Abstract
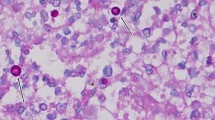
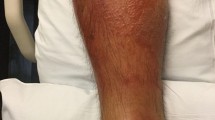
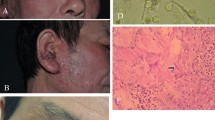
Disseminated cryptococcosis primarily affects immunosuppressed patients and has a poor outcome if diagnosis and treatment are delayed. Skin lesions are rarely manifest causing misdiagnosis. We present a case of cryptococcal cellulitis with severe pain in a kidney transplant recipient on long-term immunosuppressive therapy. Multiple organs were involved, and there was cutaneous dissemination of the lesions. Histopathology revealed abundant yeast-like cells with wide capsular halos in subcutaneous tissue, suggesting Cryptococcus spp. infection. Laser capture microdissection (LCM)-PCR on skin biopsies confirmed Cryptococcus neoformans var. grubii. A literature review of 17 cases of disseminated cryptococcosis with cutaneous cellulitis or panniculitis in HIV-negative individuals found that over half the patients (52.9%, 9/17) had a history of glucocorticoid therapy, and that the most common site was the legs (76.5%, 13/17). C. neoformans was the main pathogenic species, accounting for 88.2% (15/17) of cases. Fungal cellulitis should be included in the differential diagnosis of cellulitis that fails to respond to antimicrobial therapy in HIV-negative immunosuppressed individuals. Non-culture-based molecular techniques aid in rapid pathogen identification in histologically positive, unculturable specimens.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vilchez RA, Fung J, Kusne S. Cryptococcosis in organ transplant recipients: an overview. Am J Transplant. 2002;2(7):575–80. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-6143.2002.20701.x.
Kwon-Chung KJ, Fraser JA, Doering TL, Wang Z, Janbon G, Idnurm A, Bahn YS. Cryptococcus neoformans and Cryptococcus gattii, the etiologic agents of cryptococcosis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2014;4(7):a019760. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a019760.
Beardsley J, Sorrell TC, Chen SC. Central nervous system Cryptococcal infections in Non-HIV infected patients. J Fungi (Basel). 2019;5(3):71. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof5030071.
Fang W, Fa Z, Liao W. Epidemiology of Cryptococcus and cryptococcosis in China. Fungal Genet Biol. 2015;78:7–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fgb.2014.10.017.
Chang CC, Sorrell TC, Chen SC. Pulmonary cryptococcosis. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2015;36(5):681–91. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0035-1562895.
van Spil WE, Nooijen S, de Jong PY, Aliredjo RP, de Sévaux RG, Verhave JC. Cryptokokkenmeningitis [Cryptococcal meningitis]. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2015;159:A8478 (PMID: 25827149).
Ruan Q, Zhu Y, Chen S, Zhu L, Zhang S, Zhang W. Disseminated cryptococcosis with recurrent multiple abscesses in an immunocompetent patient: a case report and literature review. BMC Infect Dis. 2017;17(1):369. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-017-2459-9.
Noguchi H, Matsumoto T, Kimura U, Hiruma M, Kusuhara M, Ihn H. Cutaneous cryptococcosis. Med Mycol J. 2019;60(4):101–7. https://doi.org/10.3314/mmj.19.008.
Neuville S, Dromer F, Morin O, Dupont B, Ronin O, Lortholary O. French Cryptococcosis study group primary cutaneous cryptococcosis: a distinct clinical entity. Clin Infect Dis. 2003;36(3):337–47. https://doi.org/10.1086/345956.
Perfect JR, Bicanic T. Cryptococcosis diagnosis and treatment: what do we know now? Fungal Genet Biol. 2015;78:49–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fgb.2014.10.003.
Olias P, Jacobsen ID, Gruber AD. Fungal species identification from avian lung specimens by single hypha laser microdissection and PCR product sequencing. Med Mycol. 2011;49(1):56–61. https://doi.org/10.3109/13693786.2010.497172.
Westwater C, Schofield DA. Laser capture microdissection of Candida albicans from host tissue. Methods Mol Biol. 2012;845:397–409. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-61779-539-8_27.
Wang C, Zhan P, Wang L, Zeng R, Shen Y, Lv G, et al. The application of laser microdissection in molecular detection and identification of aspergillus fumigatus from murine model of acute invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. Mycopathologia. 2014;178(1–2):53–61. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-014-9777-x.
