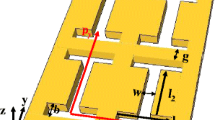
Abstract
Plasmonic metallic nanoholes are widely used to focus or image in the nanoscale field. In this article, we present the results of the design, fabrication, and plasmonic properties of a two-dimensional metallic pentagram nanohole array. The nanoholes can excite the extraordinary transmission phenomenon. We used the finite-difference time-domain method to design the transmission and the localized surface plasmon resonance electric field distribution in the near field. The focused ion beam method was used to fabricate the nanoholes. The transmittance in the far field was measured by a scanning spectrophotometer. The difference between the design and the experimental results may be caused by the conversion between the near field and the far field. The near field electric field distribution on the surface plasmonic nanoholes was measured by a near-field scanning optical microscope. From our results, we found that the maximum transmission of the nanoholes is 2.4. Therefore, our plasmonic nanohole can significantly enhance the transmission by exciting the plasmonic phenomenon on the surface of the nanostructures.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang SH, Gray S, Schatz G (2005) Surface plasmon generation and light transmission by isolated nanoholes and arrays of nanoholes in thin metal films. Opt Express 13(8):3150–3165. doi:10.1364/OPEX.13.003150
Ctistis G, Patoka P, Wang X, Kempa K, Giersig M (2007) Optical transmission through hexagonal arrays of sub-wavelength holes in thin metal films. Nano Lett 7:2926–2930. doi:10.1021/nl0712973
Ebbesen TW, Lezec HJ, Ghaemi HF, Thio T, Wolff PA (1998) Extraordinary optical transmission through sub-wavelength hole arrays. Nature 391:667–669. doi:10.1038/35570
Fu YQ, Zhou W, Lim LEN, Du C, Shi H, Wang CT, Luo X (2007) Influence of V-shaped plasmonic nanostructures on beam propagation. Appl Phys B 86:461–466. doi:10.1007/s00340-006-2502-9
Gordon R, Hughes M, Leathem B, Kavanagh KL, Brolo AG (2005) Basis and lattice polarization mechanisms for light transmission through nanohole arrays in a metal film. Nano Lett 5:1243–1246. doi:10.1021/nl0509069
Haynes CL, McFarland AD, Zhao L, Van Duyne RP, Schatz GC, Gunnarsson L, Prikulis J, Kasemo B, Käll M (2003) Nanoparticle optics: the importance of radiative dipole coupling in two-dimensional nanoparticle arrays. J Phys Chem B 107:7337–7342. doi:10.1021/jp034234r
Koerkamp KJK, Enoch S, Segerink FB, van Hulst NF, Kuipers L (2004) Strong influence of hole shape on extraordinary transmission through periodic arrays of sub-wavelength holes. Phys Rev Lett 92:183901. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.92.183901
Kunz KS, Luebbers RJ (1993) The finite difference time domain method for electromagnetics. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Leebeeck AD, Kumar LKS, de Lange V, Sinton D, Gordon R, Brolo AG (2007) On-chip surface-based detection with nanohole arrays. Anal Chem 79:4094–4100. doi:10.1021/ac070001a
Li HY, Zhou SM, Li J, Chen YL, Wang SY, Shen ZC, Chen LY, Liu H, Zhang XX (2001) Analysis of the drude model in metallic films. Appl Optics 40(34):6307–6311. doi:10.1364/AO.40.006307
Liang Y, Zhai L, Zhao X, Xu D (2005) Band-gap engineering for semiconductor nanowires through composition modulation. J Phys Chem B 109:7120–7123. doi:10.1021/jp045566e
Nagoshi K, Honda J, Sakaue H, Takahagi T, Suzuki H (2009) Direct fabrication of nanopores in a metal foil using focused ion beam with in situ measurements of the penetrating ion beam current. Rev Sci Inst 80:125102. doi:10.1063/1.3270958
Rindzevicius T, Alaverdyan Y, Dahlin A, Höök F, Sutherland D, Käll M (2005) Plasmonic sensing characteristics of single nanometric holes. Nano Lett 5:2335–2339. doi:10.1021/nl0516355
Rommel M, Jambreck JD, Ebm C, Platzgummer E, Bauer AJ, Frey L (2010) Influence of FIB patterning strategies on the shape of 3D structures: comparison of experiments with simulations. Microelectron Eng 87:1566–1568. doi:10.1016/j.mee.2009.10.054
Sonnichsen C, Duch AC, Steininger G, Koch M, von Plessen G, Feldmann J (2000) Launching surface plasmons into nano-holes in metal films. Appl Phys Lett 76:140–142. doi:10.1063/1.125682
Taflove A (1995) Computational electrodynamics: the finite-difference time-domain method. Artech House, Boston
Taflove A, Hagness S (2000) Computational electrodynamics: the finite-difference time-domain method, 2nd edn. Artech House, Boston
Yang JS, Lee SG, Park SG, Lee EH, O BH (2009) Drude model for the optical properties of a nano-scale thin metal film revisited. J Korean Phys Soc 55(6):2552–2555. doi:10.3938/jkps.55.2552
Yin L, Vlasko-Vlasov VK, Rydh A, Pearson J, Welp U, Changc S-H, Gray SK, Schatz GC, Brown DB, Kimball CW (2004) Surface plasmons at single nanoholes in Au films. Appl Phys Lett 85:467–469. doi:10.1063/1.1773362
Yuan ZC, Shi JM (2007) Collisional, nonuniform plasma sphere scattering calculation by FDTD employing a Drude model. Int J Infrared Milli Waves 28:987–992. doi:10.1007/s10762-007-9273-1
Zhou RL, Chen XS, Wang SW, Lu W, Zeng Y, Chen HB, Li HJ, Xia H, Wang LL (2008) The surface plasmon resonance of metal-film nanohole arrays. Solid State Commun 145(1–2):23–28. doi:10.1016/j.ssc.2007.10.006
Zhu SL, Li F, Luo XG, Du CL, Fu YQ (2008) A localized surface plasmon resonance nanosensor based on rhombic Ag nanoparticle array. Sens Actuators B 134:193–198. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2008.04.028
Zhu SL, Du CL, Fu YQ (2009) Detection of staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin B using localized surface plasmon resonance-based hybrid Au-Ag nanoparticles. Opt Mat 31:1608–1613. doi:10.1016/j.optmat.2009.03.009
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the A*STAR (Agency for Science, Technology, and Research), Singapore, under SERC Grant No. 0721010023.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, S., Zhou, W. Plasmonic properties of two-dimensional metallic nanoholes fabricated by focused ion beam lithography. J Nanopart Res 14, 652 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-011-0652-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-011-0652-0