Abstract
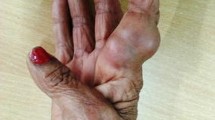
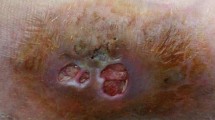
Phaeohyphomycosis is caused by a heterogeneous group of mycelial dematiaceous (phaeoid) fungi, which produce melanin pigment. This condition is often confused with chromoblastomycosis. Rhytidhysteron is a dematiaceous fungus, which has been recently found to be causing human infections. Till date only three cases of infection with Rhytidhysteron rufulum have been reported in the literature. All three cases have been from North India. Hereby, we present another two cases where Rhytidhysteron was isolated. Both the patients belonged to Chandigarh (India) and presented with subcutaneous lesions. The isolates were confirmed by ITS sequencing. Both the patients were immunocompetent and gave no history of trauma or any other predisposing factor. Phaeohyphomycosis are often missed due to lack of knowledge regarding the fungi causing the infections and there is need for clinical, pathological and microbiological correlation for effective diagnosis and treatment in these cases.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chander J. Textbook of medical mycology. 3rd ed. New Delhi: Mehta Publishers; 2009.
Kumarguru BN, Srinivas T, Jagadish MH. A case of subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis in a diabetic patient: a cryptic entity. J Glob Infect Dis. 2014;6:45–6.
Chowdhary A, Perfect J, de Hoog GS. Black molds and melanized yeasts pathogenic to humans. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2014;5:a019570.
Boehm EWA, Mugambi GK, Miller AN, Huhndorf SM, Marincowitz S, Spatafora JW, et al. A molecular phylogenetic reappraisal of the Hysteriaceae, Mytilinidiaceae and Gloniaceae (Pleosporomycetidae, Dothideomycetes) with keys to world species. Stud Mycol. 2009;64:49–84.
Pudhom K, Teerawatananond T, Chookpaiboon S. Spirobisnaphthalenes from the mangrove-derived fungus Rhytidhysteron sp. AS21B. Drugs. 2014;12:1271–80.
Barr ME. Rhytidhysteron opuntiae. Mem N Y Bot Gard. 1990;62:72.
Magnes M. Weltmonographie der Triblidiaceae. Bibl Mycol. 1997;165:127–30.
Murillo C, Albertazzi FJ, Carranzab J, Lumbsch HT, Tamayo G. Molecular data indicate that Rhytidhysteron rufulum (Ascomycetes, Patellariales) in Costa Rica consists of four distinct lineages corroborated by morphological and chemical characters. Mycol Res. 2009;113:405–16.
Chowdhary A, Guarro J, Randhawa HS, Gene J, Cano J, Jain RK, et al. A rare case of chromoblastomycosis in a renal transplant recipient caused by a non-sporulating species of Rhytidhysteron. Med Mycol. 2008;46:163–6.
Mahajan VK, Sharma V, Prabha N, Thakur K, Sharma NL, Rudramurthy SM, et al. A rare case of subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis caused by Rhytidhysteron species: a clinico-therapeutic experience. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:1485–9.
Mishra K, Das S, Goyal S, Gupta C, Rai G, Ansari MA, et al. Subcutaneous mycoses caused by Rhytidhysteron species in an immunocompetent patient. Med Mycol Case Rep. 2014;5:32–4.
Chowdhary A, Meis JF, Guarro J, de Hoog GS, Kathuria S, Arendrup MC, et al. ESCMID and ECMM joint guidelines for the diagnosis and management of systemic phaeohyphomycosis: diseases caused by black fungi. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2014;20(Suppl. 3):47–75.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chander, J., Singla, N., Kundu, R. et al. Phaeohyphomycosis Caused by Rhytidhysteron rufulum and Review of Literature. Mycopathologia 182, 403–407 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-016-0064-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-016-0064-x