 and carbon networks synthesized in the spaces of MCM-48 by electron crystallography. J Phys Chem B 106:1256–1266
Kim TW, Chung PW, Slowing II, Tsunoda M, Yeung ES, Lin VSY (2008) Structurally ordered mesoporous carbon nanoparticles as transmembrane delivery vehicle in human cancer cells. Nano Lett 8:3724–3727
Kim H, Karkamkar A, Autrey T, Chupas P, Proffen T (2009) Determination of structure and phase transition of light element nanocomposites in mesoporous silica: case study of NH3BH3 in MCM-41. J Am Chem Soc 131:13749–13755
Kim HJ, Han B, Kim YJ, Yoa SJ (2010) Characteristics of an electrostatic precipitator for submicron particles using non-metallic electrodes and collection plates. J Aerosol Sci 41:987–997
Kruk M, Jaroniec M, Ryoo R, Joo SH (2000) Characterization of MCM-48 silicas with tailored pore sizes synthesized via a highly efficient procedure. Chem Mater 12:1414–1421
Lelong G, Bhattacharyya S, Kline S, Cacciaguerra T, Gonzalez MA, Saboungi ML (2008) Effect of surfactant concentration on the morphology and texture of MCM-41 materials. J Phys Chem C 112:10674–10680
Liou TH (2003) Pyrolysis kinetics of electronic packaging material in a nitrogen atmosphere. J Hazard Mater 103:107–123
Liou TH (2004) Kinetics study of thermal decomposition of electronic packaging material. Chem Eng J 98:39–51
Liou TH (2010) Development of mesoporous structure and high adsorption capacity of biomass-based activated carbon by phosphoric acid and zinc chloride activation. Chem Eng J 158:129–142
Liou TH (2011) A green route to preparation of MCM-41 silicas with well-ordered mesostructure controlled in acidic and alkaline environments. Chem Eng J 171:1458–1468
Liou TH, Wu SJ (2009) Characteristics of microporous/mesoporous carbons prepared from rice husk under base- and acid-treated conditions. J Hazard Mater 171:693–703
Liou TH, Wu SJ (2010) Kinetics study and characteristics of silica nano-particles produced from biomass-based material. Ind Eng Chem Res 49:8379–8387
Liou TH, Yang CC (2011) Synthesis and surface characteristics of nanosilica produced from alkali-extracted rice husk ash. Mater Sci Eng B-Adv 176:521–529
Liu X, Du Y, Guo Z, Gunasekaran S, Ching CB, Chen Y, Leong SSJ, Yang Y (2009) Monodispersed MCM-41 large particles by modified pseudomorphic transformation: direct diamine functionalization and application in protein bioseparation. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 122:114–120
Liu A, Han S, Che H, Hua L (2010) Fluorescent hybrid with electron acceptor methylene viologen units inside the pore walls of mesoporous MCM-48 silica. Langmuir 26:3555–3561
Peña ML, Kan Q, Corma A, Rey F (2001) Synthesis of cubic mesoporous MCM-48 materials from the system SiO2:CTAOH/Br:H2O. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 44–45:9–16
Peng X, Cao D, Wang W (2008) Heterogeneity characterization of ordered mesoporous carbon adsorbent CMK-1 for methane and hydrogen storage: GCMC simulation and comparison with experiment. J Phys Chem C 112:13024–13036
Petitto C, Galarneau A, Driole MF, Chiche B, Alonso B, Renzo FD, Fajula F (2005) Synthesis of discrete micrometer-sized spherical particles of MCM-48. Chem Mater 17:2120–2130
Prasanth KP, Raj MC, Bajaj HC, Kim TH, Jasra RV (2010) Hydrogen sorption in transition metal modified mesoporous materials. Int J Hydrogen Energy 35:2351–2360
Ryoo R, Joo SH, Kim JM (1999) Energetically favored formation of MCM-48 from cationic—neutral surfactant mixtures. J Phys Chem B 103:7435–7440
Ryoo R, Joo SH, Kruk M, Jaroniec M (2001) Ordered mesoporous carbons. Adv Mater 13:677–681
Salgado JRC, Alcaide F, Alvarez G, Calvillo L, Lazaro MJ, Pastor E (2010) Pt–Ru electrocatalysts supported on ordered mesoporous carbon for direct methanol fuel cell. J Power Sources 195:4022–4029
Samadi-Maybodi A, Teymouri M, Vahid A, Miranbeigi A (2011) In situ incorporation of nickel nanoparticles into the mesopores of MCM-41 by manipulation of solvent-solute interaction and its activity toward adsorptive desulfurization of gas oil. J Hazard Mater 192:1667–1674
Sayari A (2000) Novel synthesis of high-quality MCM-48 silica. J Am Chem Soc 122:6504–6505
Shih LH (2001) Reverse logistics system planning for recycling electrical appliances and computers in Taiwa. Resour Conserv Recycl 32:55–72
Sing KSW, Everett DH, Haul RAW, Moscou L, Pierotti RA, Rouquerol J, Siemieniewska T (1985) Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with specific reference to the determination of surface area and porosity. Pure Appl Chem 57:603–619
Wang LZ, Shi JL, Yu J, Zhang WH, Yan DS (2000) Temperature control in the synthesis of cubic mesoporous silica materials. Mater Lett 45:273–278
Wang L, Shao Y, Zhang J (2005) Short-time formation of well-ordered cubic mesoporous MCM-48 molecular sieve with the aid of fluoride ions. Mater Lett 59:3604–3607
Wei FY, Liu ZW, Lu J, Liu ZT (2010) Synthesis of mesoporous MCM-48 using fumed silica and mixed surfactants. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 131:224–229
Ying F, Wang S, Au CT, Lai SY (2011) Highly active and stable mesoporous Au/CeO2 catalysts prepared from MCM-48 hard-template. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 142:308–315
Zhao W, Hao Z, Hu C (2005) Synthesis of MCM-48 with a high thermal and hydro-thermal stability. Mater Res Bull 40:1775–1780
Zhao D, Budhi S, Rodriguez A, Koodali RT (2010a) Rapid and facile synthesis of Ti-MCM-48 mesoporous material and the photocatalytic performance for hydrogen evolution. Int J Hydrogen Energy 35:5276–5283
Zhao W, Li Q, Wang L, Chu J, Qu J, Li S, Qi T (2010b) Synthesis of high quality MCM-48 with binary cationic—nonionic surfactants. Langmuir 26:6982–6988
Acknowledgments
The author expresses thanks to the National Science Council of Taiwan for its financial support under Project No. NSC 96-2221-E-131-001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Special Issue Editors: Mamadou Diallo, Neil Fromer, Myung S. Jhon
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Nanotechnology for Sustainable Development
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liou, TH. Recovery of silica from electronic waste for the synthesis of cubic MCM-48 and its application in preparing ordered mesoporous carbon molecular sieves using a green approach. J Nanopart Res 14, 869 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-012-0869-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-012-0869-6