Abstract
Background
Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA) constantly develops in asthmatics, which has not been fully investigated.
Objectives
This study aimed to investigate serum differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) between ABPA and asthma using the new approach isobaric tags by relative and absolute quantitation (iTRAQ).
Methods
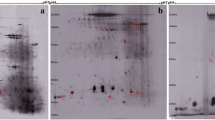
Each 16 serum samples from ABPA or asthmatic subjects were pooled and screened using iTRAQ. After bioinformatic analysis, five candidate DEPs were validated in the enlarged serum samples from additional 21 ABPA, 31 asthmatic and 20 healthy subjects using ELISA. A receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was used to estimate the diagnostic power of carnosine dipeptidase 1 (CNDP1).
Results
A total of 29 DEPs were screened out between ABPA and asthmatic groups. Over half of them were enriched in proteolysis and regulation of protein metabolic process. Further verification showed serum levels of immunoglobulin heavy constant gamma 1, α-1-acid glycoprotein 1, corticosteroid-binding globulin and vitronectin were neither differentially altered between ABPA and asthma nor consistent with the proteomic analysis. Only serum CNDP1 was significantly decreased in ABPA patients, compared with asthmatics and healthy controls (P < 0.01 and P < 0.05). The ROC analysis determined 10.73 ng/mL as the cutoff value of CNDP1, which could distinguish ABPA among asthmatics (AUC 0.770, 95%CI 0.632-0.875, P < 0.001).
Conclusions
This study firstly identified serological DEPs between ABPA and asthma using the new technique iTRAQ. Serum CNDP1 might assist the differential diagnosis of ABPA from asthma and serve as a new pathogenetic factor in fungal colonization and sensitization.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Knutsen AP. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in asthma. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2017;13(1):11–4. https://doi.org/10.1080/1744666x.2017.1232620.
Latge JP. Aspergillus fumigatus and aspergillosis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1999;12(2):310–50.
van de Veerdonk FL, Gresnigt MS, Romani L, Netea MG, Latge JP. Aspergillus fumigatus morphology and dynamic host interactions. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2017;15(11):661–74. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro.2017.90.
Denning DW, Pleuvry A, Cole DC. Global burden of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis with asthma and its complication chronic pulmonary aspergillosis in adults. Med Mycol. 2013;51(4):361–70. https://doi.org/10.3109/13693786.2012.738312.
Sockrider M, Wenzel SE, Castro M, Kulkarni H. What is allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA)? Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2014;190(6):P3–4. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.1906P3.
Hinson KF, Moon AJ, Plummer NS. Broncho-pulmonary aspergillosis; a review and a report of eight new cases. Thorax. 1952;7(4):317–33.
Mou Y, Ye L, Ye M, Yang D, Jin M. A retrospective study of patients with a delayed diagnosis of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis/allergic bronchopulmonary mycosis. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2014;35(2):192. https://doi.org/10.2500/aap.2014.35.3731.
Lotvall J, Akdis CA, Bacharier LB, Bjermer L, Casale TB, Custovic A, et al. Asthma endotypes: a new approach to classification of disease entities within the asthma syndrome. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011;127(2):355–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2010.11.037.
Woolnough KF, Richardson M, Newby C, Craner M, Bourne M, Monteiro W, et al. The relationship between biomarkers of fungal allergy and lung damage in asthma. Clin Exp Allergy. 2017;47(1):48–56. https://doi.org/10.1111/cea.12848.
Agarwal R, Sehgal IS, Dhooria S, Aggarwal AN. Developments in the diagnosis and treatment of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2016;10(12):1317–34. https://doi.org/10.1080/17476348.2016.1249853.
Overton NL, Denning DW, Bowyer P, Simpson A. Genetic susceptibility to allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in asthma: a genetic association study. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2016;12:47. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13223-016-0152-y.
Gago S, Overton NLD, Ben-Ghazzi N, Novak-Frazer L, Read ND, Denning DW, et al. Lung colonization by Aspergillus fumigatus is controlled by ZNF77. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):3835. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-06148-7.
