Abstract
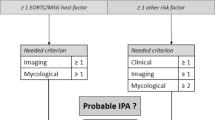
Diagnosis of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis (IPA) is challenging. The objective of the study was to assess the value of microbiological tests to the diagnosis of IPA in the absence of non-specific radiological data. A retrospective study of 23 patients with suspicion of IPA and positivity of some microbiological diagnostic tests was performed. These tests included conventional microbiological culture, detection of Aspergillus galactomannan (GM) antigen and in some patients (1 → 3)-β-d-glucan (BDG) and Aspergillus fumigatus DNA using the LightCycler® SeptiFast test. In 10 patients with hematological malignancy, 6 cases were considered ‘probable’ and 4 ‘non-classifiable.’ In 8 patients with chronic lung disease, 7 cases were classified as ‘probable’ and 1 as ‘proven,’ and in 5 patients with prolonged ICU stay (>7 days), there were 2 ‘proven’ cases, 2 ‘non-classifiable’ and 1 putative case. Microbiological culture was positive in 17 cases and 18 Aspergillus spp. were isolated (one mixed culture). A. fumigatus was the most frequent (44.4%) followed by A. tubingensis. The Aspergillus galactomannan (GM) antigen assay was positive in 21 cases (91.3%). The GM antigen and the (1 → 3)-β-d-glucan (BDG) assays were both performed in 12 cases (52.2%), being positive in 9. The SeptiFast test was performed in 7 patients, being positive in 4. In patients with non-classifiable pulmonary aspergillosis and one or more positive microbiological tests, radiological criteria may not be considered a limiting factor for the diagnosis of IPA.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pagano L, Caira M, Candoni A, Offidani M, Martino B, Specchia G, et al. Invasive aspergillosis in patients with acute myeloid leukemia: a SEIFEM-2008 registry study. Haematologica. 2010;95:644–50.
Nucci M, Nouér SA, Cappone D, Anaissie E. Early diagnosis of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in hematologic patients: an opportunity to improve the outcome. Haematologica. 2013;98:1657–60.
Holding KJ, Dworkin MS, Wan PC, Hanson DL, Klevens RM, Jones JL, et al. Aspergillosis among people infected with human immunodeficiency virus: incidence and survival. Adult and adolescent spectrum of HIV disease project. Clin Infect Dis. 2000;31:1253–7.
Bulpa P, Dive A, Sibille Y. Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur Resp J. 2007;30:782–800.
Samarakoon P, Soubani AO. Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in patients with COPD: a report of five cases and systematic review of the literature. Chron Resp Dis. 2008;5:19–27.
Barberan J, Sanz F, Hernández JL, Merlos S, Malmierca E, Garcia-Perez FJ, et al. Clinical features of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis vs. colonization in COPD patients distributed by gold stage. J Infect. 2012;65:447–52.
Wessolossky M, Welch VL, Sen A, Babu TM, Luke DR. Invasive Aspergillus infections in hospitalized patients with chronic lung disease. Infect Drug Resist. 2013;6:33–9.
Garnacho-Montero J, Amaya-Villar R, Ortiz-Leyba C, León C, Álvarez-Lerma F, Nolla-Salas J, et al. Isolation of Aspergillus spp. from the respiratory tract in critically ill patients: risk factors, clinical presentation and outcome. Crit Care. 2005;9:R91–9. doi:10.1186/cc3488.
Vandewoude KH, Blot SI, Depuydt P, Benoit D, Temmerman W, Colardyn F, et al. Clinical relevance of Aspergillus isolation from respiratory tract samples in critically patients. Crit Care. 2006;10:R31. doi:10.1.1186/cc4823.
Blot SI, Taccone FS, Van den Abeele AM, Bulpa P, Meersseman W, Brusselaers N, et al. A clinical algorithm to diagnose invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in critically patients. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012;186:56–64.
Pagano L, Caira M, Picardi M, Candoni A, Melillo L, Fianchi L, et al. Invasive aspergillosis in patients with acute leukemia: update on morbidity and mortality—SEIFEM-C Report. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;1:1524–5.
Nucci M, Nouér SA, Grazziutti M, et al. Probable invasive aspergillosis without prespecified radiological findings: proposal for inclusion of a new category of aspergillosis and implications for studying novel therapies. Clin Infect Dis. 2010;51:1273–80.
Ascioglu S, Rex JH, de Pauw B, Bennett JE, Bille J, Crokaert F, et al. Defining opportunistic invasive fungal infections in immunocompromised patients with cancer and hematopoietic stem cell transplants: an international consensus. Clin Infect Dis. 2002;34:7–14.