Zhou YB, Zhang GJ, Song YG, Sun LN, Chen YH, Sun TT, et al. Application of laser capture microdissection and polymerase chain reaction in the diagnosis of Trichoderma longibrachiatum infection: a promising diagnostic tool for “fungal contaminants” infection. Med Mycol. 2020;58(3):315–21. https://doi.org/10.1093/mmy/myz055.
Zhao Z, Ji L, Wang A, Wang X, Chen W, Wan Z, et al. A case of disseminated cryptococcosis after liver transplantation clinical and laboratory investigation. Chin J Mycol. 2008;3(5):268–71.
Han D, Li Z, Li R, Tan P, Zhang R, Li J. mNGS in clinical microbiology laboratories: on the road to maturity. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2019;45(5–6):668–85. https://doi.org/10.1080/1040841X.2019.1681933.
Meyer W, Aanensen DM, Boekhout T, Cogliati M, Diaz MR, Esposto MC, et al. Consensus multi-locus sequence typing scheme for Cryptococcus neoformans and Cryptococcus gattii. Med Mycol. 2009;47(6):561–70. https://doi.org/10.1080/13693780902953886.
Chiang B, Kamiya K, Sato A, Maekawa T, Komine M, Murata S, et al. Rapid diagnosis by mass spectrometry of disseminated cryptococcosis clinically mimicking refractory bilateral cellulitis. J Dermatol. 2019;46(10):e345–6. https://doi.org/10.1111/1346-8138.14944.
Koizumi Y, Kachi A, Tsuboi K, Muto J, Watanabe H, Asai N, et al. Clostridioides difficile-related toxic megacolon after Cryptococcus neoformans cellulitis: a complex of two rare infections in an immunocompromised host. J Infect Chemother. 2019;25(5):379–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiac.2018.12.003.
Abe N, Fujieda Y, Nagaoka K, Ohkusu M, Yasuda S, Kamei K, et al. Disseminated cryptococcosis with bronchiolitis and cellulitis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019;199(2):235–6. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201804-0697IM.
Chakradeo K, Paul Chia YY, Liu C, Mudge DW, De Silva J. Disseminated cryptococcosis presenting initially as lower limb cellulitis in a renal transplant recipient-a case report. BMC Nephrol. 2018;19(1):18. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12882-018-0815-7.
Cohen R, Babushkin F, Shapiro M, Ben-Ami R, Finn T. Cryptococcosis as a cause of nephrotic syndrome? A case report and review of the literature. IDCases. 2018;12:142–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.idcr.2018.05.004.
Ajmal S, Keating M, Wilhelm M. Multifocal soft tissue cryptococcosis in a renal transplant recipient: the importance of suspecting atypical pathogens in the immunocompromised host. Exp Clin Transplant. 2018. https://doi.org/10.6002/ect.2017.0292.
Nishioka H, Takegawa H, Kamei H. Disseminated cryptococcosis in a patient taking tocilizumab for Castleman’s disease. J Infect Chemother. 2018;24(2):138–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiac.2017.09.009.
Huong NTC, Altibi AMA, Hoa NM, Tuan LA, Salman S, Morsy S, et al. Progressive cutaneous cryptococcosis complicated with meningitis in a myasthenia gravis patient on long-term immunosuppressive therapy - a case report. BMC Infect Dis. 2017;17(1):311. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-017-2415-8.
Han G, Kwon SH, Song HJ, Jeon J. Disseminated cryptococcosis presenting as cellulitis. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2017;83(1):89–91. https://doi.org/10.4103/0378-6323.192959.
Gomes de Sousa MD, Bernardes Filho F, Barros Costa Fernandes LE, Guedes Leal CR, Rocha Magalhães C, Neto C, da Silva MA, et al. Cellulitis in a liver transplant patient as an initial manifestation of disseminated cryptococcal disease. Case Rep Dermatol. 2016;8(3):250–3. https://doi.org/10.1159/000449365.
Reddy BY, Shaigany S, Schulman L, Grossman ME. Resident rounds part III: case report: fatal cryptococcal panniculitis in a lung transplant recipient. J Drugs Dermatol. 2015;14:519–22 (PMID: 25942673).
Valente ES, Lazzarin MC, Koech BL, da Rosa RV, de Almeida R, de Oliveira UL, et al. Disseminated cryptococcosis presenting as cutaneous cellulitis in an adolescent with systemic lupus erythematosus. Infect Dis Rep. 2015;7(2):5743. https://doi.org/10.4081/idr.2015.5743.