Kniemeyer O, Ebel F, Kruger T, Bacher P, Scheffold A, Luo T, et al. Immunoproteomics of Aspergillus for the development of biomarkers and immunotherapies. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2016;10(9–10):910–21. https://doi.org/10.1002/prca.201600053.
CSRD ASGo. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of bronchial asthma. Chin J Tuberc Respir Dis. 2016;39(9):675–97.
Agarwal R, Chakrabarti A, Shah A, Gupta D, Meis JF, Guleria R, et al. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis: review of literature and proposal of new diagnostic and classification criteria. Clin Exp Allergy. 2013;43(8):850–73. https://doi.org/10.1111/cea.12141.
Mauri P, Riccio AM, Rossi R, Di Silvestre D, Benazzi L, De Ferrari L, et al. Proteomics of bronchial biopsies: galectin-3 as a predictive biomarker of airway remodelling modulation in omalizumab-treated severe asthma patients. Immunol Lett. 2014;162(1):2–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imlet.2014.08.010.
Bantscheff M, Schirle M, Sweetman G, Rick J, Kuster B. Quantitative mass spectrometry in proteomics: a critical review. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2007;389(4):1017–31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-007-1486-6.
Singh B, Singh S, Asif AR, Oellerich M, Sharma GL. Allergic aspergillosis and the antigens of Aspergillus fumigatus. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2014;15(5):403–23.
Kauffman HF, Tomee JF, van de Riet MA, Timmerman AJ, Borger P. Protease-dependent activation of epithelial cells by fungal allergens leads to morphologic changes and cytokine production. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2000;105(6 Pt 1):1185–93.
Namvar S, Warn P, Farnell E, Bromley M, Fraczek M, Bowyer P, et al. Aspergillus fumigatus proteases, Asp f 5 and Asp f 13, are essential for airway inflammation and remodelling in a murine inhalation model. Clin Exp Allergy. 2015;45(5):982–93. https://doi.org/10.1111/cea.12426.
Basu T, Seyedmousavi S, Sugui JA, Balenga N, Zhao M, Kwon Chung KJ, et al. Aspergillus fumigatus alkaline protease 1 (Alp1/Asp f13) in the airways correlates with asthma severity. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018;141(1):423.e42–425.e427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2017.07.034.
Tay TR, Bosco J, Gillman A, Aumann H, Stirling R, O’Hehir R, et al. Coexisting atopic conditions influence the likelihood of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in asthma. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2016;117(1):29e21–32e21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anai.2016.04.024.
Kalaiyarasan JAK, Puri M, Tayal D, Singhal R, Sarin R. Prevalence of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in asthmatic patients: a prospective institutional study. Indian J Tuberc. 2018;65(4):285–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijtb.2018.04.007.
Agarwal R, Aggarwal AN, Sehgal IS, Dhooria S, Behera D, Chakrabarti A. Utility of IgE (total and Aspergillus fumigatus specific) in monitoring for response and exacerbations in allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Mycoses. 2016;59(1):1–6. https://doi.org/10.1111/myc.12423.
Lou B, Xu Z, Yang G, Guo C, Zheng S, Lou H, et al. Role of Aspergillus fumigatus-specific IgE in the diagnosis of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2019;178(4):338–44. https://doi.org/10.1159/000495365.
Moulder R, Bhosale SD, Goodlett DR, Lahesmaa R. Analysis of the plasma proteome using iTRAQ and TMT-based isobaric labeling. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2018;37(5):583–606. https://doi.org/10.1002/mas.21550.
Toor A, Culibrk L, Singhera GK, Moon K-M, Prudova A, Foster LJ, et al. Transcriptomic and proteomic host response to Aspergillus fumigatus conidia in an air-liquid interface model of human bronchial epithelium. PLoS ONE. 2018;13(12):e0209652. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0209652.
Thakur R, Shankar J. Proteome analysis revealed jak/stat signaling and cytoskeleton rearrangement proteins in human lung epithelial cells during interaction with Aspergillus terreus. Curr Signal Transduct Ther. 2019;14(1):55–67. https://doi.org/10.2174/1574362413666180529123513.