De Pauw B, Walsh TJ, Donnelly JP, Stevens DA, Edwards JE, Calandra T, et al. Revised definitions of invasive fungal disease from the european organization for research and treatment of cancer/invasive fungal infections cooperative group and the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Mycoses Study Group (EORTC/MSG) Consensus Group. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;46:1813–21.
Tsitsikas DA, Morin A, Araf S, Murtagh B, Johnson G, Vinnicombe S, et al. Impacted of the revised (2008) EORTC/MSG definitions for invasive fungal disease of the rates of diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis. Med Mycol. 2012;50:538–42.
Girmenia C, Guerrisi P, Frustaci AM, Fama A, Finolezzi E, Perrone S, et al. New category of probable invasive pulmonary in hematological patients. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2012;18:990–6.
Tutar N, Metan G, Koc AN, Yilmaz I, Bozkurt I, Simsek ZO, et al. Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Multidiscip Respir Med. 2013;8:59. doi:10.1186/2049-6958-8-59.
Alastruey-Izquierdo A, Mellado E, Peláez T, et al. Population-based survey of filamentous fungi and antifungal resistance in Spain (FILPOP STUDY). Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013;57:3380–7.
Marchetti O, Lamoth F, Mikulska M, Viscoli C, Verweij P, Bretagne S. ECIL recommendations for the use of biological markers for the diagnosis of invasive fungal diseases in leukemic patients and hematopoietic SCT recipients. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2012;47:846–54.
Prattes J, Flick H, Prüller F, et al. Novel test for diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis in patients with underlying respiratory diseases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2014;190:922–9.
Mikulska M, Furfaro E, Viscoli C. Non-cultural methods for the diagnosis of invasive fungal disease. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2015;13:103–17.
Global initiative for chronic obstructive lung disease. Pocket Guide to COPD. Diagnosis, management and prevention. Updated 2015. www.goldcopd.com.
Patterson TF, Thompson GR, Denning DW, Fishman JA, Hadley S, Herbrecht R, et al. Practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of aspergillosis: 2016 update by the infectious diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2016;63:433–42.
Barouky R, Badet M, Denis M, Soubirou JL, Philit F, Guerin C. Inhaled corticosteroids in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and disseminated aspergillosis. Eur J Intern Med. 2003;14:380–2.
Balajee SA, Kano R, Baddley JW, Moser SA, Marr KA, Alexander BD, et al. Molecular identification of aspergillus species collected for the transplant-associated infection surveillance network. J Clin Microbiol. 2009;47:3138–41.
Hachem RY, Kontoyiannis DP, Chemaly RF, Jiang Y, Reitzel R, Raad I. Utility of galactomannan enzyme immunoassay and (1,3) β-d-glucan in diagnosis of invasive fungal infections: low sensitivity for aspergillus fumigatus infection in hematologic malignancy patients. J Clin Microbiol. 2009;47:129–33.
Bergeron A, Porcher R, Sulahian A, de Bazelaire C, Chagnon K, Raffoux E, et al. The strategy for the diagnosis of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis should depend on both the underlying condition and the leukocyte count of patients with hematologic malignancies. Blood. 2012;119:1831–7.
Steinmann J, Buer J, Rath PM, Paul A, Saner F. Invasive aspergillosis in two liver transplant recipients: diagnosis by SeptiFast. Transpl Infect Dis. 2009;11:175–8.
Bravo D, Blanquer J, Tormo M, Aguilar G, Borrá R, Solano C, et al. Diagnostic accuracy and potential clinical value of the LightCycler SeptiFast assay in the management of bloodstream infections occurring in neutropenic and critically ill patients. Int J Infect Dis. 2011;15:e326–31.
Mauro MV, Cavalcantia P, Peruginia D, Noto A, Sperlì D, Giraldi C. Diagnostic utility of LightCycler SeptiFast and procalcitonin assays in the diagnosis of bloodstream infection in immunocompromised patients. Diagnostic Microbiol Infect Dis. 2012;73:308–11.
Guinea J, Torres-Narbona M, Gijon P, Muñoz P, Pozo F, Peláez T, et al. Pulmonary aspergillosis in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: incidence, risk factors and outcome. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2010;16:870–7.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Marta Pulido, MD, for editing the manuscript and editorial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No funding was received for this clinical study. The authors have no conflicts of interest to be declared.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aller-García, A.I., Castro-Méndez, C., Alastruey-Izquierdo, A. et al. Case Series Study of Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis. Mycopathologia 182, 505–515 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-016-0097-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-016-0097-1