Ni W, Huang Q, Cui J. Disseminated cryptococcosis initially presenting as cellulitis in a patient suffering from nephrotic syndrome. BMC Nephrol. 2013;14:20. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2369-14-20.
Lu HC, Yang YY, Huang YL, Chen TL, Chuang CL, Lee FY, et al. Disseminated cryptococcosis initially presenting as cellulitis in a rheumatoid arthritis patient. J Chin Med Assoc. 2007;70(6):249–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1726-4901(09)70368-5.
Yoo SS, Tran M, Anhalt G, Barrett T, Vonderheid EC. Disseminated cellulitic cryptococcosis in the setting of prednisone monotherapy for pemphigus vulgaris. J Dermatol. 2003;30(5):405–10. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1346-8138.2003.tb00407.x.
Vandersmissen G, Meuleman L, Tits G, Verhaeghe A, Peetermans WE. Cutaneous cryptococcosis in corticosteroid-treated patients without AIDS. Acta Clin Belg. 1996;51(2):111–7. https://doi.org/10.1080/17843286.1996.11718496.
Sławińska M, Hlebowicz M, Iżycka-Świeszewska E, Sikorska M, Sokołowska-Wojdyło M, Smiatacz T, et al. Dermoscopic observations in disseminated cryptococcosis with cutaneous involvement. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32(6):e223–4. https://doi.org/10.1111/jdv.14744.
Husain S, Wagener MM, Singh N. Cryptococcus neoformans infection in organ transplant recipients: variables influencing clinical characteristics and outcome. Emerg Infect Dis. 2001;7(3):375–81. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid0703.010302.
Mays SR, Bogle MA, Bodey GP. Cutaneous fungal infections in the oncology patient: recognition and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2006;7(1):31–43. https://doi.org/10.2165/00128071-200607010-00004.
Peña ZG, Byers HR, Lehmer LM, Smith CA, Ragsdale BD. Mixed pneumocystis and cryptococcus cutaneous infection histologically mimicking xanthoma. Am J Dermatopathol. 2013;35(1):e6–10. https://doi.org/10.1097/DAD.0b013e318266b59a.
Atarguine H, Hocar O, Abbad F, Rais H, Idalene M, Tassi N, et al. Cryptococcose cutanée mimant un carcinome basocellulaire et révélant une atteinte systémique sur immunodéficience acquise Cutaneous cryptococcosis mimicking basal cell carcinoma and revealing systemic involvement in acquired immunodeficiency. J Mycol Med. 2015;25(2):163–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mycmed.2015.04.002.
Ramdial PK, Sing Y, Subrayan S, Calonje E. Cutaneous colesional acquired immunodeficiency syndrome associated Kaposi sarcoma and cryptococcosis. Am J Dermatopathol. 2010;32(8):780–6. https://doi.org/10.1097/DAD.0b013e3181dbc5de.
Kosaraju K, Mukhopadhyay C, Vandana KE, Yagain K, Rao NR. Multiple cutaneous swellings in an immunocompetent host–cryptococcosis overlooked. Braz J Infect Dis. 2011;15(4):394–6 (PMID: 21861014).
Sun HY, Alexander BD, Lortholary O, Dromer F, Forrest GN, Lyon GM, et al. Cutaneous cryptococcosis in solid organ transplant recipients. Med Mycol. 2010;48(6):785–91. https://doi.org/10.3109/13693780903496617.
Bauzá A, Redondo P, Rubio M. Primary cutaneous cryptococcal cellulitis secondary to insect bite in an immunosupressed patient after liver transplantation. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2005;30(3):241–3. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2230.2004.01706.x.
Chen SC, Meyer W, Sorrell TC. Cryptococcus gattii infections. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2014;27(4):980–1024. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.00126-13.
Sacht GL, Lima AM, Perdomo YC, Boigues RS, Takita LC, Filho HG. Disseminated cryptococcosis with cutaneous involvement in an immunocompetent patient. An Bras Dermatol. 2016;91(6):832–4. https://doi.org/10.1590/abd1806-4841.20165478.
Rachadi H, Senouci K, Lyagoubi M, Benzekri A, Mansouri S, Ramli I, et al. Nodules multiples du visage révélant une cryptococcose disséminée chez un patient immunocompétent [Multiple facial nodules revealing disseminated cryptococcosis in an immunocompetent patient]. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2016;143(4):289–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annder.2015.12.019.
