Abstract
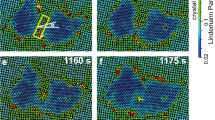
The coalescence process of copper oxide particles of 3∼ ∼8 nm was studied by in-situ HRTEM observation with no external heating. We found that merging of two particles is much faster as compared to the reshaping process. The coalescence of pre-aligned nanoparticles leads to the formation of a single nanocrystal. The lattice mismatch between two merged misaligned particles can be released by structural relaxation in small nanoparticles and by interface movement in large nanoparticles. Surface atom migration is the leading mechanism during the whole coalescence process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcantar N.A., Park C., Pan J.M., Israelachvili J.N. (2003). Acta Materialia, 51:31
Buffat P.A. (2003). Mater. Chem. Phys. 81:368
Cho A. (2003). Science 299:1684
Flueli M., Buffat P.A., Borel J.P. (1988). Surf. Sci. 202:343
Liao J., Zhang Y., Yu W., Xu L., Ge C., Liu J., Cu N. (2003). Colloids Surf. A 223:177
Long N.J., Marzke R.F., Mckelvy M., Glaunsinger W.S. (1986). Ultramicroscopy 20:15
Nakaso K., Shimada M., Okuyama K., Deppert K. (2002). Aerosol Sci. 33:1061
Park S.J., Kim S., Lee S., Khim Z.G., Char K., Hyeon T. (2000). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 122:8581
Rankin J., Sheldon B.W. (1995). Mat. Sci. Eng. A 204:48
Schiotz J., Jacobsen W. (2003). Science 301:1357
Seydel C. (2003). Science 300:80
Swihart M.T. (2003). Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 8:127
Wang J., Gao L. (2003). Inorg. Chem. Commun. 6:877
Yeadon M., Yang J.C., Averback R.S., Bullard J.W., Olynick D.L., Gibson J.M. (1997). Appl. Phys. Lett. 71:1631
Zhang W.J., PalDey S., Deevi S. (2005). Appl. Catal. A 295:201
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Drs. Firooz Rasouli, Sarojini Deevi and Sohini PalDey for their valuable contributions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W., Miser, D. Coalescence of oxide nanoparticles: In situ HRTEM observation. J Nanopart Res 8, 1027–1032 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-005-9056-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-005-9056-3