Gustafsson PM, Oxelius V-A, Nilsson S, Kjellman B. Association between Gm allotypes and asthma severity from childhood to young middle age. Respir Med. 2008;102(2):266–72.
Liu JY, Wang Y, Wang YZ, Zhu JW, Dai FD. Screening serum differential proteins for childhood asthma at different control levels by isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantification-based proteomic technology. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2017;39(6):817–26. https://doi.org/10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.2017.06.014.
Salazar-Peláez LM, Abraham T, Herrera AM, Correa MA, Ortega JE, Paré PD, et al. Vitronectin expression in the airways of subjects with asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(3):e0119717. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0119717.
James B, Milstien S, Spiegel S. ORMDL3 and allergic asthma: from physiology to pathology. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019;144(3):634–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2019.07.023.
Wu H, Romieu I, Sienra-Monge JJ, Li H, del Rio-Navarro BE, London SJ. Genetic variation in ORM1-like 3 (ORMDL3) and gasdermin-like (GSDML) and childhood asthma. Allergy. 2009;64(4):629–35. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1398-9995.2008.01912.x.
Arner P, Henjes F, Schwenk JM, Darmanis S, Dahlman I, Iresjo BM, et al. Circulating carnosine dipeptidase 1 associates with weight loss and poor prognosis in gastrointestinal cancer. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(4):e0123566. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0123566.
Schwenk JM, Igel U, Neiman M, Langen H, Becker C, Bjartell A, et al. Toward next generation plasma profiling via heat-induced epitope retrieval and array-based assays. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2010;9(11):2497–507. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.M110.001560.
Yadav AK, Sinha N, Kumar V, Bhansali A, Dutta P, Jha V. Association of CTG repeat polymorphism in carnosine dipeptidase 1 (CNDP1) gene with diabetic nephropathy in north Indians. Indian J Med Res. 2016;144(1):32–7. https://doi.org/10.4103/0971-5916.193280.
Dietl A-M, Binder U, Bauer I, Shadkchan Y, Osherov N, Haas H. Arginine auxotrophy affects siderophore biosynthesis and attenuates virulence of Aspergillus fumigatus. Genes (Basel). 2020;11(4):423. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11040423.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge all the subjects for their participation. This work was supported by grants from the National R&D Program (2016YFC1304000, 2016YFC1304002) and Shanghai Top-Priority Clinical Key Disciplines Construction Project (2017ZZ02013). In addition, it was also supported by Instrumental Analysis Center of Shenzhen University for providing research instruments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HC and DS performed the experiments and analyzed the data, and HC drafted the writing. XX, YM and XS collected the serum samples and acquired the clinical data. LY, SL and DW provided guidance on experiments and bioinformatic analysis. MJ and YW conceived the ideas and organized this study. All authors have read and approved this final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Vishnu Chaturvedi.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11046_2020_506_MOESM2_ESM.xlsx
Supplementary material 2: Gene ontology annotation (biological process) of differentially expressed proteins between ABPA and asthma. (XLSX 179 kb)
11046_2020_506_MOESM3_ESM.xlsx
Supplementary material 3: Gene ontology annotation (cellular component) of differentially expressed proteins between ABPA and asthma. (XLSX 24 kb)
11046_2020_506_MOESM4_ESM.xlsx
Supplementary material 4: Gene ontology annotation (molecular function) of differentially expressed proteins between ABPA and asthma. (XLSX 19 kb)
11046_2020_506_MOESM5_ESM.xlsx
Supplementary material 5: KEGG pathway and enrichment analysis of differentially expressed proteins between ABPA and asthma. (XLSX 11 kb)
11046_2020_506_MOESM6_ESM.xlsx
Supplementary material 6: The protein–protein interaction network of differentially expressed proteins between ABPA and asthma. (XLSX 10 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, H., Shuai, D., Xue, X. et al. Proteomic Analysis of Serum Differentially Expressed Proteins Between Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis and Asthma. Mycopathologia 186, 1–13 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-020-00506-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-020-00506-0