Abstract
Background
Onychomycosis is a common disease. Topical treatment is usually not effective due to limitation of trans-nail delivery of antifungal drugs. Successful treatment of deep-seated nail infections remains elusive as the delivery of efficacious levels of antifungal drug to the site of action is very difficult.
Objectives
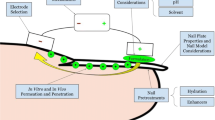
To evaluate the influence of several parameters including; the effect of low electrical current, incubation time and the presence of electrolyte (NaCl or KCl) on the penetration of terbinafine through the nail plate into the nail bed, using various formulations and concentrations of terbinafine HCl.
Methods
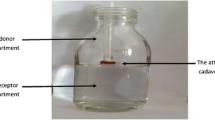
Iontophoresis was applied across porcine and human nail in vitro to assess its efficiency in enhancing delivery of terbinafine HCl.
Results
In this study, we have demonstrated that an optimal electrolyte concentration (1% NaCl or KCl) is required for an effective delivery. There is a significant increase in drug delivery into the nail and into the receiving compartment in the presence of 3% DMSO.
Conclusions
This study demonstrates the efficacy of iontophoresis in enhancing the trans-nail delivery of terbinafine. Clinical studies are needed to evaluate the feasibility, efficacy and safety of iontophoresis of terbinafine in onychomycosis in human.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Scher RK. Onychomycosis: therapeutic update. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999;40(Suppl):S21–6.
Elewski BE, Charif MA. Prevalence of onychomycosis in patients attending a dermatology clinic in northeastern Ohio for other conditions. Arch Dermatol. 1997;133:1172–3.
Ghannoum MA, Hajjeh RA, Scher R, et al. A large-scale North American study of fungal isolates from nails: the frequency of onychomycosis, fungal distribution, and antifungal susceptibility patterns. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;43:641–8.
Baran R, Hay RJ, Garduno JI. Review of antifungal therapy, part I: treatment rationale, including specific patient populations. J Dermatolog Treat. 2008;19:72–81.
Baran R, Hay RJ, Garduno JI. Review of antifungal therapy, part II: treatment rationale, including specific patient populations. J Dermatolog Treat. 2008;19:168–75.
Mehregan DR, Gee SL. The cost effectiveness of testing for onychomycosis versus empiric treatment of onychodystrophies with oral antifungal agents. Cutis. 1999;64:407–10.
Gupta AK, Tu LQ. Therapies for onychomycosis: a review. Dermatol Clin. 2006;24:375–9.
Hay RJ, Mackie RM, Clayton YM. Tioconazole nail solution—an open study of its efficacy in onychomycosis. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1987;12:175–7.
Shemer A, Trau H, Davidovici B, et al. Onychomycosis- rationalization of topical treatment. IMAJ. 2008;10:415–6.
Petranyi G, Meingassner JG, Meith H. Antifungal activity of the allylamine derivative terbinafine in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987;31:1365–8.
Kim JH, Lee CH, Choi HK. A method to measure the amount of drug penetrated across the nail plate. Pharm Res. 2001;18:1468–71.
Murthy SN, Wiskirchen DE, Bowers CP. Iontophoretic drug delivery across human nail. J Pharm Sci. 2007;96:305–11.
Murthy SN, Waddell DC, Shivakumar HN, Balaji A, Bowers CP. Iontophoretic permselective property of human nail. J Dermatol Sci. 2007;46:150–2.
Nair AB, Vaka SR, Sammeta SM, Kim HD, Friden PM, Chakraborty B, et al. Trans-ungual iontophoretic delivery of terbinafine. J Pharm Sci. 2009;98:1788–96.
Hao J, Li SK. Transungual iontophoretic transport of polar neutral and positively charged model permeants: effects of electrophoresis and electroosmosis. J Pharm Sci. 2008;97:893–905.
Hao J, Smith KA, Li SK. Chemical method to enhance transungual transport and iontophoresis efficiency. Int J Pharm. 2008;357:61–9.
Hao J, Li SK. Mechanistic study of electroosmotic transport across hydrated nail plates: effects of pH and ionic strength. J Pharm Sci. 2008;97:1–12.
Kumar MG, Lin S. Transdermal iontophoresis: impact on skin integrity as evaluated by various methods. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst. 2008;25:381–401.
Dixit N, Baboota S, Ahuja A, Ali J. Iontophoresis—an approach for controlled drug delivery: a review. Curr Drug Deliv. 2007;4:1–10.
Nolan LM, Corish J, Corrigan OI, Fitzpatrick D. Iontophoretic and chemical enhancement of drug delivery. Part I: across artificial membranes. Int J Pharm. 2003;257:41–55.
Nolan LM, Corish J, Corrigan OI, Fitzpatrick D. Combined effects of iontophoretic and chemical enhancement on drug delivery. II. Transport across human and murine skin. Int J Pharm. 2007;341:114–24.
Amichai B, Nitzan B, Mosckovitz R, Shemer A. Iontophoretic terbinafine delivery in onychomycosis—a preliminary study. Br J Dermatol. 2009 Epub ahead of print.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amichai, B., Mosckovitz, R., Trau, H. et al. Iontophoretic Terbinafine HCL 1.0% Delivery Across Porcine and Human Nails. Mycopathologia 169, 343–349 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-009-9265-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-009-9265-x