Abstract
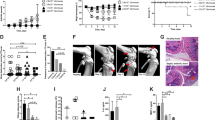
Paracoccidioidomycosis (PCM), a disease caused by the fungus Paracoccidioides brasiliensis (Pb), is highly prevalent in Brazil, where it is the principal cause of death by systemic mycoses. The disease primarily affects men aged 30–50 year old and usually starts as a pulmonary focus and then may spread to other organs and systems, including the joints. The present study aimed to develop an experimental model of paracoccidioidomycotic arthritis. Two-month-old male Wistar rats (n = 48) were used, divided in 6 groups: test groups EG/15 and EG/45 (received one dose of 100 μl of saline containing 105 Pb viable yeasts in the knee); heat killed Pb-group HK/15 and HK/45 (received a suspension of 105 Pb nonviable yeasts in the knee) and control groups CG/15 and CG/45 (received only sterile saline in the knee). The rats were killed 15 and 45 days postinoculation. In contrast with the control rats, the histopathology of the joints of rats of the test groups (EG/15 and EG/45) revealed a picture of well-established PCM arthritis characterized by extensive sclerosing granulomatous inflammation with numerous multiple budding fungal cells. The X-ray examination revealed joint alterations in these groups. Only metabolic active fungi evoked inflammation. The experimental model was able to induce fungal arthritis in the knees of the rats infected with metabolic active P. brasiliensis. The disease tended to be regressive and restrained by the immune system. No evidence of fungal dissemination to the lungs was observed.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borges-Walmsley MI, Chen X, Walmsley AR. The pathobiology of Paracoccidioides brasiliensis. Trends Microbiol. 2002;10(2):80–7.
San-Blas G, Restrepo A, Clemons K, Stevens DA, San-Blas F, Puccia R, Travassos LR, Figueroa JI, Hamilton AJ, Bartholomew MA, et al. Paracoccidioidomycosis. J Med Vet Mycol. 1992;30(1):59–71.
Fornajeiro N, Maluf ML, Takahachi G, Svidzinski TI. Inquérito epidemiológico sobre a paracoccidioidomicose utilizando a gp43 em dois municípios do noroeste do Paraná, Brasil. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2005;38(2):191–3.
Marques SA. Paracoccidioidomicose: atualização epidemiológica, clínica e terapêutica. An Bras Dermatol. 2003;78(2):135–50.
Franco MF, Montenegro MRG, Mendes RP, Marcos AS, Dillon NL, Mota NGS. Paracoccidioidomycosis: a recently proposed classification of its clinical forms. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 1987;20(2):129–32.
Pereira RM, Bucaretchi F, Barison EM, Tresoldi AT. Paracoccidioidomycosis in children: clinical presentation, follow-up and outcome. Rev Inst Med Trop S Paulo. 2004;46(3):127–31.
Bertolo MB, Vilarinho ST, Amstalden EMI, Ingrid EM, Muhib A, Regina FR. Blastomicose articular. Rev Bras Reumatol. 1990;30(6):178–80.
Severo LC, Agostini AA, Londero AT. Acometimento ósseo na paracoccidioidomicose crônica disseminada. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 1996;29(3):241–4.
Figueiredo GC, Figueiredo ECQ, Tavares-Neto J. Artrite fúngica: análise secundária de dados. Rev Bras Ortop. 2002;37(7):259–69.
Beaman L, Pappagianis D, Benjamini E. Significance of T cells in resistance to experimental murine coccidioidomycosis. Infect Immun. 1977;17(3):580–5.
Roldán JC, Tabares AM, Gómez BL, Aristizábal BE, Cock AM, Restrepo A. The oral route in the pathogenesis of paracoccidioidomycosis: an experimental study in BALB/c mice infected with P. brasiliensis conidia. Mycopathologia. 2001;151(2):57–62.
Gesztesi JL, Dias MA, de Souza AR, de Almeida SR, Lopes JD, Mariano M. Subcutaneous infection of mice with Paracoccidioides brasiliensis induces a peculiar pattern of inflammatory and immune responses. Mycopathologia. 1999;145(1):7–14.
Price MF, Wilkinson LD, Layne OG. Plate method for detection of phospholipase activity in Candida albicans. Sabouraudia. 1982;20(1):7–14.
Assis CM, Gandra RF, Gambale W, Shimizu MT, Paula CR. Biosynthesis of chondroitinase and hyaluronidase by different strains of Paracoccidioides brasiliensis. J Med Microbiol. 2003;52(6):479–81.
Rocha FF, Campos MG. Monoartrite como manifestação de paracoccidioidomicose/Monoarthritis as manifestation of paracoccidioidomycoses. Rev Panam Infectol. 2007;9(1):31–3.
MacDonald PB, Black GB, MacKenzie R. Orthopaedic manifestations of blastomycosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1990;72(6):860–4.
Picado CHF, Garcia FL, Marcondes CRR. Resultado tardio da infecção isolada no quadril por Paracoccidioides brasiliensis. Acta Ortop Bras. 2006;14(2):97–9.
Da Silva FC, Svidzinski TI, Patussi EV, Cardoso CP, De Oliveira Dalalio MM, Hernandes L. Morphologic organization of pulmonary granulomas in mice infected with Paracoccidioides brasiliensis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2009;80(5):798–804.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a Grant from Fundação Araucária-Fundo Paraná/SETI and CNPq.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Loth, E.A., Biazin, S.K., Paula, C.R. et al. Experimental Model of Arthritis Induced by Paracoccidioides brasiliensis in Rats. Mycopathologia 174, 187–191 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-012-9537-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-012-9537-8