Dora JM, Kelbert S, Deutschendorf C, Cunha VS, Aquino VR, Santos RP, et al. Cutaneous cryptococccosis due to Cryptococcus gattii in immunocompetent hosts: case report and review. Mycopathologia. 2006;161(4):235–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-006-0277-5.
Tilak R, Prakash P, Nigam C, Tilak V, Gambhir IS, Gulati AK. Cryptococcal meningitis with an antecedent cutaneous cryptococcal lesion. Dermatol Online J. 2009;15(9):12 (PMID: 19930999).
Bernardeschi C, Foulet F, Ingen-Housz-Oro S, Ortonne N, Sitbon K, Quereux G, et al. Cutaneous invasive aspergillosis: retrospective multicenter study of the French invasive-aspergillosis registry and literature review. Med (Baltim). 2015;94(26):e1018. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000001018.
Krishnan N, Patel B, Palfrey W, Isache C. Rapidly progressive necrotizing cellulitis secondary to Candida tropicalis infection in an immunocompromised host. IDCases. 2020;19:e00691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.idcr.2019.e00691.
Guarner J, Brandt ME. Histopathologic diagnosis of fungal infections in the 21st century. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2011;24(2):247–80. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.00053-10.
Emmert-Buck MR, Bonner RF, Smith PD, Chuaqui RF, Zhuang Z, Goldstein SR, et al. Laser capture microdissection. Science. 1996;274(5289):998–1001. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.274.5289.998.
Lehmann BD, Jovanović B, Chen X, Estrada MV, Johnson KN, Shyr Y, et al. Refinement of triple-negative breast cancer molecular subtypes: implications for neoadjuvant chemotherapy selection. PLoS ONE. 2016;11(6):e0157368. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0157368.
Yamada A, Umeki K, Saeki Y, Hashikura Y, Nomura H, Yamamoto I, et al. Detection of microbial genes in a single leukocyte by polymerase chain reaction following laser capture microdissection. J Microbiol Methods. 2018;155:42–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mimet.2018.11.005.
Civita P, Franceschi S, Aretini P, Ortenzi V, Menicagli M, Lessi F, et al. Laser capture microdissection and RNA-Seq analysis: high sensitivity approaches to explain histopathological heterogeneity in human glioblastoma FFPE archived tissues. Front Oncol. 2019;9:482. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2019.00482.
Du R, Feng Y, Liu LN, Liu YB, Ye H, Lü XJ, et al. (2020) Pathogen diagnosis of a febrile HIV case by the metagenomic next-generation sequencing. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban, 51:257–60. https://doi.org/10.12182/20200360605
Zhu YM, Ai JW, Xu B, Cui P, Cheng Q, Wu H, et al. Rapid and precise diagnosis of disseminated T marneffei infection assisted by high-throughput sequencing of multifarious specimens in a HIV-negative patient: a case report. BMC Infect Dis. 2018;18(1):379. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-018-3276-5.
Xing XW, Zhang JT, Ma YB, Zheng N, Yang F, Yu SY. Apparent performance of metagenomic next-generation sequencing in the diagnosis of cryptococcal meningitis: a descriptive study. J Med Microbiol. 2019;68(8):1204–10. https://doi.org/10.1099/jmm.0.000994.
Wilson MR, Naccache SN, Samayoa E, Biagtan M, Bashir H, Yu G, et al. Actionable diagnosis of neuroleptospirosis by next-generation sequencing. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(25):2408–17. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1401268.
Salzberg SL, Breitwieser FP, Kumar A, Hao H, Burger P, Rodriguez FJ, et al. Next-generation sequencing in neuropathologic diagnosis of infections of the nervous system. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. 2016;3(4):e251. https://doi.org/10.1212/NXI.0000000000000251.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the patient for allowing us to report this case and to Beijing Natural Science Foundation for their support [No. 7194326].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ruoyu Li and Yinggai Song designed and supervised the research and data analysis. Yinggai Song and Xiao Liu conducted research and drafted the manuscript. G. Sybren de Hoog contributed to design the study and the analysis of the data.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Yuping Ran.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, Y., Liu, X., de Hoog, G.S. et al. Disseminated Cryptococcosis Presenting as Cellulitis Diagnosed by Laser Capture Microdissection: A Case Report and Literature Review. Mycopathologia 186, 423–433 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-021-00543-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-021-00543-3